Leprosy in children and adolescents under 15 years old in an urban centre in Brazil
- PMID: 27223655
- PMCID: PMC4909033
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760160002
Leprosy in children and adolescents under 15 years old in an urban centre in Brazil
Abstract
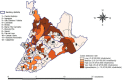
This original study describes the intra-urban distribution of cases of leprosy in residents under 15 years old in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil; the study also identifies the environment in which Mycobacterium leprae is being transmitted. The cases were distributed by operational classification, clinical forms, type of contact and the addresses were geo-referenced by neighborhood. Between 2007 and 2011, were reported 145 cases of leprosy in target population living in Salvador, corresponding to detection rates of 6.21, 6.14, 5.58, 5.41 and 6.88/100,000 inhabitants, respectively. The spatial distribution of the disease was focal. Of the 157 neighborhoods of Salvador, 44 (28.6%) notified cases of leprosy and in 22 (50%) of these were detected more than 10 cases per 100,000 inhabitants. The infectious forms were found in 40% of cases. Over 90% of cases had been living in Salvador for more than five years. Overall, 52.6% reported having had contact with another infected individual inside the household and 25% in their social circle. In Salvador, M. leprae transmission is established. The situation is a major concern, since transmission is intense at an early age, indicating that this endemic disease is expanding and contacts extend beyond individual households.
Figures
References
-
- Aagaard-Hansen J, Nombela N, Alvar J. Population movement: a key factor in the epidemiology of neglected tropical diseases. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15(11):1281–1288. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira IN, Evangelista MSN, Alvarez RR. Distribuição espacial da hanseníase na população escolar em Paracatu - Minas Gerais, realizada por meio da busca ativa (2004 a 2006) Rev Bras Epidemiol. 2007;10(4):555–557.
-
- Fine PEM, Sterne JAC, Ponnighaus JM, Bliss L, Saul J, Chihana A, et al. Household and dwelling contact as risk factors for leprosy in northern Malawi. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;146(1):91–102. - PubMed
-
- Fine PEM. Leprosy: the epidemiology of a slow bacterium. Epidemiol Rev. 1982;4(1):161–188. - PubMed
-
- Fine PEM. Reflections on the elimination of leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1992;60(1):71–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical