High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with increased carotid artery intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 27220111
- PMCID: PMC5217917
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12541
High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with increased carotid artery intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Emerging evidence suggests that the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a novel potential marker of inflammatory responses. The objective was to evaluate the association between NLR and carotid artery intima-media thickness (cIMT) in type 2 diabetes.
Materials and methods: We carried out a case-control study involving 320 patients with type 2 diabetes, and 250 age-, sex- and body mass index-matched healthy controls who all underwent carotid ultrasonography and took a blood examination. We divided the diabetes patients into two groups according to cIMT: 188 diabetes patients with high cIMT and 132 diabetes patients with low cIMT, and compared baseline characteristics and NLR between the two groups and healthy controls.
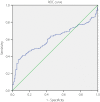
Results: The mean NLR was significantly higher in the group of diabetes patients with high cIMT than the group of diabetes patients with low cIMT, who in turn showed a significantly higher NLR compared with control participants. Logistic regression analysis showed that the NLR was an independent risk factor for diabetes patients with high cIMT (odds ratio 140.89, 95% CI 1.71-11615.30, P = 0.028). Based on the receiver operating characteristic curve, use of the NLR as an indicator for diabetes patients with high cIMT diagnosis was projected to be 3.16, and yielded a sensitivity and specificity of 36.2% and 93.2%, respectively, with an area under the curve of 0.606 (95% CI 0.544-0.667).
Conclusions: High NLR might be a potential biomarker for the increased cIMT in type 2 diabetes patients. Future studies are required to validate our findings.
Keywords: Carotid artery intima-media thickness; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel markers of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in Behçet's disease patients with ocular involvement: epicardial fat thickness, carotid intima media thickness, serum ADMA level, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Mar;35(3):701-8. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2907-0. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 25744156
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and its relation with pro-inflammatory mediators, visceral adiposity and carotid intima-media thickness in population with obesity.Eur J Clin Invest. 2019 May;49(5):e13085. doi: 10.1111/eci.13085. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Eur J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30740673
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio may predict subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with psoriasis.Echocardiography. 2014 Oct;31(9):1095-104. doi: 10.1111/echo.12511. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Echocardiography. 2014. PMID: 24447343 Clinical Trial.
-
Relationship of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio with Carotid Plaque Vulnerability and Occurrence of Vulnerable Carotid Plaque in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jun 21;2021:6894623. doi: 10.1155/2021/6894623. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34250090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carotid artery intima media thickness can predict the response to phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors in patients with moderate erectile dysfunction.Sex Med. 2023 Jul 31;11(3):qfad042. doi: 10.1093/sexmed/qfad042. eCollection 2023 Jun. Sex Med. 2023. PMID: 37529683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the status of carotid intima-media thickness and lipid profiles in type 2 diabetes mellitus.BMJ Open. 2024 Nov 9;14(11):e087496. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-087496. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39521468 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the Relationship between Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Disease Severity in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Cells. 2024 Mar 3;13(5):442. doi: 10.3390/cells13050442. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474406 Free PMC article.
-
Mediterranean diet, neutrophil count, and carotid intima-media thickness in secondary prevention: the CORDIOPREV study.Eur Heart J. 2025 Feb 21;46(8):719-729. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae836. Eur Heart J. 2025. PMID: 39661486 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combing NLR, V20 and mean lung dose to predict radiation induced lung injury in patients with lung cancer treated with intensity modulated radiation therapy and chemotherapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 6;8(46):81387-81393. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19032. eCollection 2017 Oct 6. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29113398 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) for Predicting Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020 May 19;16:437-443. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S244623. eCollection 2020. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020. PMID: 32547040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National diabetes statistics report, 2014. Available from http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statics/2014StatisticsReport.htlm Accessed January 5, 2015.
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas, 6th edn Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, 2013.
-
- Nathan DM. Long‐term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993; 328: 1676–1685. - PubMed
-
- Bots ML, Hoes AW, Koudstaal PJ, et al Common carotid intima‐media thickness and risk of stroke and myocardial infarction: the Rotterdam Study. Circulation 1997; 96: 1432–1437. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical