The Clinical Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Ultra-Pulsed Fractional CO2 Laser Therapy for Facial Rejuvenation
- PMID: 27222038
- PMCID: PMC5314998
- DOI: 10.1089/rej.2016.1823
The Clinical Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Ultra-Pulsed Fractional CO2 Laser Therapy for Facial Rejuvenation
Abstract
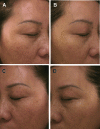
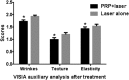
Ultra-pulsed fractional CO2 laser is an efficient, precise, and safe therapeutic intervention for skin refreshing, although accompanied with prolonged edema and erythema. In recent years, autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has been proven to promote wound and soft tissue healing and collagen regeneration. To investigate whether the combination of PRP and ultra-pulsed fractional CO2 laser had a synergistic effect on therapy for facial rejuvenation. Totally, 13 facial aging females were treated with ultra-pulsed fractional CO2 laser. One side of the face was randomly selected as experimental group and injected with PRP, the other side acted as the control group and was injected with physiological saline at the same dose. Comprehensive assessment of clinical efficacy was performed by satisfaction scores, dermatologists' double-blind evaluation and the VISIA skin analysis system. After treatment for 3 months, subjective scores of facial wrinkles, skin texture, and skin elasticity were higher than that in the control group. Similarly, improvement of skin wrinkles, texture, and tightness in the experimental group was better compared with the control group. Additionally, the total duration of erythema, edema, and crusting was decreased, in the experimental group compared with the control group. PRP combined with ultra-pulsed fractional CO2 laser had a synergistic effect on facial rejuvenation, shortening duration of side effects, and promoting better therapeutic effect.
Keywords: adverse events; combination therapy; recovery time; synergistic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Puizina-Ivic N. Skin aging. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2008;17:47–54 - PubMed
-
- Kohl E, Meierhofer J, Koller M, Zeman F, Groesser L, Karrer S, Hohenleutner U, Landthaler M, Hohenleutner S. Fractional carbon dioxide laser resurfacing of rhytides and photoaged skin—a prospective clinical study on patient expectation and satisfaction. Lasers Surg Med 2015;47:111–119 - PubMed
-
- Yaar M, Eller MS, Gilchrest BA. Fifty years of skin aging. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 2002;7:51–58 - PubMed
-
- Agrawal N, Smith G, Heffelfinger R. Ablative skin resurfacing. Facial Plast Surg 2014;30:55–61 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
