White matter involvement in a family with a novel PDGFB mutation
- PMID: 27227165
- PMCID: PMC4867655
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000077
White matter involvement in a family with a novel PDGFB mutation
Abstract
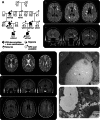
Primary familial brain calcification (PFBC) (formerly idiopathic basal ganglia calcification; Fahr disease) is an autosomal dominant cerebral microvascular calcifying disorder with variable clinical and imaging features.(1) Four causative genes have been identified: SLC20A2,(2) PDGFRB,(3) PDGFB,(4) and XPR1.(5).
Figures
References
-
- Nicolas G, Charbonnier C, de Lemos RR, et al. Brain calcification process and phenotypes according to age and sex: lessons from SLC20A2, PDGFB, and PDGFRB mutation carriers. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2015;168:586–594. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Li Y, Shi L, et al. Mutations in SLC20A2 familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification with phosphate homeostasis. Nat Genet 2012;44:254–256. - PubMed
-
- Nicolas G, Pottier C, Maltete D, et al. Mutation of the PDGFRB gene as a cause of idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. Neurology 2013;80:181–187. - PubMed
-
- Keller A, Westenberger A, Sobrido MJ, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding PDGF-B cause brain calcifications in humans and mice. Nat Genet 2013;45:1077–1082. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
