Antivascular and antitumor properties of the tubulin-binding chalcone TUB091
- PMID: 27224920
- PMCID: PMC5362409
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9527
Antivascular and antitumor properties of the tubulin-binding chalcone TUB091
Abstract
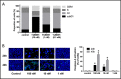
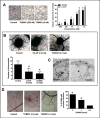
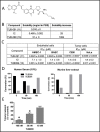
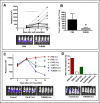
We investigated the microtubule-destabilizing, vascular-targeting, anti-tumor and anti-metastatic activities of a new series of chalcones, whose prototype compound is (E)-3-(3''-amino-4''-methoxyphenyl)-1-(5'-methoxy-3',4'-methylendioxyphenyl)-2-methylprop-2-en-1-one (TUB091). X-ray crystallography showed that these chalcones bind to the colchicine site of tubulin and therefore prevent the curved-to-straight structural transition of tubulin, which is required for microtubule formation. Accordingly, TUB091 inhibited cancer and endothelial cell growth, induced G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis at 1-10 nM. In addition, TUB091 displayed vascular disrupting effects in vitro and in the chicken chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay at low nanomolar concentrations. A water-soluble L-Lys-L-Pro derivative of TUB091 (i.e. TUB099) showed potent antitumor activity in melanoma and breast cancer xenograft models by causing rapid intratumoral vascular shutdown and massive tumor necrosis. TUB099 also displayed anti-metastatic activity similar to that of combretastatin A4-phosphate. Our data indicate that this novel class of chalcones represents interesting lead molecules for the design of vascular disrupting agents (VDAs). Moreover, we provide evidence that our prodrug approach may be valuable for the development of anti-cancer drugs.
Keywords: cancer; drug research; tubulin; vascular-disrupting.
Conflict of interest statement
Maria-Dolores Canela is currently working at Teva Pharmaceuticals as Medical Advisor.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A review on synthetic chalcone derivatives as tubulin polymerisation inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):9-38. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1976772. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34894980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conformational mimetics of the α-methyl chalcone TUB091 binding tubulin: Design, synthesis and antiproliferative activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Mar 25;148:337-348. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.02.019. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29471122
-
Identification of novel non-toxic and anti-angiogenic α-fluorinated chalcones as potent colchicine binding site inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):339-354. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.2014831. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34979843 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modelling of new naphthalene-chalcone derivatives as potential anticancer agents on MCF-7 breast cancer cells by targeting tubulin colchicine binding site.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):139-144. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1690479. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31724435 Free PMC article.
-
Tubulin colchicine binding site inhibitors as vascular disrupting agents in clinical developments.Curr Med Chem. 2015;22(11):1348-60. doi: 10.2174/0929867322666150114163732. Curr Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25620094 Review.
Cited by
-
Capsaicin synergizes with camptothecin to induce increased apoptosis in human small cell lung cancers via the calpain pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Apr 1;129:54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28104436 Free PMC article.
-
Chalcone: A Privileged Structure in Medicinal Chemistry.Chem Rev. 2017 Jun 28;117(12):7762-7810. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00020. Epub 2017 May 10. Chem Rev. 2017. PMID: 28488435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular interactions at the colchicine binding site in tubulin: An X-ray crystallography perspective.Drug Discov Today. 2022 Mar;27(3):759-776. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.12.001. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Drug Discov Today. 2022. PMID: 34890803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on synthetic chalcone derivatives as tubulin polymerisation inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):9-38. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1976772. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34894980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chalcone Derivatives: Role in Anticancer Therapy.Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 16;11(6):894. doi: 10.3390/biom11060894. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34208562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:714–726. - PubMed
-
- Tozer GM, Kanthou C, Baguley BC. Disrupting tumour blood vessels. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:423–435. - PubMed
-
- McKeage MJ, Baguley BC. Disrupting established tumor blood vessels: an emerging therapeutic strategy for cancer. Cancer. 2010;116:1859–1871. - PubMed
-
- Greene LM, Meegan MJ, Zisterer DM. Combretastatins: More Than Just Vascular Targeting Agents? J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015;355:212–227. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

