MicroRNA-146a suppresses ROCK1 allowing hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 27221467
- PMCID: PMC4879631
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26697
MicroRNA-146a suppresses ROCK1 allowing hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
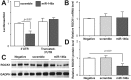
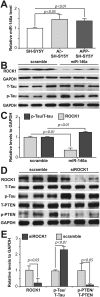
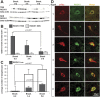
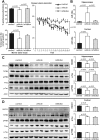
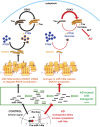
MicroRNA-146a is upregulated in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here, we show that the rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) is a target of microRNA-146a in neural cells. Knockdown of ROCK1 mimicked the effects of microRNA-146a overexpression and induced abnormal tau phosphorylation, which was associated with inhibition of phosphorylation of the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN). The ROCK1/PTEN pathway has been implicated in the neuronal hyperphosphorylation of tau that occurs in AD. To determine the function of ROCK1 in AD, brain tissue from 17 donors with low, intermediate or high probability of AD pathology were obtained and analyzed. Data showed that ROCK1 protein levels were reduced and ROCK1 colocalised with hyperphosphorylated tau in early neurofibrillary tangles. Intra-hippocampal delivery of a microRNA-146a specific inhibitor (antagomir) into 5xFAD mice showed enhanced hippocampal levels of ROCK1 protein and repressed tau hyperphosphorylation, partly restoring memory function in the 5xFAD mice. Our in vitro and in vivo results confirm that dysregulation of microRNA-146a biogenesis contributes to tau hyperphosphorylation and AD pathogenesis, and inhibition of this microRNA could be a viable novel in vivo therapy for AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-125b induces tau hyperphosphorylation and cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease.EMBO J. 2014 Aug 1;33(15):1667-80. doi: 10.15252/embj.201387576. Epub 2014 Jul 7. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 25001178 Free PMC article.
-
miR-200c suppression increases tau hyperphosphorylation by targeting 14-3-3γ in early stage of 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar 6;18(5):2220-2234. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66604. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35342350 Free PMC article.
-
miR-106b inhibits tau phosphorylation at Tyr18 by targeting Fyn in a model of Alzheimer's disease.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Sep 16;478(2):852-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.037. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27520374
-
Tau pathology in Alzheimer disease and other tauopathies.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Jan 3;1739(2-3):198-210. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2004.09.008. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 15615638 Review.
-
The Ambiguous Relationship of Oxidative Stress, Tau Hyperphosphorylation, and Autophagy Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:352723. doi: 10.1155/2015/352723. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26171115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A microRNA signature that correlates with cognition and is a target against cognitive decline.EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Nov 8;13(11):e13659. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202013659. Epub 2021 Oct 11. EMBO Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34633146 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs as Influencers of Cell-Cell Communication in Tumor Microenvironment.Cells. 2020 Jan 15;9(1):220. doi: 10.3390/cells9010220. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31952362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Membrane Transporters and MicroRNA Regulation in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):8739-8758. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04135-2. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38558361 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in tear fluids predict underlying molecular changes associated with Alzheimer's disease.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Mar 20;6(6):e202201757. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201757. Print 2023 Jun. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 36941055 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Non-Coding RNA in Alzheimer's Disease Pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 6;24(15):12498. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512498. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

