FOXP2-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphomas exhibit a poor response to R-CHOP therapy and distinct biological signatures
- PMID: 27224915
- PMCID: PMC5288160
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9507
FOXP2-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphomas exhibit a poor response to R-CHOP therapy and distinct biological signatures
Abstract
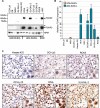
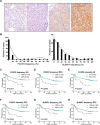
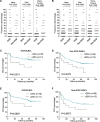
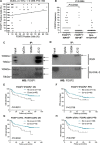
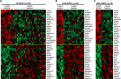
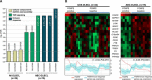
FOXP2 shares partially overlapping normal tissue expression and functionality with FOXP1; an established diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) oncogene and marker of poor prognosis. FOXP2 is expressed in the plasma cell malignancy multiple myeloma but has not been studied in DLBCL, where a poor prognosis activated B-cell (ABC)-like subtype display partially blocked plasma cell differentiation. FOXP2 protein expression was detected in ABC-DLBCL cell lines, and in primary DLBCL samples tumoral FOXP2 protein expression was detected in both germinal center B-cell-like (GCB) and non-GCB DLBCL. In biopsies from DLBCL patients treated with immunochemotherapy (R-CHOP), ≥ 20% nuclear tumoral FOXP2-positivity (n = 24/158) correlated with significantly inferior overall survival (OS: P = 0.0017) and progression-free survival (PFS: P = 0.0096). This remained significant in multivariate analysis against either the international prognostic index score or the non-GCB DLBCL phenotype (P < 0.05 for both OS and PFS). Expression of BLIMP1, a marker of plasmacytic differentiation that is commonly inactivated in ABC-DLBCL, did not correlate with patient outcome or FOXP2 expression in this series. Increased frequency of FOXP2 expression significantly correlated with FOXP1-positivity (P = 0.0187), and FOXP1 co-immunoprecipitated FOXP2 from ABC-DLBCL cells indicating that these proteins can co-localize in a multi-protein complex. FOXP2-positive DLBCL had reduced expression of HIP1R (P = 0.0348), which is directly repressed by FOXP1, and exhibited distinct patterns of gene expression. Specifically in ABC-DLBCL these were associated with lower expression of immune response and T-cell receptor signaling pathways. Further studies are warranted to investigate the potential functional cooperativity between FOXP1 and FOXP2 in repressing immune responses during the pathogenesis of high-risk DLBCL.
Keywords: FOXP2; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Engelhard M, Brittinger G, Huhn D, Gerhartz HH, Meusers P, Siegert W, Thiel E, Wilmanns W, Aydemir U, Bierwolf S, Griesser H, Tiemann M, Lennert K. Subclassification of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas according to the Kiel classification: distinction of centroblastic and immunoblastic lymphomas is a significant prognostic risk factor. Blood. 1997;89:2291–2297. - PubMed
-
- Diebold J, Anderson JR, Armitage JO, Connors JM, Maclennan KA, Muller-Hermelink HK, Nathwani BN, Ullrich F, Weisenburger DD. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic analysis of 444 cases classified according to the updated Kiel classification. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:97–104. - PubMed
-
- De Paepe P, Achten R, Verhoef G, Wlodarska I, Stul M, Vanhentenrijk V, Praet M, De Wolf-Peeters C. Large cleaved and immunoblastic lymphoma may represent two distinct clinicopathologic entities within the group of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7060–7068. - PubMed
-
- Ott G, Ziepert M, Klapper W, Horn H, Szczepanowski M, Bernd HW, Thorns C, Feller AC, Lenze D, Hummel M, Stein H, Muller-Hermelink HK, Frank M, et al. Immunoblastic morphology but not the immunohistochemical GCB/nonGCB classifier predicts outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the RICOVER-60 trial of the DSHNHL. Blood. 2010;116:4916–4925. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

