Qinggan Huoxue Recipe suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in alcoholic liver fibrosis through TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- PMID: 27217701
- PMCID: PMC4870076
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4695
Qinggan Huoxue Recipe suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in alcoholic liver fibrosis through TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the mechanism by which Qinggan Huoxue Recipe (QGHXR) inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in rats with alcoholic liver fibrosis (ALF).
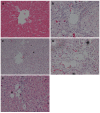
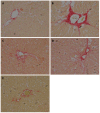
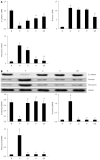
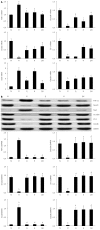
Methods: A total of 75 male SD rats were used to induce ALF. Serum biochemical indicators, including alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, laminin and hyaluronidase, were measured. Liver histopathological changes were evaluated using hematoxylin-eosin and Sirius red staining. EMT was examined by analyzing the expression of the epithelial marker E-cadherin and the mesenchymal markers vimentin and fibronectin using RT-PCR and Western blot. The inhibitory effect of QGHXR on EMT markers, as well as its effect on molecules associated with the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1/Smad signaling pathway, including TGF-β1, Smad3, snail, occludin, ZO-1 and claudin, was also examined.
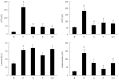
Results: Compared with normal control rats, ALF rats exhibited a decrease in E-cadherin levels (mRNA: ALF 0.16 ± 0.05 vs control 1.00 ± 0.08; protein: ALF 0.09 ± 0.05 vs control 0.70 ± 0.17, P < 0.01) and an increase in vimentin and fibronectin levels (mRNA: 11.43 ± 0.39 vs 1.00 ± 0.19 and 9.91 ± 0.34 vs 1.00 ± 0.44, respectively, P < 0.01; protein: 1.13 ± 0.42 vs 0.09 ± 0.03 and 1.16 ± 0.43 vs 0.09 ± 0.00, respectively, P < 0.01). This indicates that EMT occurred in ALF rats. In addition, the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway was activated in ALF rats, as evidenced by the increase in TGF-β1 and snail levels (mRNA: 1.76 ± 0.12 vs 1.00 ± 0.05 and 6.98 ± 0.41 vs 1.00 ± 0.10, respectively, P < 0.01; protein: 1.43 ± 0.05 vs 0.12 ± 0.03 and 1.07 ± 0.29 vs 0.07 ± 0.02, respectively, P < 0.01) and the decrease in Smad3 levels (mRNA: 0.05 ± 0.01 vs 1.00 ± 0.12, P < 0.01; protein: 0.06 ± 0.05 vs 0.89 ± 0.12, P < 0.01). Furthermore, levels of the tight junction markers occludin, ZO-1 and claudin decreased in ALF rats compared with healthy control rats (mRNA: 0.60 ± 0.09 vs 1.00 ± 0.12, 0.11 ± 0.00 vs 1.00 ± 0.12 and 0.60 ± 0.01 vs 1.00 ± 0.08, respectively, P < 0.01; protein: 0.05 ± 0.01 vs 0.87 ± 0.40, 0.09 ± 0.05 vs 0.89 ± 0.18 and 0.04 ± 0.03 vs 0.95 ± 0.21, respectively, P < 0.01). In ALF rats treated with QGHXR, E-cadherin levels increased (mRNA: QGHXR 0.67 ± 0.04 vs ALF model 0.16 ± 0.05, P < 0.01; protein: QGHXR 0.66 ± 0.21 vs ALF model 0.09 ± 0.05, P < 0.01), and vimentin and fibronectin levels decreased (mRNA: 6.57 ± 1.05 vs 11.43 ± 0.39 and 1.45 ± 1.51 vs 9.91 ± 0.34, respectively, P < 0.01; protein: 0.09 ± 0.03 vs 1.13 ± 0.42 and 0.10 ± 0.01 vs 1.16 ± 0.43, respectively, P < 0.01). In addition, QGHXR inhibited the expression of TGF-β1 and increased the expression of Smad3 (mRNA: 1.03 ± 0.11 vs 1.76 ± 0.12, 0.70 ± 0.10 vs 0.05 ± 0.01, respectively, P < 0.05 and P < 0.01; protein: 0.12 ± 0.03 vs 1.43 ± 0.05 and 0.88 ± 0.20 vs 0.06 ± 0.05, respectively, P < 0.01). QGHXR treatment also reduced the levels of the EMT-inducing transcription factor snail (mRNA: 2.28 ± 0.33 vs 6.98 ± 0.41, P < 0.01; protein: 0.08 ± 0.02 vs 1.07 ± 0.29, P < 0.01) and increased the occludin, ZO-1 and claudin levels (mRNA: 0.73 ± 0.05 vs 0.60 ± 0.09, 0.57 ± 0.04 vs 0.11 ± 0.00 and 0.68 ± 0.03 vs 0.60 ± 0.01, respectively, P < 0.01, P < 0.01 and P < 0.05; protein: 0.92 ± 0.50 vs 0.05 ± 0.01, 0.94 ± 0.22 vs 0.09 ± 0.05 and 0.94 ± 0.29 vs 0.04 ± 0.03, respectively, P < 0.01). The effects of QGR and HXR on the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway were similar to that of QGHXR; however, the QGR- and HXR-induced changes in vimentin mRNA levels, the QGR-induced changes in fibronectin mRNA levels and the HXR-induced changes in snail and TGF-β1 mRNA levels were not significant.
Conclusion: Qinggan Huoxue Recipe inhibits EMT in ALF rats by modulating the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway, suggesting that the mechanism underlying the amelioration of ALF induced by QGHXR is associated with this pathway.
Keywords: Alcoholic liver fibrosis; Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; QGHXR; Snail; Transforming growth factor-β1/Smad.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baicalin and puerarin reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway in vitro.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Sep;16(3):1968-1974. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6400. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30186426 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of Qinggan Huoxue Recipe and its separated recipes on the expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rats with alcoholic liver injury].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008 Nov;6(11):1145-51. doi: 10.3736/jcim20091108. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18990340 Chinese.
-
[Attenuation and mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis in rats with alcohol-induced liver injury by qinggan huoxue recipe and its disassembled formulas].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2011 May;31(5):653-8. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21812268 Chinese.
-
ROS-Nrf2 pathway mediates the development of TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the activation of Notch signaling.Eur J Cell Biol. 2021 Sep-Nov;100(7-8):151181. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2021.151181. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Eur J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34763128 Review.
-
Cytokines as drivers: Unraveling the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in COVID-19 lung fibrosis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Dec 17;686:149118. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.10.050. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37931361 Review.
Cited by
-
Paeonol attenuates aging MRC-5 cells and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of premalignant HaCaT cells induced by aging MRC-5 cell-conditioned medium.Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Feb;439(1-2):117-129. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3141-7. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28801702
-
Qinggan Huoxue Recipe attenuates Alcoholic Liver Disease by suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling pathway based on network pharmacology.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Jan 31;20(3):346-358. doi: 10.7150/ijms.80329. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36860681 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Combined with Platelet-Rich Plasma during Preventive and Therapeutic Stages of Intrauterine Adhesion in a Rat Model.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 17;10(2):476. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020476. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203684 Free PMC article.
-
Qinggan Huoxue Recipe Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Injury by Suppressing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Through LXR-LPCAT3.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 31;13:824185. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.824185. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35431945 Free PMC article.
-
Lnc-LFAR1 affects intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma proliferation, invasion, and EMT by regulating the TGFβ/Smad signaling pathway.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Jul 1;12(7):2455-2461. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31934072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kong D, Zhang F, Shao J, Wu L, Zhang X, Chen L, Lu Y, Zheng S. Curcumin inhibits cobalt chloride-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition associated with interference with TGF-β/Smad signaling in hepatocytes. Lab Invest. 2015;95:1234–1245. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

