Large B-cell lymphoma in a dog: A cyto-histopathological evaluation and Immunophenotyping according to WHO classification for canine lymphomas
- PMID: 27226892
- PMCID: PMC4867042
Large B-cell lymphoma in a dog: A cyto-histopathological evaluation and Immunophenotyping according to WHO classification for canine lymphomas
Abstract
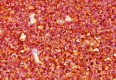
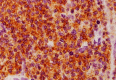
In the present study, we described cyto-histopathological features and immunophenotyping of the large B-cell lymphoma in an 8-year-old mixed breed dog with applying the World Health Organization (WHO) system of classification of canine lymphomas. In fine-needle aspiration (FNA), lymph nodes were involved by neoplastic cells of intermediate to large size with deep blue cytoplasm; consist of centroblasts, immunoblast and medium-sized cells. Histopathologically, the follicles and sinuses of lymph nodes were replaced by sheets of numerous immunoblasts (less than 90.0% of total cells) and centroblasts. Numerous mitotic figures were also observed. Immunohistochemical analysis presented that the neoplastic cells express B-cell phenotype CD20 and CD79a, but do not stain for T phenotype CD3. On the basis of cytology, histopathology and immunohistochemical findings, the present tumor was diagnosed as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, high-grade centroblastic type (DLBCL-CB) according to WHO histological classification. Applying this classification system for diagnosis of canine lymphomas is very useful and has a high accuracy and consistency. However, further co-operative studies between clinicians and pathologists should be performed, in order to improve the effectiveness of this classification.
Keywords: Canine lymphomas; Cyto-histopathological features; Immunohistochemistry.
Figures


References
-
- Lobetti RG. Lymphoma in 3 related Rottweilers from a single household. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 2009;80:103–105. - PubMed
-
- Mortier F, Daminet S, Vandenabeele S, et al. Canine lymphoma: A retrospective study (2009 – 2010) Vlaams Diergen Tijds. 2012;81:341–351.
-
- Parodi AL. Classification of malignant lymphoma in domestic animals: History and conceptual evolution. Eur J Vet Pathol. 2001;7:43–50.
-
- Harris N, Jaffe ES, Stein H, et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: A proposal from the international lymphoma study group. Blood. 1994;84:1361–1392. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
