Performance of Bio-Rad and Limiting Antigen Avidity Assays in Detecting Recent HIV Infections Using the Quebec Primary HIV-1 Infection Cohort
- PMID: 27224023
- PMCID: PMC4880343
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156023
Performance of Bio-Rad and Limiting Antigen Avidity Assays in Detecting Recent HIV Infections Using the Quebec Primary HIV-1 Infection Cohort
Abstract
Background: Accurate and practical biologic tools to estimate HIV incidence is crucial to better monitor the epidemic and evaluate the effectiveness of HIV prevention and treatment programs.
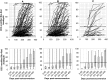
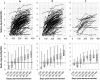
Methods: We evaluated two avidity assays to measure recent HIV infection: the Sedia HIV-1 LAg-Avidity EIA (Sedia Biosciences, Portland) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-modified Bio-Rad-Avidity assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Mississauga, ON). Longitudinal specimens (n = 473) obtained from 123 treatment-naive seroconverted individuals enrolled in the Primary HIV-1 Infection (PHI) cohort of Quebec were used to determine the average time an individual is considered to be recently infected (mean duration of recent infection; MDRI), for the two avidity assays alone and in combination using a nonparametric survival method analysis. A total of 420 specimens from individuals with established HIV infection (90 individuals from the PHI cohort of Quebec and 330 individuals from the Laboratoire de santé publique du Quebec (LSPQ) serobank) were also tested to investigate false recency rate (FRR).
Results: The CDC-modified Bio-Rad-Avidity gave an estimated MDRI of 234 days (95% CI 220-249) at the avidity index cutoff of 30% while the Sedia-LAg-Avidity assay gave an estimated MDRI of 120 days (95% CI 109-132) at the normalized optical density (ODn) cutoff of 1.5. The FRR among individuals with established HIV infection was 10.2% (7.5%-13.5%) with the CDC-modified Bio-Rad-Avidity assay as compared to 6.0% (3.9%-8.7%) with the Sedia-LAg-Avidity assay. When optimizing a multiassay algorithm (MAA) that includes sequentially the CDC-modified Bio-Rad-Avidity assay then the Sedia-LAg-Avidity assay EIA (avidity index/ODn: 30%/1.7), the MDRI was 136 days (95% CI 123-148) and the FRR, 3.3% (95% CI 1.8-5.6).
Conclusion: Multiassay algorithms that include the CDC-modified Bio-Rad-Avidity assay and the Sedia-LAg-Avidity assay performed better than each avidity assay alone. Such 2-assay algorithm that starts with the CDC-modified Bio-Rad-Avidity assay followed by the Sedia-LAg-Avidity assay allowed a better classification of HIV-1 infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Performance comparison of the Maxim and Sedia Limiting Antigen Avidity assays for HIV incidence surveillance.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 26;14(7):e0220345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220345. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31348809 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Evaluation of a Modified Fourth-Generation Human Immunodeficiency Virus Enzyme Immunoassay for Cross-Sectional Incidence Estimation in Clade B Populations.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2016 Aug;32(8):756-62. doi: 10.1089/AID.2015.0198. Epub 2016 May 5. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2016. PMID: 26988426 Free PMC article.
-
Short Communication: Comparison of Maxim and Sedia Limiting Antigen Assay Performance for Measuring HIV Incidence.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2017 Jun;33(6):555-557. doi: 10.1089/aid.2016.0245. Epub 2017 Mar 20. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2017. PMID: 28318310 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of limiting antigen avidity enzyme immunoassay for detection of recent HIV-1 infection to expand supported applications.J Virus Erad. 2022 Sep 7;8(3):100085. doi: 10.1016/j.jve.2022.100085. eCollection 2022 Sep. J Virus Erad. 2022. PMID: 36124229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moving towards a reliable HIV incidence test - current status, resources available, future directions and challenges ahead.Epidemiol Infect. 2017 Apr;145(5):925-941. doi: 10.1017/S0950268816002910. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Epidemiol Infect. 2017. PMID: 28004622 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low CD4 count was characterized in recent HIV CRF01_AE infection and it rapidly increased to reach a peak in the first year since ART initiation.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 31;25(1):443. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10799-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40165131 Free PMC article.
-
Short Communication: Validation of the Asante HIV-1 Rapid Recency Assay for Detection of Recent HIV-1 Infections in Uganda.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021 Dec;37(12):893-896. doi: 10.1089/AID.2020.0279. Epub 2021 Feb 25. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021. PMID: 33499732 Free PMC article.
-
A Short-Term Assessment of Nascent HIV-1 Transmission Clusters Among Newly Diagnosed Individuals Using Envelope Sequence-Based Phylogenetic Analyses.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2019 Oct;35(10):906-919. doi: 10.1089/AID.2019.0142. Epub 2019 Sep 10. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2019. PMID: 31407606 Free PMC article.
-
The related factors of new HIV infection among older men in Sichuan, China: a case-control study.Epidemiol Infect. 2022 Aug 15;150:e156. doi: 10.1017/S0950268822001352. Epidemiol Infect. 2022. PMID: 35968710 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Humoral Immune Responses against Capsid Protein p24 and Transmembrane Glycoprotein gp41 of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 in China.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 1;11(11):e0165874. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165874. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27802337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fiamma A, Lissouba P, Amy OE, Singh B, Laeyendecker O, Quinn TC, et al. Can HIV incidence testing be used for evaluating HIV intervention programs? A reanalysis of the Orange Farm male circumcision trial (ANRS-1265). BMC infectious diseases. 2010;10:137 10.1186/1471-2334-10-137 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS/WHO Working Group on Global HIV/AIDS/STI Surveillance. When and how to use assays for recent infection to estimate HIV incidence at a population level. 2011:1–48.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

