Dietary α-linolenic acid-rich flaxseed oil prevents against alcoholic hepatic steatosis via ameliorating lipid homeostasis at adipose tissue-liver axis in mice
- PMID: 27220557
- PMCID: PMC4879538
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26826
Dietary α-linolenic acid-rich flaxseed oil prevents against alcoholic hepatic steatosis via ameliorating lipid homeostasis at adipose tissue-liver axis in mice
Abstract
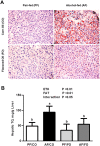
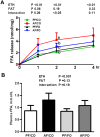
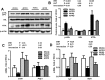
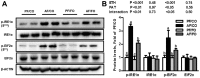
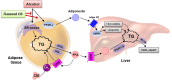
Low levels of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in serum and liver tissue biopsies are the common characteristics in patients with alcoholic liver disease. The α-linolenic acid (ALA) is a plant-derived n-3 PUFA and is rich in flaxseed oil. However, the impact of ALA on alcoholic fatty liver is largely unknown. In this study, we assessed the potential protective effects of ALA-rich flaxseed oil (FO) on ethanol-induced hepatic steatosis and observed that dietary FO supplementation effectively attenuated the ethanol-induced hepatic lipid accumulation in mice. Ethanol exposure stimulated adipose lipolysis but reduced fatty acid/lipid uptake, which were normalized by FO. Our investigations into the corresponding mechanisms demonstrated that the ameliorating effect of FO might be associated with the lower endoplasmic reticulum stress and normalized lipid metabolism in adipose tissue. In the liver, alcohol exposure stimulated hepatic fatty acid uptake and triglyceride synthesis, which were attenuated by FO. Additionally, dietary FO upregulated plasma adiponectin concentration, hepatic adiponectin receptor 2 expression, and the activation of hepatic adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. Collectively, dietary FO protects against alcoholic hepatic steatosis by improving lipid homeostasis at the adipose tissue-liver axis, suggesting that dietary ALA-rich flaxseed oil might be a promising approach for prevention of alcoholic fatty liver.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Flaxseed Oil Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance in Mice by Rescuing the Adaption to ER Stress.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Oct 17;66(41):10729-10740. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03906. Epub 2018 Sep 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30145885
-
Impact of dietary precursor ALA versus preformed DHA on fatty acid profiles of eggs, liver and adipose tissue and expression of genes associated with hepatic lipid metabolism in laying hens.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017 Apr;119:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2017.01.010. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017. PMID: 28410665
-
Flaxseed oil ameliorates alcoholic liver disease via anti-inflammation and modulating gut microbiota in mice.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Feb 22;16(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0431-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28228158 Free PMC article.
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
-
Adiponectin and alcoholic fatty liver disease.IUBMB Life. 2008 Dec;60(12):790-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.124. IUBMB Life. 2008. PMID: 18709650 Review.
Cited by
-
α-Linolenic acid prevents hepatic steatosis and improves glucose tolerance in mice fed a high-fat diet.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018 Oct 29;73:e150. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2018/e150. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018. PMID: 30379219 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Flaxseed Oil Prevents Western-Type Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Apolipoprotein-E Knockout Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3256241. doi: 10.1155/2017/3256241. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29081885 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated systemic total bile acids escalate susceptibility to alcohol-associated liver disease.iScience. 2024 Sep 13;27(10):110940. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110940. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39398234 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic profiling of serum alterations and biomarker discovery in feline hepatic liposis.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 6;15(1):7891. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91770-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40050321 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary camellia seed oil attenuates liver injury in mice chronically exposed to alcohol.Front Nutr. 2022 Oct 11;9:1026740. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1026740. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36313120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rehm J. et al. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. The Lancet. 373, 2223–2233 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Altamirano J. & Bataller R. Alcoholic liver disease: pathogenesis and new targets for therapy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8, 491–501 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Rogers C. Q., Ajmo J. M. & You M. Adiponectin and alcoholic fatty liver disease. IUBMB life. 60, 790–797 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

