Viral Evasion and Manipulation of Host RNA Quality Control Pathways
- PMID: 27226372
- PMCID: PMC4984649
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00607-16
Viral Evasion and Manipulation of Host RNA Quality Control Pathways
Abstract
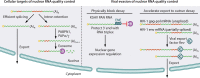
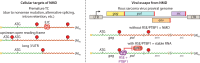
Viruses have evolved diverse strategies to maximize the functional and coding capacities of their genetic material. Individual viral RNAs are often used as substrates for both replication and translation and can contain multiple, sometimes overlapping open reading frames. Further, viral RNAs engage in a wide variety of interactions with both host and viral proteins to modify the activities of important cellular factors and direct their own trafficking, packaging, localization, stability, and translation. However, adaptations increasing the information density of small viral genomes can have unintended consequences. In particular, viral RNAs have developed features that mark them as potential targets of host RNA quality control pathways. This minireview focuses on ways in which viral RNAs run afoul of the cellular mRNA quality control and decay machinery, as well as on strategies developed by viruses to circumvent or exploit cellular mRNA surveillance.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Wagschal A, Rousset E, Basavarajaiah P, Contreras X, Harwig A, Laurent-Chabalier S, Nakamura M, Chen X, Zhang K, Meziane O, Boyer F, Parrinello H, Berkhout B, Terzian C, Benkirane M, Kiernan R. 2012. Microprocessor, Setx, Xrn2, and Rrp6 co-operate to induce premature termination of transcription by RNAPII. Cell 150:1147–1157. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

