Persistent Organic Pollutants and the Association with Maternal and Infant Thyroid Homeostasis: A Multipollutant Assessment
- PMID: 27219111
- PMCID: PMC5226691
- DOI: 10.1289/EHP152
Persistent Organic Pollutants and the Association with Maternal and Infant Thyroid Homeostasis: A Multipollutant Assessment
Abstract
Background: Disruption of thyroid homeostasis has been indicated in human studies targeting effects of persistent organic pollutants (POPs). Influence on the maternal thyroid system by POPs is of special interest during pregnancy because such effects could impair infant thyroid homeostasis.
Objectives: We investigated the association between POPs and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones (THs) in mother and child pairs from the Northern Norway Mother-and-Child Contaminant Cohort Study (MISA).
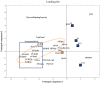
Methods: Nineteen POPs and 10 thyroid parameters were analyzed in serum from 391 pregnant women in their second trimester. In addition, TSH concentrations in heel-prick samples from the infants were analyzed by the Norwegian Newborn Screening program. Association studies with a multipollutant approach were performed using multivariate analyses; partial least squares (PLS) regression, hierarchical clustering, and principal component analysis (PCA).
Results: Several POPs were significantly associated with TSH and THs: a) PFOS was positively associated with TSH; b) PCBs, HCB, and nonachlors were inversely associated with T3, T4, and FT4; and, c) PFDA and PFUnDA were inversely associated with T3 and FT3. After mutual adjustments for the other contaminants, only PFDA and PFUnDA remained significantly associated with T3 and FT3, respectively. Infants born to mothers within the highest TSH quartile had 10% higher mean concentrations of TSH compared with children born to mothers in the lowest TSH quartile.
Conclusion: The present results suggest that background exposures to POPs can alter maternal thyroid homeostasis. This research contributes to the understanding of multipollutant exposures using multivariate statistical approaches and highlights the complexity of investigating environmental concentrations and mixtures in regard to maternal and infant thyroid function. Citation: Berg V, Nøst TH, Pettersen RD, Hansen S, Veyhe AS, Jorde R, Odland JØ, Sandanger TM. 2017. Persistent organic pollutants and the association with maternal and infant thyroid homeostasis: a multipollutant assessment. Environ Health Perspect 125:127-133; http://dx.doi.org/10.1289/EHP152.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abalovich M, Amino N, Barbour LA, Cobin RH, De Groot LJ, Glinoer D, et al. Management of thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy and postpartum: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(8) suppl:S1–S47. - PubMed
-
- Akins JR, Waldrep K, Bernert JT., Jr The estimation of total serum lipids by a completely enzymatic ‘summation’ method. Clin Chim Acta. 1989;184:219–226. - PubMed
-
- Berbel P, Mestre JL, Santamaría A, Palazón I, Franco A, Graells M, et al. Delayed neurobehavioral development in children born to pregnant women with mild hypothyroxinemia during the first month of gestation: the importance of early iodine supplementation. Thyroid. 2009;19:511–519. - PubMed
-
- Berg V, Nøst TH, Hansen S, Elverland A, Veyhe AS, Jorde R, et al. Assessing the relationship between perfluoroalkyl substances, thyroid hormones and binding proteins in pregnant women; a longitudinal mixed effects approach. Environ Int. 2015;77:63–69. - PubMed
-
- Berg V, Nøst TH, Huber S, Rylander C, Hansen S, Veyhe AS, et al. Maternal serum concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and their predictors in years with reduced production and use. Environ Int. 2014;69:58–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

