Case Report of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Features of Primary Hepatic Neuroendocrine Tumor: A CARE-Compliant Article
- PMID: 27227910
- PMCID: PMC4902334
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003450
Case Report of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Features of Primary Hepatic Neuroendocrine Tumor: A CARE-Compliant Article
Abstract
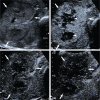
Primary hepatic neuroendocrine tumors (PHNETs) are very rare and their clinical features and treatment outcomes are not well understood. It is difficult to reach a proper diagnosis before biopsy or resection. The aim of this study was to analyze the imaging features of PHNETs on contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS). The clinical characteristics, CEUS findings, pathological features, treatment and prognosis of 6 patients with PHNET treated in our hospital were retrospectively analyzed.Most PHNETs occurred in middle-aged patients, and the most common clinical manifestation was right upper quadrant palpable mass and abdominal pain. Multiple small anechoic intralesional cavities occurred frequently in PHNET. Multilocular cystic with internal septation or monolocular with wall nodule could also be detected. On contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS), heterogeneous hyperenhancement in the arterial phase and wash-out hypoenhancement were observed in most patients, while computed tomography scanning yielded similar results. Diagnosis of PHNET was confirmed by immunohistochemical result and follow-up with the absence of extrahepatic primary sites. Five patients received surgical resection and 2 cases exhibited recurrence. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization was performed in 1 patient with recurrence. Only 1 patient received conservative care. The median overall survival in 5 patients who underwent surgical treatment was 27 months (18-36 months). PHNET is a rare tumor, and its diagnosis is difficult. The CEUS features reported in this series may enrich the knowledge base for characterization of PHNET.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Scarsbrook AF, Ganeshan A, Statham J, et al. Anatomic and functional imaging of metastatic carcinoid tumors. Radiographics 2007; 27:455–477. - PubMed
-
- Gravante G, De Liguori Carino N, Overton J, et al. Primary carcinoids of the liver: a review of symptoms, diagnosis and treatments. Dig Surg 2008; 25:364–368. - PubMed
-
- Asakawa T, Tomioka T, Abe K, et al. Primary hepatic carcinoid tumor. J Gastroenterol 1999; 34:123–127. - PubMed
-
- Pilichowska M, Kimura N, Ouchi A, et al. Primary hepatic carcinoid and neuroendocrine carcinoma: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of five cases. Pathol Int 1999; 49:318–324. - PubMed
-
- Knox CD, Anderson CD, Lamps LW, et al. Long-term survival after resection for primary hepatic carcinoid tumor. Ann Surg Oncol 2003; 10:1171–1175. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

