Transdermal delivery of Diltiazem HCl from matrix film: Effect of penetration enhancers and study of antihypertensive activity in rabbit model
- PMID: 27222758
- PMCID: PMC4856784
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2015.09.001
Transdermal delivery of Diltiazem HCl from matrix film: Effect of penetration enhancers and study of antihypertensive activity in rabbit model
Abstract
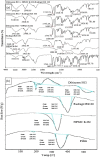
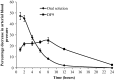
The present investigation focused on the development of Diltiazem HCl (DTH) matrix film and its characterization by in-vitro, ex-vivo and in-vivo methods. Films were prepared by solvent casting method by taking different ratios of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose K4M (HPMC K4M) and Eudragit RS100. Various parameters of the films were analyzed such as mechanical property using tensile tester, interaction study by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), in-vitro drug release through cellulose acetate membrane, ex-vivo permeation study using abdominal skin of rat employing Franz diffusion cell, and in-vivo antihypertensive activity using rabbit model. The FTIR studies confirmed the absence of interaction between DTH and selected polymers. Thermal analysis showed the shifting of endothermic peak of DTH in film, indicating the dispersion of DTH in molecular form throughout the film. Incorporation of 1,8-cineole showed highest flux (89.7 μg/cm(2)/h) of DTH compared to other penetration enhancers such as capsaicin, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and N-methyl pyrrolidone (NMP). Photomicrographs of histology study on optimized formulation (DF9) illustrated disruption of stratum corneum (SC) supporting the ex-vivo results. The in-vivo antihypertensive activity results demonstrated that formulation DF9 was effective in reducing arterial blood pressure in normotensive rabbits. SEM analysis of films kept for stability study (40 ± 2 °C/75% ± 5%RH for 3 months) revealed the formation of drug crystals which may be due to higher temperature. The findings of the study provide a better alternative dosage form of DTH for the effective treatment of hypertension with enhanced patient compliance.
Keywords: Antihypertensive activity; Eudragit RS100; Matrix film; Penetration enhancers; Stratum corneum.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Formulation of Polymers-Based Methotrexate Patches and Investigation of the Effect of Various Penetration Enhancers: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Characterization.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 30;14(11):2211. doi: 10.3390/polym14112211. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35683883 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Characterization of Agarose/HPMC Buccal Films Bearing Ondansetron HCl In Vitro and In Vivo: Enhancement Using Iontophoretic and Chemical Approaches.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Mar 25;2022:1662194. doi: 10.1155/2022/1662194. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9841865. doi: 10.1155/2024/9841865. PMID: 35372569 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Development of carvedilol transdermal patches: evaluation of physicochemical, ex vivo and mechanical properties.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2008 Nov-Dec;62(6):391-401. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2008. PMID: 19634343
-
In vitro and In vivo characterization of the transdermal delivery of sertraline hydrochloride Films.Daru. 2011;19(6):424-32. Daru. 2011. PMID: 23008688 Free PMC article.
-
Design of novel miconazole nitrate transdermal films based on Eudragit RS100 and HPMC hybrids: preparation, physical characterization, in vitro and ex vivo studies.Drug Deliv. 2015 Dec;22(8):1078-1085. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2013.875604. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24455998
Cited by
-
Fabrication of a Ti porous microneedle array by metal injection molding for transdermal drug delivery.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 10;12(2):e0172043. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172043. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28187179 Free PMC article.
-
Pluronic lecithin organogel (PLO) of diltiazem hydrochloride: effect of solvents/penetration enhancers on ex vivo permeation.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016 Jun;6(3):243-53. doi: 10.1007/s13346-015-0276-5. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 26754742
-
The Influence of Microneedles on the Percutaneous Penetration of Selected Antihypertensive Agents: Diltiazem Hydrochloride and Perindopril Erbumine.Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(10):1449-1458. doi: 10.2174/1567201815666180730125941. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 30058488 Free PMC article.
-
TRPA1-dependent reversible opening of tight junction by natural compounds with an α,β-unsaturated moiety and capsaicin.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 2;8(1):2251. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20526-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29396565 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacodynamic Studies of Pravastatin Sodium Nanoemulsion Loaded Transdermal Patch for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Feb 8;25(2):34. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02746-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38332233
References
-
- Michiels C.F., Hove C.E.V., Martinet W., De-Meyer G.R.Y., Fransen P. L-type Ca2+ channel blockers inhibit the window contraction of mouse aorta segments with high affinity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;738:170–178. - PubMed
-
- Puche J.J., Garcia-Coret M.J., Villalba F.L., Mahmoud I.A., Roig J.V. Local treatment of a chronic anal fissure with diltiazem vs. nitroglycerin. A comparative study. Cir Espan (Eng ed) 2010;87:224–230. - PubMed
-
- Adibkia K., Shokri J., Barzegar-Jalali M., Solduzian M., Javadzadeh Y. Effect of solvent type on retardation properties of diltiazem HCl form liquisolid tablets. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2014;113:10–14. - PubMed
-
- Bhunia T., Giri A., Nasim T., Chattopadhyay D., Bandyopadhyay A. Uniquely different PVA–xanthan gum irradiated membranes as transdermal diltiazem delivery device. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;95:252–261. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

