Mechanical properties of the everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold compared to the metallic everolimus-eluting stent
- PMID: 27225486
- PMCID: PMC4880814
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-016-0296-1
Mechanical properties of the everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold compared to the metallic everolimus-eluting stent
Abstract
Background: Everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) represent an innovative treatment option for coronary artery disease. Clinical and angiographic results seem promising, however, data on its immediate procedural performance are still scarce. The aim of our study was to assess the mechanical properties of BVS by Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in clinical routine.
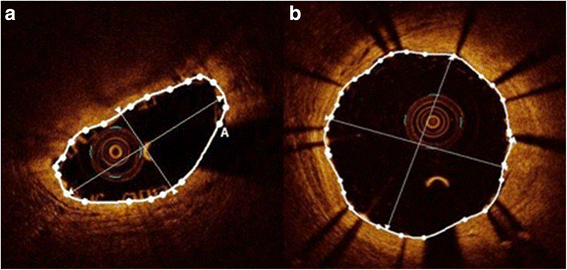
Methods: Post-implantation OCT images of 40 BVS were retrospectively compared to those of 40 metallic everolimus-eluting stents (EES). Post-procedural device related morphological features were assessed. This included incidences of gross underexpansion and the stent eccentricity index (SEI, minimum/maximum diameter) as a measure for focal radial strength.
Results: Patients receiving BVS were younger than those with EES (54.0 ± 11.2 years versus 61.7 ± 11.4 years, p = 0.012), the remaining baseline, vessel and lesion characteristics were comparable between groups. Lesion pre-dilatation was more frequently performed and inflation time was longer in the BVS than in the EES group (n = 34 versus n = 23, p = 0.006 and 44.2 ± 12.8 versus 25.6 ± 8.4 seconds, p < 0.001, respectively). There were no significant differences in maximal inflation pressures and post-dilatation frequencies with non-compliant balloons between groups. Whereas gross device underexpansion was not significantly different, SEI was significantly lower in the BVS group (n = 12 (30 %) versus n = 14 (35 %), p = 0.812 and 0.69 ± 0.08 versus 0.76 ± 0.09, p < 0.001, respectively). There was no difference in major adverse cardiac event-rate at six months.
Conclusion: Our data show that focal radial expansion was significantly reduced in BVS compared to EES in a clinical routine setting using no routine post-dilatation protocol. Whether these findings have impact on scaffold mid-term results as well as on clinical outcome has to be investigated in larger, randomized trials.
Keywords: Bioresorbable Scaffold; Drug-Eluting Stent; Optical Coherence Tomography.
Figures
References
-
- Grube E, Dawkins K, Guagliumi G, Banning A, Zmudka K, Colombo A, Thuesen L, Hauptman K, Marco J, Wijns W, Joshi A, Mascioli S. TAXUS VI final 5-year results: a multicentre, randomised trial comparing polymer-based moderate-release paclitaxel-eluting stent with a bare metal stent for treatment of long, complex coronary artery lesions. EuroIntervention. 2009;4:572–7. doi: 10.4244/EIJV4I5A97. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moses JW, Leon MB, Popma JJ, Fitzgerald PJ, Holmes DR, O'Shaughnessy C, Caputo RP, Kereiakes DJ, Williams DO, Teirstein PS, Jaeger JL, Kuntz RE. SIRIUS Investigators. Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1315–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa035071. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stettler C, Wandel S, Allemann S, Kastrati A, Morice MC, Schörnig A, Pfisterer ME, Stone GW, Leon MB, de Lezo JS, Goy JJ, Park SJ, Sabaté M, Suttorp MJ, Kelbaek H, Spaulding C, Menichelli M, Vermeersch P, Dirksen MT, Cervinka P, Petronio AS, Nordmann AJ, Diem P, Meier B, Zwahlen M, Reichenbach S, Trelle S, Windecker S, Jüni P. Outcomes associated with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: a collaborative network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2007;370:937–48. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61444-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Daemen J, Wenaweser P, Tsuchida K, Abrecht L, Vaina S, Morger C, Kukreja N, Jüni P, Sianos G, Hellige G, van Domburg RT, Hess OM, Boersma E, Meier B, Windecker S, Serruys PW. Early and late coronary stent thrombosis of sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in routine clinical practice: data from a large two-institutional cohort study. Lancet. 2007;369:667–78. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60314-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical