DUSP8 Regulates Cardiac Ventricular Remodeling by Altering ERK1/2 Signaling
- PMID: 27225478
- PMCID: PMC4938738
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.308238
DUSP8 Regulates Cardiac Ventricular Remodeling by Altering ERK1/2 Signaling
Abstract
Rationale: Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling regulates the growth response of the adult myocardium in response to increased cardiac workload or pathological insults. The dual-specificity phosphatases (DUSPs) are critical effectors, which dephosphorylate the MAPKs to control the basal tone, amplitude, and duration of MAPK signaling.
Objective: To examine DUSP8 as a regulator of MAPK signaling in the heart and its impact on ventricular and cardiac myocyte growth dynamics.
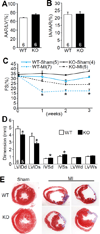
Methods and results: Dusp8 gene-deleted mice and transgenic mice with inducible expression of DUSP8 in the heart were used here to investigate how this MAPK-phosphatase might regulate intracellular signaling and cardiac growth dynamics in vivo. Dusp8 gene-deleted mice were mildly hypercontractile at baseline with a cardiac phenotype of concentric ventricular remodeling, which protected them from progressing towards heart failure in 2 surgery-induced disease models. Cardiac-specific overexpression of DUSP8 produced spontaneous eccentric remodeling and ventricular dilation with heart failure. At the cellular level, adult cardiac myocytes from Dusp8 gene-deleted mice were thicker and shorter, whereas DUSP8 overexpression promoted cardiac myocyte lengthening with a loss of thickness. Mechanistically, activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 were selectively increased in Dusp8 gene-deleted hearts at baseline and following acute pathological stress stimulation, whereas p38 MAPK and c-Jun N-terminal kinases were mostly unaffected.
Conclusions: These results indicate that DUSP8 controls basal and acute stress-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 signaling in adult cardiac myocytes that then alters the length-width growth dynamics of individual cardiac myocytes, which further alters contractility, ventricular remodeling, and disease susceptibility.
Keywords: dilated cardiomyopathy; disease susceptibility; dual-specificity phosphatase; heart failure; myocardium.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No financial or other conflicts of interest exist with any of the authors.
Figures



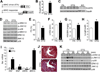
Similar articles
-
Regulation of cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling through the dual-specificity MAPK phosphatases (DUSPs).J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Dec;101:44-49. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.08.018. Epub 2016 Aug 27. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27575022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-specificity phosphatase 14 protects the heart from aortic banding-induced cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction through inactivation of TAK1-P38MAPK/-JNK1/2 signaling pathway.Basic Res Cardiol. 2016 Mar;111(2):19. doi: 10.1007/s00395-016-0536-7. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Basic Res Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26891723
-
Unrestrained p38 MAPK activation in Dusp1/4 double-null mice induces cardiomyopathy.Circ Res. 2013 Jan 4;112(1):48-56. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.272963. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 22993413 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 regulate the balance between eccentric and concentric cardiac growth.Circ Res. 2011 Jan 21;108(2):176-83. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.231514. Epub 2010 Dec 2. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21127295 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 10 Negatively Regulates Cardiac Remodeling by Blocking Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Protein Kinase 1/2 Signaling.Hypertension. 2016 Jan;67(1):86-98. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05957. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 26573707 Review.
Cited by
-
Type 2 diabetes risk gene Dusp8 regulates hypothalamic Jnk signaling and insulin sensitivity.J Clin Invest. 2020 Nov 2;130(11):6093-6108. doi: 10.1172/JCI136363. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32780722 Free PMC article.
-
Ethyl pyruvate inhibits LPS induced IPEC-J2 inflammation and apoptosis through p38 and ERK1/2 pathways.Cell Cycle. 2019 Oct;18(20):2614-2628. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1653106. Epub 2019 Sep 1. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31475609 Free PMC article.
-
Ponatinib-induced cardiotoxicity: delineating the signalling mechanisms and potential rescue strategies.Cardiovasc Res. 2019 Apr 15;115(5):966-977. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz006. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30629146 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatases: No Longer Undruggable?Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 Jan 20;63:617-636. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-051921-121923. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36662585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfibrillar-Associated Protein 4 Regulates Stress-Induced Cardiac Remodeling.Circ Res. 2021 Mar 19;128(6):723-737. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317146. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33530700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kyriakis JM, Avruch J. Mammalian mapk signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: A 10-year update. Physiol Rev. 2012;92:689–737. - PubMed
-
- Goldsmith ZG, Dhanasekaran DN. G protein regulation of mapk networks. Oncogene. 2007;26:3122–3142. - PubMed
-
- Hall A. Rho gtpases and the control of cell behaviour. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33:891–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

