Lysosomal Dysfunction Caused by Cellular Accumulation of Silica Nanoparticles
- PMID: 27226546
- PMCID: PMC4933175
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.710947
Lysosomal Dysfunction Caused by Cellular Accumulation of Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
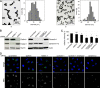
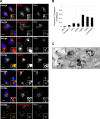
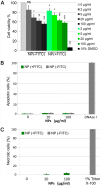
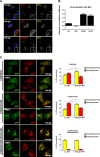
Nanoparticles (NPs) are widely used as components of drugs or cosmetics and hold great promise for biomedicine, yet their effects on cell physiology remain poorly understood. Here we demonstrate that clathrin-independent dynamin 2-mediated caveolar uptake of surface-functionalized silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) impairs cell viability due to lysosomal dysfunction. We show that internalized SiNPs accumulate in lysosomes resulting in inhibition of autophagy-mediated protein turnover and impaired degradation of internalized epidermal growth factor, whereas endosomal recycling proceeds unperturbed. This phenotype is caused by perturbed delivery of cargo via autophagosomes and late endosomes to SiNP-filled cathepsin B/L-containing lysosomes rather than elevated lysosomal pH or altered mTOR activity. Given the importance of autophagy and lysosomal protein degradation for cellular proteostasis and clearance of aggregated proteins, these results raise the question of beneficial use of NPs in biomedicine and beyond.
Keywords: autophagy; caveolae; endocytosis; endosome; lysosome; silica nanoparticles.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures







References
-
- Sengupta S., Eavarone D., Capila I., Zhao G., Watson N., Kiziltepe T., and Sasisekharan R. (2005) Temporal targeting of tumour cells and neovasculature with a nanoscale delivery system. Nature 436, 568–572 - PubMed
-
- Santra S., Zhang P., Wang K., Tapec R., and Tan W. (2001) Conjugation of biomolecules with luminophore-doped silica nanoparticles for photostable biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 73, 4988–4993 - PubMed
-
- Zhang F. F., Wan Q., Li C. X., Wang X. L., Zhu Z. Q., Xian Y. Z., Jin L. T., and Yamamoto K. (2004) Simultaneous assay of glucose, lactate, l-glutamate and hypoxanthine levels in a rat striatum using enzyme electrodes based on neutral red-doped silica nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 380, 637–642 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

