Clinicopathological Features Associated With the Prognosis of Patients With Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma: Usefulness of the Ki-67 Index
- PMID: 27227935
- PMCID: PMC4902359
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003736
Clinicopathological Features Associated With the Prognosis of Patients With Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma: Usefulness of the Ki-67 Index
Abstract
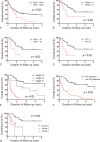
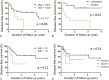
Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is a rare tumor with a poor prognosis. Identification of clinicopathological features and molecular prognostic markers is important for the treatment of ACC. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical and histopathological features of ACC for prognostic prediction.This retrospective cohort study included 86 patients pathologically confirmed with ACC in a single center. Ki-67 index was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded samples.The median age of the 86 (46 male and 40 female) patients with ACC was 49 years old (range 21-78), and the mean primary tumor size was 12.2 ± 5.2 cm. ACCs were incidentally found in 29 patients (34%). Three patients (3%) had bilateral ACC, and 59 patients (69%) had distant metastasis (37 synchronous and 22 metachronous). Twenty-four patients (28%) had symptoms from hormone excess or mass effects, and 25 patients (29%) had nonspecific symptoms. The 5-year survival rate for ACC was 28%. Sixty patients underwent surgical treatment, including 37 patients with an R0 resection. Tumor size, Ki-67 index, stage, and resection status were independently associated with overall survival by multivariate analysis. In patients with R0 resection, recurrence was significantly associated with larger tumor size and functional tumor.Tumor size, Ki-67 index, stage, and resection status are important prognostic indicators of survival in ACC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Myxoid and Sarcomatoid Variants of Adrenocortical Carcinoma: Analysis of Rare Variants in Single Tertiary Care Center.J Korean Med Sci. 2017 May;32(5):764-771. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.5.764. J Korean Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28378549 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between glucocorticoids and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes on the prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 May;8(1):e000469. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000469. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32474412 Free PMC article.
-
European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of adrenocortical carcinoma in adults, in collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors.Eur J Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 1;179(4):G1-G46. doi: 10.1530/EJE-18-0608. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30299884
-
Treatment of Adrenocortical Carcinoma.Surg Pathol Clin. 2019 Dec;12(4):997-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.path.2019.08.010. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Surg Pathol Clin. 2019. PMID: 31672303 Review.
-
Approach to patients with European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumor stages I and II adrenocortical carcinomas.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2021 Jun 1;28(3):265-270. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000626. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2021. PMID: 33709971 Review.
Cited by
-
Adrenocortical Carcinoma: a Therapeutic Challenge - 44 Cases from a Single Tertiary Care Center in India.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2022 Jun;13(2):251-259. doi: 10.1007/s13193-021-01440-3. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35782795 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Performance of the 7th and 8th Editions of the American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Manual for Adrenocortical Carcinoma.World J Surg. 2020 Feb;44(2):544-551. doi: 10.1007/s00268-019-05136-2. World J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31493191
-
Overexpression of HSD17B4 exerts tumor suppressive function in adrenocortical carcinoma and is not associated with hormone excess.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 1;8(70):114736-114745. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22827. eCollection 2017 Dec 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29383116 Free PMC article.
-
Open versus minimally invasive surgery for suspected adrenocortical carcinoma.Transl Androl Urol. 2021 May;10(5):2246-2263. doi: 10.21037/tau.2020.01.11. Transl Androl Urol. 2021. PMID: 34159107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rottlerin as a novel chemotherapy agent for adrenocortical carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 4;8(14):22825-22834. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15221. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baudin E. Adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2015; 44:411–434. - PubMed
-
- Gurzu S, Jung I. Adrenocortical carcinoma: update of clinical features and diagnosis. Global J Oncol 2013; 1:42–49.
-
- Gurzu S, Szentirmay Z, Bara T, et al. Myxoid variant of adrenocortical carcinoma: a report of two illustrative cases and a brief review of the literature. Pathology 2014; 46:83–85. - PubMed
-
- Assie G, Letouze E, Fassnacht M, et al. Integrated genomic characterization of adrenocortical carcinoma. Nat Genet 2014; 46:607–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

