PredictSNP2: A Unified Platform for Accurately Evaluating SNP Effects by Exploiting the Different Characteristics of Variants in Distinct Genomic Regions
- PMID: 27224906
- PMCID: PMC4880439
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004962
PredictSNP2: A Unified Platform for Accurately Evaluating SNP Effects by Exploiting the Different Characteristics of Variants in Distinct Genomic Regions
Abstract
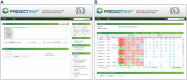
An important message taken from human genome sequencing projects is that the human population exhibits approximately 99.9% genetic similarity. Variations in the remaining parts of the genome determine our identity, trace our history and reveal our heritage. The precise delineation of phenotypically causal variants plays a key role in providing accurate personalized diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of inherited diseases. Several computational methods for achieving such delineation have been reported recently. However, their ability to pinpoint potentially deleterious variants is limited by the fact that their mechanisms of prediction do not account for the existence of different categories of variants. Consequently, their output is biased towards the variant categories that are most strongly represented in the variant databases. Moreover, most such methods provide numeric scores but not binary predictions of the deleteriousness of variants or confidence scores that would be more easily understood by users. We have constructed three datasets covering different types of disease-related variants, which were divided across five categories: (i) regulatory, (ii) splicing, (iii) missense, (iv) synonymous, and (v) nonsense variants. These datasets were used to develop category-optimal decision thresholds and to evaluate six tools for variant prioritization: CADD, DANN, FATHMM, FitCons, FunSeq2 and GWAVA. This evaluation revealed some important advantages of the category-based approach. The results obtained with the five best-performing tools were then combined into a consensus score. Additional comparative analyses showed that in the case of missense variations, protein-based predictors perform better than DNA sequence-based predictors. A user-friendly web interface was developed that provides easy access to the five tools' predictions, and their consensus scores, in a user-understandable format tailored to the specific features of different categories of variations. To enable comprehensive evaluation of variants, the predictions are complemented with annotations from eight databases. The web server is freely available to the community at http://loschmidt.chemi.muni.cz/predictsnp2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

