Use, complications, and costs of stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer
- PMID: 27224858
- PMCID: PMC4974119
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.30101
Use, complications, and costs of stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for localized prostate cancer has potential advantages over traditional radiotherapies. Herein, the authors compared national trends in use, complications, and costs of SBRT with those of traditional radiotherapies.
Methods: The authors identified men who underwent SBRT, intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), brachytherapy, and proton beam therapy as primary treatment of prostate cancer between 2004 and 2011 from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER)-Medicare linked data. Temporal trend of therapy use was assessed using the Cochran-Armitage test. Two-year outcomes were compared using the chi-square test. Median treatment costs were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis test.
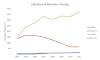
Results: A total of 542 men received SBRT, 9647 received brachytherapy, 23,408 received IMRT, and 800 men were treated with proton beam therapy. There was a significant increase in the use of SBRT and proton beam therapy (P<.001), whereas brachytherapy use decreased (P<.001). A higher percentage of patients treated with SBRT and brachytherapy had low-grade cancer (Gleason score ≤ 6 vs ≥ 7) compared with individuals treated with IMRT and proton beam therapy (54.0% and 64.2% vs 35.2% and 49.6%, respectively; P<.001). SBRT compared with brachytherapy and IMRT was associated with equivalent gastrointestinal toxicity but more erectile dysfunction at 2-year follow-up (P<.001). SBRT was associated with more urinary incontinence compared with IMRT and proton beam therapy but less compared with brachytherapy (P<.001, respectively). The median cost of SBRT was $27,145 compared with $17,183 for brachytherapy, $37,090 for IMRT, and $54,706 for proton beam therapy (P<.001).
Conclusions: The use of SBRT and proton beam therapy for localized prostate cancer has increased over time. Despite men of lower disease stage undergoing SBRT, SBRT was found to be associated with greater toxicity but lower health care costs compared with IMRT and proton beam therapy. Cancer 2016;122:2496-504. © 2016 American Cancer Society.
Keywords: health care costs; prostate cancer; proton beam therapy; radiosurgery; radiotherapy; stereotactic body radiotherapy; toxicity.
© 2016 American Cancer Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Use, Complications, and Costs of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Localized Prostate Cancer.J Urol. 2016 Dec;196(6):1676-1677. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.09.064. Epub 2016 Sep 15. J Urol. 2016. PMID: 27845107 No abstract available.
-
Urinary toxicity after stereotactic body radiotherapy: The boy who cried wolf?Cancer. 2017 Feb 1;123(3):531-532. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30432. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27997685 No abstract available.
-
Reply to Urinary toxicity after stereotactic body radiotherapy: The boy who cried wolf?Cancer. 2017 Feb 1;123(3):532-533. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30433. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27997689 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Comparative Toxicities and Cost of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy, Proton Radiation, and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Among Younger Men With Prostate Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2018 Jun 20;36(18):1823-1830. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.75.5371. Epub 2018 Mar 21. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29561693 Free PMC article.
-
Second malignancy probabilities in prostate cancer patients treated with SBRT and other contemporary radiation techniques.Radiother Oncol. 2021 Aug;161:241-250. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2021.06.023. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Radiother Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34171451
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy versus intensity-modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer: comparison of toxicity.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Apr 20;32(12):1195-201. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.53.8652. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24616315 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy for prostate cancer-a review.Chin Clin Oncol. 2017 Sep;6(Suppl 2):S10. doi: 10.21037/cco.2017.06.05. Chin Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28917248 Review.
-
[Toxicity and quality of life comparison of iodine 125 brachytherapy and stereotactic radiotherapy for prostate cancers].Cancer Radiother. 2017 Oct;21(6-7):478-490. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2017.07.043. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Cancer Radiother. 2017. PMID: 28888746 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Reducing PTV margins for prostate SBRT with motion compensation and gating techniques.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 Apr;24(4):e13861. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13861. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36478148 Free PMC article.
-
Making radiation therapy more effective in the era of precision medicine.Precis Clin Med. 2020 Dec 1;3(4):272-283. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbaa038. eCollection 2020 Dec. Precis Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 35692625 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Ablative Therapies for Solid Tumors: Recent Advances and Clinical Applications.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan 1;18:1533033819830720. doi: 10.1177/1533033819830720. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30922170 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
3D-printed brachytherapy in patients with cervical cancer: improving efficacy and safety outcomes.Radiat Oncol. 2024 Nov 2;19(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02536-0. Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39488692 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Toxicities and Cost of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy, Proton Radiation, and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Among Younger Men With Prostate Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2018 Jun 20;36(18):1823-1830. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.75.5371. Epub 2018 Mar 21. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29561693 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical