Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Omarigliptin, a Once-Weekly Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitor, After Single and Multiple Doses in Healthy Subjects
- PMID: 27225334
- PMCID: PMC5111764
- DOI: 10.1002/jcph.773
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Omarigliptin, a Once-Weekly Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitor, After Single and Multiple Doses in Healthy Subjects
Abstract
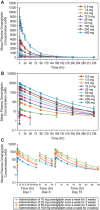
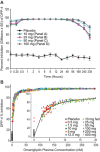
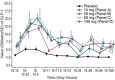
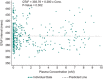
The pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of omarigliptin, a novel once-weekly DPP-4 inhibitor, were assessed following single and multiple doses in healthy subjects. Absorption was rapid, and food did not influence single-dose PK. Accumulation was minimal, and steady state was reached after 2 to 3 weeks. Weekly (area under the curve) AUC and Cmax displayed dose proportionality within the dose range studied at steady state. The average renal clearance of omarigliptin was ∼2 L/h. DPP-4 inhibition ranged from ∼77% to 89% at 168 hours following the last of 3 once-weekly doses over the dose range studied. Omarigliptin resulted in ∼2-fold increases in weighted average postprandial active GLP-1. Omarigliptin acts by stabilizing active GLP-1, which is consistent with its mechanism of action as a DPP-4 inhibitor. Administration of omarigliptin was generally well tolerated in healthy subjects, and both the PK and PD profiles support once-weekly dosing. A model-based assessment of QTc interval risk from the single ascending dose study predicted a low risk of QTc prolongation within the likely clinical dose range, a finding later confirmed in a thorough QT trial.
Keywords: DPP-4 activity; omarigliptin; once-weekly; pharmacokinetics; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2016, The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Figures
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas, 6th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2013. http://www.idf.org/sites/default/files/Atlas‐poster‐2014_EN.pdf.
-
- Cramer JA. A systematic review of adherence with medications for diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1218–1224. - PubMed
-
- Cheong C, Barner JC, Lawson KA, Johnsrud MT. Patient adherence and reimbursement amount for antidiabetic fixed‐dose combination products compared with dual therapy among Texas Medicaid recipients. Clin Ther. 2008;30:1893–1907. - PubMed
-
- Paes AH, Bakker A, Soe‐Agnie CJ. Impact of dosage frequency on patient compliance. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:1512–1517. - PubMed
-
- Johnston SS, Nguyen H, Felber E, et al. Retrospective study of adherence to glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonist therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the United States. Adv Ther. 2014;31:1119–1133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

