Implications of High Rates of Metastatic Prostate Cancer in BRCA2 Mutation Carriers
- PMID: 27225637
- PMCID: PMC5470321
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.23204
Implications of High Rates of Metastatic Prostate Cancer in BRCA2 Mutation Carriers
Abstract
Background: Patients with germline BRCA2 gene mutations (BRCA2mut) have more aggressive prostate cancer. Analysis of all reported germline BRCA2mut prostate cancer cases allows better understanding of the clinicopathologic features and survival outcomes of these men.
Methods: A systematic review was performed with the MEDLINE database to capture articles evaluating clinicopathologic characteristics of men with BRCA2mut associated prostate cancer. Inclusion criteria were at least five subjects, confirmation of BRCA2mut status, and data for at least 2 clinical parameters of disease. Meta-analysis was performed on outcomes data. Chi-squared tests were used to compare disease features among men undergoing formal versus ad hoc screening, as well as an age of diagnosis less than versus greater than 65 years. Rates of metastatic disease among BRCA2mut cases were compared to rates among non-carrier control subjects and the general population using the SEER database.
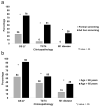
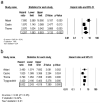
Results: Twelve out of 289 studies met our inclusion criteria, representing 261 BRCA2mut men. Among carriers, the median age at diagnosis was 62 years and median PSA was 15 ng/dl with 95% of men having a PSA>3. Over 40% of BRCA2mut patients had T3/T4 disease and over 25% were metastatic at presentation. Survival was worse in BRCA2mut men with prostate cancer when compared to non-BRCA2mut subjects. BRCA2mut carriers had significantly higher rates of metastatic disease (18%) versus non-carrier controls (8%) and the SEER population (4%).
Conclusions: BRCA2mut carriers are more likely to have poor risk of prostate cancer at presentation and exhibit worse oncologic outcomes relative to non-carriers, including a fourfold increase in metastatic disease. Younger men and those undergoing formal screening present with less advanced disease which supports a need for earlier identification and screening protocols. Additionally, this population may benefit from alternative therapeutic paradigms. Prostate 76:1135-1145, 2016. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: BRCA2; aggressive; metastatic; prostate; screening.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-occurring BRCA2/SPOP Mutations Predict Exceptional Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor Sensitivity in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Eur Urol Oncol. 2024 Aug;7(4):877-887. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.11.014. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Eur Urol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38072760 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Risk-reducing bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy in women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 24;8(8):CD012464. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012464.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30141832 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Contribution of Inherited DNA-Repair Gene Mutations to Hormone-Sensitive and Castrate-Resistant Metastatic Prostate Cancer and Implications for Clinical Outcome.JCO Precis Oncol. 2019 Sep 17;3:PO.19.00067. doi: 10.1200/PO.19.00067. eCollection 2019. JCO Precis Oncol. 2019. PMID: 32923857 Free PMC article.
-
A Case-Based Clinical Approach to the Investigation, Management and Screening of Families with BRCA2 Related Prostate Cancer.Appl Clin Genet. 2021 May 20;14:255-266. doi: 10.2147/TACG.S261737. eCollection 2021. Appl Clin Genet. 2021. PMID: 34295175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Best of the 2016 AUA Annual Meeting: Highlights From the 2016 American Urological Association Annual Meeting, May 6-10, 2016, San Diego, CA.Rev Urol. 2016;18(3):159-173. doi: 10.3909/riu0717. Rev Urol. 2016. PMID: 27833468 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Genetic Education for Men (GEM) Trial: Development of Web-Based Education for Untested Men in BRCA1/2-Positive Families.J Cancer Educ. 2021 Feb;36(1):72-84. doi: 10.1007/s13187-019-01599-y. J Cancer Educ. 2021. PMID: 31402434 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
TP53 alterations of hormone-naïve prostate cancer in the Chinese population.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021 Jun;24(2):482-491. doi: 10.1038/s41391-020-00302-3. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021. PMID: 33214693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29. - PubMed
-
- Robinson D, Van Allen EM, Wu YM, Schultz N, Lonigro RJ, Mosquera JM, Montgomery B, Taplin ME, Pritchard CC, Attard G, Beltran H, Abida W, Bradley RK, Vinson J, Cao X, Vats P, Kunju LP, Hussain M, Feng FY, Tomlins SA, Cooney KA, Smith DC, Brennan C, Siddiqui J, Mehra R, Chen Y, Rathkopf DE, Morris MJ, Solomon SB, Durack JC, Reuter VE, Gopalan A, Gao J, Loda M, Lis RT, Bowden M, Balk SP, Gaviola G, Sougnez C, Gupta M, Yu EY, Mostaghel EA, Cheng HH, Mulcahy H, True LD, Plymate SR, Dvinge H, Ferraldeschi R, Flohr P, Miranda S, Zafeiriou Z, Tunariu N, Mateo J, Perez-Lopez R, Demichelis F, Robinson BD, Schiffman M, Nanus DM, Tagawa ST, Sigaras A, Eng KW, Elemento O, Sboner A, Heath EI, Scher HI, Pienta KJ, Kantoff P, de Bono JS, Rubin MA, Nelson PS, Garraway LA, Sawyers CL, Chinnaiyan AM. Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell. 2015;161(5):1215–1228. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kote-Jarai Z, Leongamornlert D, Saunders E, Tymrakiewicz M, Castro E, Mahmud N, Guy M, Edwards S, O’Brien L, Sawyer E, Hall A, Wilkinson R, Dadaev T, Goh C, Easton D, Collaborators U, Goldgar D, Eeles R. BRCA2 is a moderate penetrance gene contributing to young-onset prostate cancer: Implications for genetic testing in prostate cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2011;105(8):1230–1234. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mateo J, Carreira S, Sandhu S, Miranda S, Mossop H, Perez-Lopez R, Nava Rodrigues D, Robinson D, Omlin A, Tunariu N, Boysen G, Porta N, Flohr P, Gillman A, Figueiredo I, Paulding C, Seed G, Jain S, Ralph C, Protheroe A, Hussain S, Jones R, Elliott T, McGovern U, Bianchini D, Goodall J, Zafeiriou Z, Williamson CT, Ferraldeschi R, Riisnaes R, Ebbs B, Fowler G, Roda D, Yuan W, Wu YM, Cao X, Brough R, Pemberton H, A’Hern R, Swain A, Kunju LP, Eeles R, Attard G, Lord CJ, Ashworth A, Rubin MA, Knudsen KE, Feng FY, Chinnaiyan AM, Hall E, de Bono JS. DNA-repair defects and olaparib in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1697–1708. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castro E, Goh C, Olmos D, Saunders E, Leongamornlert D, Tymrakiewicz M, Mahmud N, Dadaev T, Govindasami K, Guy M, Sawyer E, Wilkinson R, Ardern-Jones A, Ellis S, Frost D, Peock S, Evans DG, Tischkowitz M, Cole T, Davidson R, Eccles D, Brewer C, Douglas F, Porteous ME, Donaldson A, Dorkins H, Izatt L, Cook J, Hodgson S, Kennedy MJ, Side LE, Eason J, Murray A, Antoniou AC, Easton DF, Kote-Jarai Z, Eeles R. Germline BRCA mutations are associated with higher risk of nodal involvement, distant metastasis, and poor survival outcomes in prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(14):1748–1757. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

