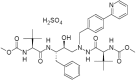
Trace Level Determination of Mesityl Oxide and Diacetone Alcohol in Atazanavir Sulfate Drug Substance by a Gas Chromatography Method
- PMID: 27222607
- PMCID: PMC4871184
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1507-05
Trace Level Determination of Mesityl Oxide and Diacetone Alcohol in Atazanavir Sulfate Drug Substance by a Gas Chromatography Method
Abstract
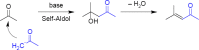
A capillary gas chromatography method with a short run time, using a flame ionization detector, has been developed for the quantitative determination of trace level analysis of mesityl oxide and diacetone alcohol in the atazanavir sulfate drug substance. The chromatographic method was achieved on a fused silica capillary column coated with 5% diphenyl and 95% dimethyl polysiloxane stationary phase (Rtx-5, 30 m x 0.53 mm x 5.0 µm). The run time was 20 min employing programmed temperature with a split mode (1:5) and was validated for specificity, sensitivity, precision, linearity, and accuracy. The detection and quantitation limits obtained for mesityl oxide and diacetone alcohol were 5 µg/g and 10 µg/g, respectively, for both of the analytes. The method was found to be linear in the range between 10 µg/g and 150 µg/g with a correlation coefficient greater than 0.999, and the average recoveries obtained in atazanavir sulfate were between 102.0% and 103.7%, respectively, for mesityl oxide and diacetone alcohol. The developed method was found to be robust and rugged. The detailed experimental results are discussed in this research paper.
Keywords: Atazanavir sulfate; Development; Diacetone alcohol; GC-FID; Mesityl oxide; Validation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of thermolabile residual solvents in a spray dried dispersion using static headspace gas chromatography.J Sep Sci. 2019 Mar;42(6):1222-1229. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201801024. Epub 2019 Jan 22. J Sep Sci. 2019. PMID: 30618204
-
Development and validation of a gas chromatography method for the trace level determination of allylamine in sevelamer hydrochloride and sevelamer carbonate drug substances.Sci Pharm. 2013 Nov 14;82(1):117-28. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1309-12. Print 2014 Jan-Mar. Sci Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24634846 Free PMC article.
-
Direct separation, identification and quantification of epimers 22R and 22S of budesonide by capillary gas chromatography on a short analytical column with Rtx-5 stationary phase.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2004 Apr 25;803(2):191-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2003.12.038. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15063325
-
SPME-GC determination of potential volatile organic leachables in aqueous-based pharmaceutical formulations packaged in overwrapped LDPE vials.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008 Jul 15;47(3):526-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2008.02.004. Epub 2008 Feb 14. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008. PMID: 18372139
-
Stability-Indicating Method Development and Validation for Busulfan Drug Substance by Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detector.J Chromatogr Sci. 2021 Jan 14;59(2):112-119. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmaa093. J Chromatogr Sci. 2021. PMID: 33290539
References
-
- Fukushima K, Terasaka S, Haraya K, Kodera S, Seki Y, Wada A, Ito Y, Shibata N, Sugioka N, Takada K. Pharmaceutical approach to HIV protease inhibitor atazanavir for bioavailability enhancement based on solid dispersion system. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30:733–738. http://dx.doi.org/10.1248/bpb.30.733 . - PubMed
-
- Croom KF, Dhillon S, Keam SJ. Atazanavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV-1 infection. Drugs. 2009;69:1107–1140. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200969080-00009 . - PubMed
-
- Swainston Harrison T, Scott LJ. Atazanavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV infection. Drugs. 2005;65:2309–2336. http://dx.doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200565160-00010 . - PubMed
-
- United States Pharmacopeia–National Formulary. USP37-NF32 S1, <467>Residual solvents
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
