Vascular composition data supporting the role of N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the prevention of cardiovascular disease events
- PMID: 27222841
- PMCID: PMC4867859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.03.101
Vascular composition data supporting the role of N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the prevention of cardiovascular disease events
Abstract
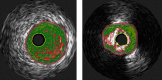
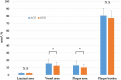
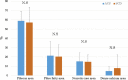
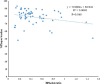
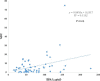
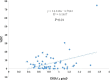
N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are thought to have protective effects against cardiovascular disease. Here, we report the relationship between serum PUFA concentrations and plaque composition, as evaluated by virtual histology-intravascular ultrasound (VH-IVUS). Consecutive patients (n=61) who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) were pre-operatively examined using VH-IVUS to assess the composition of culprit plaques. Gray-scale IVUS and VH-IVUS data of fibrous, fibro-fatty, necrotic core, and dense calcium regions of plaques were estimated at the minimal luminal area sites of culprit lesions. Serum levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and PUFAs, including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and arachidonic acid (AA), were compared between patients with (ACS, n=27) and without acute coronary syndrome (non-ACS, n=34) before PCI. Multiple logistic regression analysis of the data showed that EPA/AA under the median was more highly associated with ACS than hsCRP over the median. In addition, EPA/AA was negatively correlated with the percentage of fibrous plaque regions and EPA/AA and DHA/AA were positively correlated with the percentage of dense calcium regions in plaques. Furthermore, the correlation index of EPA/AA was the most highly (R=0.513) correlated with the percentage of dense calcium regions in plaques.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Eicosapentaenoic acid; N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; Stable coronary disease; Virtual histology-intravascular ultrasound.
Figures

References
-
- Hong M.K., Mintz G.S., Lee C.W., Suh J., Kim J.H., Park D.W., Lee S.W., Kim Y.H., Cheong S.S., Kim J.J., Park S.W., Park S.J. Comparison of virtual histology to intravascular ultrasound of culprit coronary lesions in acute coronary syndrome and target coronary lesions in stable angina pectoris. Am. J. Cardiol. 2007;100:953–959. - PubMed
-
- Boden W.E., O׳Rourke R.A., Teo K.K., Hartigan P.M., Maron D.J., Kostuk W.J., Knudtson M., Dada M., Casperson P., Harris C.L., Chaitman B.R., Shaw L., Gosselin G., Nawaz S., Title L.M., Gau G., Blaustein A.S., Booth D.C., Bates E.R., Spertus J.A., Berman D.S., Mancini G.B., Weintraub W.S., COURAGE Trial Research Group Optimal medical therapy with or without PCI for stable coronary disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2007;356:1503–1516. - PubMed
-
- Hong Y.J., Jeong M.H., Choi Y.H., Ko J.S., Lee M.G., Kang W.Y., Lee S.E., Kim S.H., Park K.H., Sim D.S., Yoon N.S., Youn H.J., Kim K.H., Park H.W., Kim J.H., Ahn Y., Cho J.G., Park J.C., Kang J.C. Impact of plaque components on no-reflow phenomenon after stent deployment in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a virtual histology-intravascular ultrasound analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2011;32:2059–2066. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Surmely J.F., Nasu K., Fujita H., Terashima M., Matsubara T., Tsuchikane E., Ehara M., Kinoshita Y., Zheng Q.X., Tanaka N., Katoh O., Suzuki T. Coronary plaque composition of culprit/target lesions according to the clinical presentation: a virtual histology intravascular ultrasound analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2006;27:2939–2944. - PubMed
-
- Mintz G.S., Nissen S.E., Anderson W.D., Bailey S.R., Erbel R., Fitzgerald P.J., Pinto F.J., Rosenfield K., Siegel R.J., Tuzcu E.M., Yock P.G. American College of Cardiology clinical expert consensus document on standards for acquisition, measurement and reporting of intravascular ultrasound studies (ivus). A report of the american college of cardiology task force on clinical expert consensus documents. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001;237:1478–1492. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

