KIBRA promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation and motility
- PMID: 27220053
- PMCID: PMC4880424
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.13718
KIBRA promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation and motility
Abstract
KIBRA is a regulator of the Hippo-yes-associated protein (YAP) pathway, which plays a critical role in tumorigenesis. In the present study, we show that KIBRA is a positive regulator in prostate cancer cell proliferation and motility. We found that KIBRA is transcriptionally upregulated in androgen-insensitive LNCaPC4-2 and LNCaP-C81 cells compared to parental androgen-sensitive LNCaP cells. Ectopic expression of KIBRA enhances cell proliferation, migration and invasion in both immortalized and cancerous prostate epithelial cells. Accordingly, knockdown of KIBRA reduces migration, invasion and anchorage-independent growth in LNCaP-C4-2/C81 cells. Moreover, KIBRA expression is induced by androgen signaling and KIBRA is partially required for androgen receptor signaling activation in prostate cancer cells. In line with these findings, we further show that KIBRA is overexpressed in human prostate tumors. Our studies uncover unexpected results and identify KIBRA as a tumor promoter in prostate cancer.
Keywords: AR signaling; KIBRA; motility; proliferation; prostate cancer.
© 2016 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures


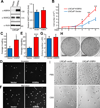

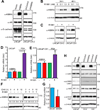
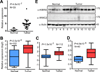
References
-
- Kremerskothen J, Plaas C, Buther K, Finger I, Veltel S, Matanis T, Liedtke T, Barnekow A. Characterization of KIBRA, a novel WW domain-containing protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;300:862–867. - PubMed
-
- Papassotiropoulos A, Stephan DA, Huentelman MJ, Hoerndli FJ, Craig DW, Pearson JV, Huynh KD, Brunner F, Corneveaux J, Osborne D, Wollmer MA, Aerni A, Coluccia D, Hanggi J, Mondadori CR, Buchmann A, Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Henke K, de Quervain DJ. Common Kibra alleles are associated with human memory performance. Science. 2006;314:475–478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

