Discovery of high affinity anti-ricin antibodies by B cell receptor sequencing and by yeast display of combinatorial VH:VL libraries from immunized animals
- PMID: 27224530
- PMCID: PMC4968101
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2016.1190059
Discovery of high affinity anti-ricin antibodies by B cell receptor sequencing and by yeast display of combinatorial VH:VL libraries from immunized animals
Abstract
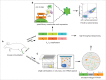
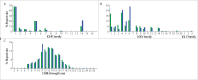
Ricin is a toxin that could potentially be used as a bioweapon. We identified anti-ricin A chain antibodies by sequencing the antibody repertoire from immunized mice and by selecting high affinity antibodies using yeast surface display. These methods led to the isolation of multiple antibodies with high (sub-nanomolar) affinity. Interestingly, the antibodies identified by the 2 independent approaches are from the same clonal lineages, indicating for the first time that yeast surface display can identify native antibodies. The new antibodies represent well-characterized reagents for biodefense diagnostics and therapeutics development.
Keywords: Antibody repertoire analysis; next-generation sequencing; ricin A chain; yeast surface display.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antibody isolation from immunized animals: comparison of phage display and antibody discovery via V gene repertoire mining.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2012 Oct;25(10):539-49. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzs060. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2012. PMID: 22988130
-
Next-Generation DNA Sequencing of VH/VL Repertoires: A Primer and Guide to Applications in Single-Domain Antibody Discovery.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1701:425-446. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7447-4_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29116520
-
Stepwise engineering of heterodimeric single domain camelid VHH antibodies that passively protect mice from ricin toxin.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 20;288(51):36538-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.519207. Epub 2013 Nov 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24202178 Free PMC article.
-
Cognizance of Molecular Methods for the Generation of Mutagenic Phage Display Antibody Libraries for Affinity Maturation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 15;20(8):1861. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081861. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30991723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian cell display and somatic hypermutation in vitro for human antibody discovery.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2014 Mar;11(1):56-64. doi: 10.2174/15701638113109990037. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2014. PMID: 23978037 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare, high-affinity anti-pathogen antibodies from human repertoires, discovered using microfluidics and molecular genomics.MAbs. 2017 Nov/Dec;9(8):1282-1296. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2017.1371383. Epub 2017 Aug 28. MAbs. 2017. PMID: 28846502 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody repertoire analysis of mouse immunization protocols using microfluidics and molecular genomics.MAbs. 2019 Jul;11(5):870-883. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2019.1583995. Epub 2019 Mar 21. MAbs. 2019. PMID: 30898066 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of Antibodies with Tailored Properties by Application of High-Throughput Multiparameter Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting of Yeast-Displayed Immune Libraries.Mol Biotechnol. 2018 Oct;60(10):727-735. doi: 10.1007/s12033-018-0109-0. Mol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30076531 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Landscape of Nanobodies and Their Neutralizing Applications against SARS-CoV-2 Virus.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Jun 5;6(7):925-942. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00042. eCollection 2023 Jul 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37470012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient yeast surface-display of novel complex synthetic cellulosomes.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Aug 7;17(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-0971-2. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 30086751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lord JM, Roberts LM, Robertus JD. Ricin: structure, mode of action, and some current applications. J Fed Am Societies Exp Biol 1994; 8:201-8; PMID:8119491. - PubMed
-
- Audi J, Belson M, Patel M, Schier J, Osterloh J. Ricin Poisoning A Comprehensive Review. J Am Med Assoc 2005; 294:2342-51; PMID:16278363; http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.294.18.2342 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mayor S. UK doctors warned after ricin poison found in police raid. Br Med J 2003; 326:126; PMID:12531838; http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.326.7381.126 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maddaloni M, Cooke C, Wilkinson R, Stout AV, Eng L, Pincus SH. Immunological Characteristics Associated with the Protective Efficacy of Antibodies to Ricin. J Immunol 2004; 172:6221-8; PMID:15128810; http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.172.10.6221 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
