Responses of the hands and feet to cold exposure
- PMID: 27227009
- PMCID: PMC4843861
- DOI: 10.1080/23328940.2015.1008890
Responses of the hands and feet to cold exposure
Abstract
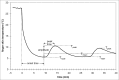
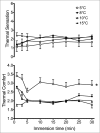
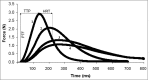
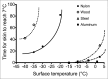
An initial response to whole-body or local exposure of the extremities to cold is a strong vasoconstriction, leading to a rapid decrease in hand and foot temperature. This impairs tactile sensitivity, manual dexterity, and muscle contractile characteristics while increasing pain and sympathetic drive, decreasing gross motor function, occupational performance, and survival. A paradoxical and cyclical vasodilatation often occurs in the fingers, toes, and face, and this has been termed the hunting response or cold-induced vasodilatation (CIVD). Despite being described almost a century ago, the mechanisms of CIVD are still disputed; research in this area has remained largely descriptive in nature. Recent research into CIVD has brought increased standardization of methodology along with new knowledge about the impact of mediating factors such as hypoxia and physical fitness. Increasing mechanistic analysis of CIVD has also emerged along with improved modeling and prediction of CIVD responses. The present review will survey work conducted during this century on CIVD, its potential mechanisms and modeling, and also the broader context of manual function in cold conditions.
Keywords: cold-induced vasodilatation; finger blood flow; manual function; sympathetic nervous system.
Figures



References
-
- Taylor NAS, Machado-Moreira CA, van den Heuvel AMJ, Caldwell JN. Hands and feet: physiological insulators, radiators and evaporators. Eur J Appl Physiol 2014; 114:2037-60; PMID:25011493; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2940-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Romanovsky AA. Skin temperature: its role in thermoregulation. Acta Physiol 2014; 210:498-507; PMID:24716231; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/apha.12231 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oksa J, Hosio S, Mäkinen T, Lindholm H, Rintamäki H, Rissanen S, Latvala J, Vaara K, Oksa P. Muscular, cardiorespiratory and thermal strain of mast and pole workers. Ergonomics 2014; 57:669-78; PMID:24655301; http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2014.895854 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bridgman SA. Thermal status of antarctic divers. Aviat Space Environ Med 1990; 61:795-801; PMID:2241743. - PubMed
-
- Cheung SS, Montie DL, White MD, Behm D. Changes in manual dexterity following short-term hand and forearm immersion in 10°C water. Aviat Space Environ Med 2003; 74:990-3; PMID:14503680. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
