FKBP14 overexpression contributes to osteosarcoma carcinogenesis and indicates poor survival outcome
- PMID: 27223089
- PMCID: PMC5129977
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9524
FKBP14 overexpression contributes to osteosarcoma carcinogenesis and indicates poor survival outcome
Abstract
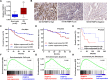
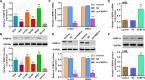
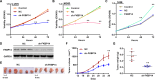
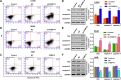
The FK506-binding protein 14 (FKBP14) is a subfamily of immunophilins, has been implicated in various biochemical processes. However, its effects on the primary malignant bone tumor, osteosarcoma, are unclear. Here, we reported that FKBP14 may be an oncogene as it overexpressed in osteosarcoma tissues and cell lines, and FKBP14 expression was correlated with metastases, recurrence, tumor maximum diameter and poor survival time. FKBP14 was associated with the biological pathways including cell cycle, apoptosis and metastasis. Furthermore, we detected FKBP14 knockdown induced cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, invasion and adhesion in vitro. FKBP14 knockdown decreased the protein levels of PCNA, CDK1 and CCNB1 that promotes cell cycle, increased Bax, caspase-3 and caspase-7 protein involved in promoting cell apoptosis, and increased KIF4A expression as well as decreased SMC4 and TMEM33 proteins that contribute to cell invasion and adhesion. In addition, FKBP14 knockdown also caused a significant inhibition in tumor growth in vivo. Then, we found that the protein RhoA was identified as a binding partner of FKBP14. Taken together, FKBP14 may act as an oncogene in osteosarcoma via suppressing apoptosis and promoting invasion and adhesion in osteosarcoma carcinogenesis. FKBP14 may be a prognostic factor and potential target for osteosarcoma treatment.
Keywords: FKBP14; GSEA; apoptosis; osteosarcoma; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effects of FKBP14 on human cervical cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):4265-4272. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7043. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28731139
-
TRIM66 overexpresssion contributes to osteosarcoma carcinogenesis and indicates poor survival outcome.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 15;6(27):23708-19. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4291. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26247633 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-361 inhibits osteosarcoma cell lines invasion and proliferation by targeting FKBP14.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jan;22(1):79-86. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201801_14103. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29364473
-
RNAi-mediated silencing of AQP1 expression inhibited the proliferation, invasion and tumorigenesis of osteosarcoma cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(9):1332-40. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1070983. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26176849 Free PMC article.
-
How the NOTCH pathway contributes to the ability of osteosarcoma cells to metastasize.Cancer Treat Res. 2009;152:479-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-0284-9_28. Cancer Treat Res. 2009. PMID: 20213410 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Significance and Potential Mechanisms of the RNA Methyltransferase KIAA1429 in Osteosarcoma.J Cancer. 2024 Jan 1;15(1):126-139. doi: 10.7150/jca.86630. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38164289 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and analysis of genes associated with epithelial ovarian cancer by integrated bioinformatics methods.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 18;16(6):e0253136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253136. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34143800 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Nov 14;13(21):24050-24070. doi: 10.18632/aging.203585. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34775374 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of FKBP14 in Gastric Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Dec 30;12:11567-11577. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S221943. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31920344 Free PMC article.
-
FKBP14 Promotes The Proliferation And Migration Of Colon Carcinoma Cells Through Targeting IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Nov 1;12:9069-9076. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S222555. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31802914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacci G, Rocca M, Salone M, Balladelli A, Ferrari S, Palmerini E, Forni C, Briccoli A. High grade osteosarcoma of the extremities with lung metastases at presentation: treatment with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and simultaneous resection of primary and metastatic lesions. J Surg Oncol. 2008;98:415–420. - PubMed
-
- Kager L, Zoubek A, Pötschger U, Kastner U, Flege S, Kempf-Bielack B, Branscheid D, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Winkelmann W. Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: presentation and outcome of patients treated on neoadjuvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group protocols. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2011–2018. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

