Polydopamine Nanoparticles as a Versatile Molecular Loading Platform to Enable Imaging-guided Cancer Combination Therapy
- PMID: 27217836
- PMCID: PMC4876627
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.14431
Polydopamine Nanoparticles as a Versatile Molecular Loading Platform to Enable Imaging-guided Cancer Combination Therapy
Abstract
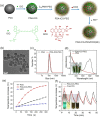
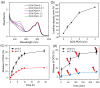
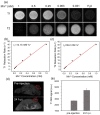
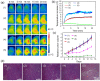
Cancer combination therapy to treat tumors with different therapeutic approaches can efficiently improve treatment efficacy and reduce side effects. Herein, we develop a theranostic nano-platform based on polydopamine (PDA) nanoparticles, which then are exploited as a versatile carrier to allow simultaneous loading of indocyanine green (ICG), doxorubicin (DOX) and manganese ions (PDA-ICG-PEG/DOX(Mn)), to enable imaging-guided chemo & photothermal cancer therapy. In this system, ICG acts as a photothermal agent, which shows red-shifted near-infrared (NIR) absorbance and enhanced photostability compared with free ICG. DOX, a model chemotherapy drug, is then loaded onto the surface of PDA-ICG-PEG with high efficiency. With Mn(2+) ions intrinsically chelated, PDA-ICG-PEG/DOX(Mn) is able to offer contrast under T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. In a mouse tumor model, the MR imaging-guided combined chemo- & photothermal therapy achieves a remarkable synergistic therapeutic effect compared with the respective single treatment modality. This work demonstrates that PDA nanoparticles could serve as a versatile molecular loading platform for MR imaging guided combined chemo- & photothermal therapy with minimal side effects, showing great potential for cancer theranostics.
Keywords: Combination therapy; Indocyanine green; Magnetic resonance imaging.; Nano-Drug delivery system; Polydopamine.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Coates A, Abraham S, Kaye SB, Sowerbutts T, Frewin C, Fox RM. et al. On the receiving end—patient perception of the side-effects of cancer chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer and Clin Onco. 1983;19:203–8. - PubMed
-
- Min KH, Park K, Kim Y-S, Bae SM, Lee S, Jo HG. et al. Hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles-encapsulated camptothecin enhance the drug stability and tumor targeting in cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2008;127:208–18. - PubMed
-
- Sonvico F, Mornet S, Vasseur S, Dubernet C, Jaillard D, Degrouard J. et al. Folate-Conjugated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Solid Tumor Targeting as Potential Specific Magnetic Hyperthermia Mediators: Synthesis, Physicochemical Characterization, and in Vitro Experiments. Bioconjugate Chem. 2005;16:1181–8. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Wang C, Wang X, Wang X, Cheng L, Li Y. et al. Mesoporous Silica Coated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as a Multifunctional Light-Responsive Platform for Cancer Combination Therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25:384–92.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

