Sympathetic neural signaling via the β2-adrenergic receptor suppresses T-cell receptor-mediated human and mouse CD8(+) T-cell effector function
- PMID: 27222010
- PMCID: PMC5241047
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201646395
Sympathetic neural signaling via the β2-adrenergic receptor suppresses T-cell receptor-mediated human and mouse CD8(+) T-cell effector function
Abstract
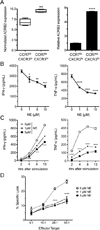
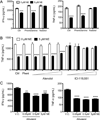
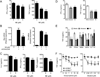
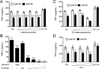
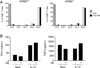
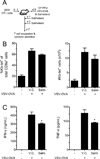
Postganglionic sympathetic neurons innervate secondary lymphoid organs and secrete norepinephrine (NE) as the primary neurotransmitter. NE binds and signals through five distinct members of the adrenergic receptor family. In this study, we show elevated expression of the β2-adrenergic receptor (ADRB2) on primary human CD8(+) effector memory T cells. Treatment of both human and murine CD8(+) T cells with NE decreased IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion and suppressed their cytolytic capacity in response to T-cell receptor (TCR) activation. The effects of NE were specifically reversed by β2-specific antagonists. Adrb2(-/-) CD8(+) T cells were completely resistant to the effects of NE. Further, the ADRB2-specific pharmacological ligand, albuterol, significantly suppressed effector functions in both human and mouse CD8(+) T cells. While both TCR activation and stimulation with IL-12 + IL-18 were able to induce inflammatory cytokine secretion, NE failed to suppress IFN-γ secretion in response to IL-12 + IL18. Finally, the long-acting ADRB2-specific agonist, salmeterol, markedly reduced the cytokine secretion capacity of CD8(+) T cells in response to infection with vesicular stomatitis virus. This study reveals a novel intrinsic role for ADRB2 signaling in CD8(+) T-cell function and underscores the novel role this pathway plays in adaptive T-cell responses to infection.
Keywords: CD8+ T cells; Cytokine; Cytolysis; Norepinephrine; β2-Adrenergic receptor.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The β2-adrenergic receptor controls inflammation by driving rapid IL-10 secretion.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Nov;74:176-185. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 30195028 Free PMC article.
-
β-Adrenergic signaling blocks murine CD8+ T-cell metabolic reprogramming during activation: a mechanism for immunosuppression by adrenergic stress.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 Jan;68(1):11-22. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2243-8. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30229289 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine preferentially modulates memory CD8 T cell function inducing inflammatory cytokine production and reducing proliferation in response to activation.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 May;46:168-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.01.015. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25653192 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-nonspecific activation of CD8+ T lymphocytes by cytokines: relevance to immunity, autoimmunity, and cancer.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2008 Sep-Oct;56(5):311-23. doi: 10.1007/s00005-008-0033-2. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2008. PMID: 18836862 Review.
-
The sympathetic nerve--an integrative interface between two supersystems: the brain and the immune system.Pharmacol Rev. 2000 Dec;52(4):595-638. Pharmacol Rev. 2000. PMID: 11121511 Review.
Cited by
-
α-Synuclein and Noradrenergic Modulation of Immune Cells in Parkinson's Disease Pathogenesis.Front Neurosci. 2018 Sep 11;12:626. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00626. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30258347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The β2-adrenergic receptor controls inflammation by driving rapid IL-10 secretion.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Nov;74:176-185. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 30195028 Free PMC article.
-
Chemogenetic activation of locus coeruleus neurons ameliorates the severity of multiple sclerosis.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Sep 1;20(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02865-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37658434 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the role of cell signaling versus CD8+ T cell modulation in propranolol antitumor activity.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Sep;100(9):1299-1306. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02238-8. Epub 2022 Jul 27. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35895125
-
Radiation Therapy Exacerbates Tumor-Promoting Innervation and Nerve Signaling in Rectal Cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023 Mar 1;115(3):733-745. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.09.080. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023. PMID: 36202180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Felten DL, Felten SY, Carlson SL, Olschowka JA, Livnat S. Noradrenergic and peptidergic innervation of lymphoid tissue. J Immunol. 1985;135:755s–765s. - PubMed
-
- Felten DL, Ackerman KD, Wiegand SJ, Felten SY. Noradrenergic sympathetic innervation of the spleen: I. Nerve fibers associate with lymphocytes and macrophages in specific compartments of the splenic white pulp. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18:28–36. 118–121. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu N, Hori T, Nakane H. An interleukin-1 beta-induced noradrenaline release in the spleen is mediated by brain corticotropin-releasing factor: an in vivo microdialysis study in conscious rats. Brain Behav Immun. 1994;8:14–23. - PubMed
-
- Francis J, MohanKumar SM, MohanKumar PS. Correlations of norepinephrine release in the paraventricular nucleus with plasma corticosterone and leptin after systemic lipopolysaccharide: blockade by soluble IL-1 receptor. Brain Res. 2000;867:180–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

