Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases in the Bacterial World
- PMID: 27223819
- PMCID: PMC11575706
- DOI: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0002-2016
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases in the Bacterial World
Abstract
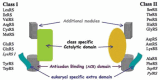
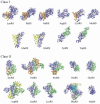
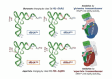
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRSs) are modular enzymes globally conserved in the three kingdoms of life. All catalyze the same two-step reaction, i.e., the attachment of a proteinogenic amino acid on their cognate tRNAs, thereby mediating the correct expression of the genetic code. In addition, some aaRSs acquired other functions beyond this key role in translation. Genomics and X-ray crystallography have revealed great structural diversity in aaRSs (e.g., in oligomery and modularity, in ranking into two distinct groups each subdivided in 3 subgroups, by additional domains appended on the catalytic modules). AaRSs show huge structural plasticity related to function and limited idiosyncrasies that are kingdom or even species specific (e.g., the presence in many Bacteria of non discriminating aaRSs compensating for the absence of one or two specific aaRSs, notably AsnRS and/or GlnRS). Diversity, as well, occurs in the mechanisms of aaRS gene regulation that are not conserved in evolution, notably between distant groups such as Gram-positive and Gram-negative Bacteria. The review focuses on bacterial aaRSs (and their paralogs) and covers their structure, function, regulation, and evolution. Structure/function relationships are emphasized, notably the enzymology of tRNA aminoacylation and the editing mechanisms for correction of activation and charging errors. The huge amount of genomic and structural data that accumulated in last two decades is reviewed, showing how the field moved from essentially reductionist biology towards more global and integrated approaches. Likewise, the alternative functions of aaRSs and those of aaRS paralogs (e.g., during cell wall biogenesis and other metabolic processes in or outside protein synthesis) are reviewed. Since aaRS phylogenies present promiscuous bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryal features, similarities and differences in the properties of aaRSs from the three kingdoms of life are pinpointed throughout the review and distinctive characteristics of bacterium-like synthetases from organelles are outlined.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases in the Bacterial World.EcoSal Plus. 2012 Nov;5(1). doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.4.2.1. EcoSal Plus. 2012. PMID: 26442825
-
Evolution of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases--analysis of unique domain architectures and phylogenetic trees reveals a complex history of horizontal gene transfer events.Genome Res. 1999 Aug;9(8):689-710. Genome Res. 1999. PMID: 10447505
-
Neurodegenerative Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease as a case study to decipher novel functions of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 5;294(14):5321-5339. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV118.002955. Epub 2019 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30643024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive characterization of mRNAs associated with yeast cytosolic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.RNA Biol. 2021 Dec;18(12):2605-2616. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1935116. Epub 2021 Jun 10. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 34039240 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Catalysts and Substrates for Activity of Class Ib Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases and Implications for Pharmacology.Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(6):616-33. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150819110018. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26286212 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-Protein Interactions of Seryl-tRNA Synthetases with Emphasis on Human Counterparts and Their Connection to Health and Disease.Life (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;14(1):124. doi: 10.3390/life14010124. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional analysis of Rossmann-like domains reveals convergent evolution of topology and reaction pathways.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Dec 23;15(12):e1007569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007569. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31869345 Free PMC article.
-
Serine-Threonine Kinases Encoded by Split hipA Homologs Inhibit Tryptophanyl-tRNA Synthetase.mBio. 2019 Jun 18;10(3):e01138-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01138-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31213559 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmodium apicoplast tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase recognizes an unusual, simplified identity set in cognate tRNATyr.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 28;13(12):e0209805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209805. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30592748 Free PMC article.
-
X-shaped structure of bacterial heterotetrameric tRNA synthetase suggests cryptic prokaryote functions and a rationale for synthetase classifications.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Sep 27;49(17):10106-10119. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab707. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34390350 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

