Intermediate-Range Migration Furnishes a Narrow Margin of Efficiency in the Two-Strategy Competition
- PMID: 27219327
- PMCID: PMC4878735
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155787
Intermediate-Range Migration Furnishes a Narrow Margin of Efficiency in the Two-Strategy Competition
Abstract
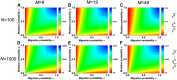
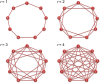
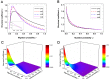
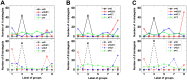
It is well-known that the effects of spatial selection on the two-strategy competition can be quantified by the structural coefficient σ under weak selection. We here calculate the accurate value of σ in group-structured populations of any finite size. In previous similar models, the large population size has been explicitly required for obtaining σ, and here we analyze quantitatively how large the population should be. Unlike previous models which have only involved the influences of the longest and the shortest migration rang on σ, we consider all migration ranges together. The new phenomena are that an intermediate range maximizes σ for medium migration probabilities which are of the tiny minority and the maximum value is slightly larger than those for other ranges. Furthermore, we find the ways that migration or mutation changes σ can vary significantly through determining analytically how the high-frequency steady states (distributions of either strategy over all groups) impact the expression of σ obtained before. Our findings can be directly used to resolve the dilemma of cooperation and provide a more intuitive understanding of spatial selection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of migration on the multi-strategy selection in finite group-structured populations.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 21;6:35114. doi: 10.1038/srep35114. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27767074 Free PMC article.
-
The σ law of evolutionary dynamics in community-structured population.J Theor Biol. 2012 Aug 7;306:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.04.024. Epub 2012 Apr 25. J Theor Biol. 2012. PMID: 22554982
-
Probability of fixation under weak selection: a branching process unifying approach.Theor Popul Biol. 2006 Jun;69(4):419-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2006.01.002. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Theor Popul Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504230
-
Coalescent approximation for structured populations in a stationary random environment.Theor Popul Biol. 2010 Nov;78(3):192-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2010.06.008. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Theor Popul Biol. 2010. PMID: 20619285 Review.
-
The social structure and strategies of delphinids: predictions based on an ecological framework.Adv Mar Biol. 2007;53:195-294. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2881(07)53003-8. Adv Mar Biol. 2007. PMID: 17936137 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of migration on the multi-strategy selection in finite group-structured populations.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 21;6:35114. doi: 10.1038/srep35114. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27767074 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary multiplayer games on graphs with edge diversity.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Apr 1;15(4):e1006947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006947. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 30933968 Free PMC article.
-
Individual mobility promotes punishment in evolutionary public goods games.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 25;7(1):14015. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12823-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29070844 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

