Current and Future Theranostic Applications of the Lipid-Calcium-Phosphate Nanoparticle Platform
- PMID: 27217828
- PMCID: PMC4876619
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.14689
Current and Future Theranostic Applications of the Lipid-Calcium-Phosphate Nanoparticle Platform
Abstract
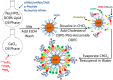
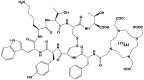
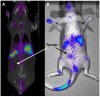
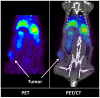
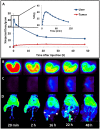
Over the last four years, the Lipid-Calcium-Phosphate (LCP) nanoparticle platform has shown success in a wide range of treatment strategies, recently including theranostics. The high specific drug loading of radiometals into LCP, coupled with its ability to efficiently encapsulate many types of cytotoxic agents, allows a broad range of theranostic applications, many of which are yet unexplored. In addition to providing an overview of current medical imaging modalities, this review highlights the current theranostic applications for LCP using SPECT and PET, and discusses potential future uses of the platform by comparing it with both systemically and locally delivered clinical radiotherapy options as well as introducing its applications as an MRI contrast agent. Strengths and weaknesses of LCP and of nanoparticles in general are discussed, as well as caveats regarding the use of fluorescence to determine the accumulation or biodistribution of a probe.
Keywords: Cancer; LCP.; Nanoparticle; PET; SIRT; SPECT; Theranostic.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Duncan R, Gaspar R. Nanomedicine(s) under the microscope. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(6):2101–41. - PubMed
-
- Graham FL, van der Eb AJ. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973;52(2):456–67. - PubMed
-
- Maitra A. Calcium phosphate nanoparticles: second-generation nonviral vectors in gene therapy. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2005;5(6):893–905. - PubMed
-
- Sokolova VV, Radtke I, Heumann R, Epple M. Effective transfection of cells with multi-shell calcium phosphate-DNA nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2006;27(16):3147–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

