Developmental origins of inflammatory and immune diseases
- PMID: 27226490
- PMCID: PMC4986419
- DOI: 10.1093/molehr/gaw036
Developmental origins of inflammatory and immune diseases
Abstract
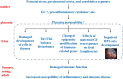
Epidemiological and experimental animal studies show that suboptimal environments in fetal and neonatal life exert a profound influence on physiological function and risk of diseases in adult life. The concepts of the 'developmental programming' and Developmental Origins of Health and Diseases (DOHaD) have become well accepted and have been applied across almost all fields of medicine. Adverse intrauterine environments may have programming effects on the crucial functions of the immune system during critical periods of fetal development, which can permanently alter the immune function of offspring. Immune dysfunction may in turn lead offspring to be susceptible to inflammatory and immune diseases in adulthood. These facts suggest that inflammatory and immune disorders might have developmental origins. In recent years, inflammatory and immune disorders have become a growing health problem worldwide. However, there is no systematic report in the literature on the developmental origins of inflammatory and immune diseases and the potential mechanisms involved. Here, we review the impacts of adverse intrauterine environments on the immune function in offspring. This review shows the results from human and different animal species and highlights the underlying mechanisms, including damaged development of cells in the thymus, helper T cell 1/helper T cell 2 balance disturbance, abnormal epigenetic modification, effects of maternal glucocorticoid overexposure on fetal lymphocytes and effects of the fetal hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis on the immune system. Although the phenomena have already been clearly implicated in epidemiologic and experimental studies, new studies investigating the mechanisms of these effects may provide new avenues for exploiting these pathways for disease prevention.
Keywords: T cells; adverse intrauterine environment; developmental origins; inflammatory and immune diseases; thymus.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Blumer N, Herz U, Wegmann M, Renz H. Prenatal lipopolysaccharide-exposure prevents allergic sensitization and airway inflammation, but not airway responsiveness in a murine model of experimental asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 2005;35:397–402. - PubMed
-
- Blumer N, Sel S, Virna S, Patrascan CC, Zimmermann S, Herz U, Renz H, Garn H. Perinatal maternal application of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG suppresses allergic airway inflammation in mouse offspring. Clin Exp Allergy 2007;37:348–357. - PubMed
-
- Brown N, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS. Induction of apoptosis in murine fetal thymocytes following perinatal exposure to diethylstilbestrol. Int J Toxicol 2006;25:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Chambers ES, Hawrylowicz CM. The impact of vitamin D on regulatory T cells. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2011;11:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Cheraghi M, Salvi S. Environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) and respiratory health in children. Eur J Pediatr 2009;168:897–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

