Specific endothelial heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor deletion ameliorates renal injury induced by chronic angiotensin II infusion
- PMID: 27226110
- PMCID: PMC5142238
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00377.2015
Specific endothelial heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor deletion ameliorates renal injury induced by chronic angiotensin II infusion
Abstract
Transactivation of EGF receptor (EGFR) by angiotensin II (Ang II) plays important roles in the initiation and progression of chronic kidney diseases. Studies suggest that heparin-binding EGF-like factor (HB-EGF) may be a critical mediator in this process, but its role in vivo has not been investigated. In the current study, we found that in response to Ang II infusion, kidneys from endothelial HB-EGF deletion mice had significantly reduced EGFR activation compared with controls. Meanwhile, deletion of endothelial HB-EGF expression decreased Ang II infusion related renal injury, as demonstrated by 1) less albuminuria; 2) less glomerulosclerosis; 3) preserved endothelial integrity and decreased podocyte injury, as shown by greater glomerular tuft area and WT1-positive cells, and fewer apoptotic cells measured by cleaved caspase 3 staining; 4) reduced inflammation in the perivascular area and interstitium measured by F4/80 and CD3 immunostaining; and 5) reduced renal fibrosis. In conclusion, our results suggest that shedding of HB-EGF from endothelium plays an important role in Ang II-induced renal injury by linking Ang II-AT1R with EGFR transactivation. Inhibition of HB-EGF shedding could be a potential therapeutic strategy for chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: angiotensin II; chronic kidney disease; heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like factor.
Figures
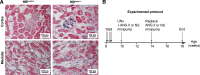
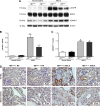


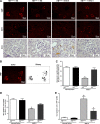
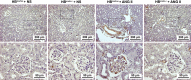
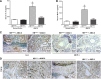
Comment in
-
Can we fight chronic kidney disease by targeting endothelial HB-EGF?Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):F406-8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00345.2016. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27335378 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A novel function of angiotensin II in skin wound healing. Induction of fibroblast and keratinocyte migration by angiotensin II via heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factor-mediated EGF receptor transactivation.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 12;281(19):13209-13216. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509771200. Epub 2006 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16543233
-
Angiotensin II signaling and HB-EGF shedding via metalloproteinase in glomerular mesangial cells.Kidney Int. 2001 Dec;60(6):2153-63. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00067.x. Kidney Int. 2001. PMID: 11737589
-
B-cell lymphoma/leukaemia 10 and angiotensin II-induced kidney injury.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Apr 1;116(5):1059-1070. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz169. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31241148
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in acute and chronic kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2013 May;83(5):804-10. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.435. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23325080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Cells. 2022 Oct 28;11(21):3416. doi: 10.3390/cells11213416. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can we fight chronic kidney disease by targeting endothelial HB-EGF?Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):F406-8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00345.2016. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27335378 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
CircRNA_30032 promotes renal fibrosis in UUO model mice via miRNA-96-5p/HBEGF/KRAS axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 11;13(9):12780-12799. doi: 10.18632/aging.202947. Epub 2021 May 11. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33973871 Free PMC article.
-
CD148 agonistic antibody alleviates renal injury induced by chronic angiotensin II infusion in mice.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Mar 31;26(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04070-x. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40165104 Free PMC article.
-
EGF receptor in organ development, tissue homeostasis and regeneration.J Biomed Sci. 2025 Feb 19;32(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12929-025-01119-9. J Biomed Sci. 2025. PMID: 39966897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
iRhom2 promotes lupus nephritis through TNF-α and EGFR signaling.J Clin Invest. 2018 Apr 2;128(4):1397-1412. doi: 10.1172/JCI97650. Epub 2018 Mar 5. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29369823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arkonac BM, Foster LC, Sibinga NE, Patterson C, Lai K, Tsai JC, Lee ME, Perrella MA, Haber E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 273: 4400–4405, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Asakura M, Kitakaze M, Takashima S, Liao Y, Ishikura F, Yoshinaka T, Ohmoto H, Node K, Yoshino K, Ishiguro H, Asanuma H, Sanada S, Matsumura Y, Takeda H, Beppu S, Tada M, Hori M, Higashiyama S. Cardiac hypertrophy is inhibited by antagonism of ADAM12 processing of HB-EGF: metalloproteinase inhibitors as a new therapy. Nat Med 8: 35–40, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Beerli RR, Hynes NE. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides activate distinct subsets of ErbB receptors and differ in their biological activities. J Biol Chem 271: 6071–6076, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Bollee G, Flamant M, Schordan S, Fligny C, Rumpel E, Milon M, Schordan E, Sabaa N, Vandermeersch S, Galaup A, Rodenas A, Casal I, Sunnarborg SW, Salant DJ, Kopp JB, Threadgill DW, Quaggin SE, Dussaule JC, Germain S, Mesnard L, Endlich K, Boucheix C, Belenfant X, Callard P, Endlich N, Tharaux PL. Epidermal growth factor receptor promotes glomerular injury and renal failure in rapidly progressive crescentic glomerulonephritis. Nat Med 17: 1242–1250, 2011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boukhalfa G, Desmouliere A, Rondeau E, Gabbiani G, Sraer JD. Relationship between alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and fibrotic changes in human kidney. Exp Nephrol 4: 241–247, 1996. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

