Psychological preparation and postoperative outcomes for adults undergoing surgery under general anaesthesia
- PMID: 27228096
- PMCID: PMC8687603
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008646.pub2
Psychological preparation and postoperative outcomes for adults undergoing surgery under general anaesthesia
Abstract
Background: In a review and meta-analysis conducted in 1993, psychological preparation was found to be beneficial for a range of outcome variables including pain, behavioural recovery, length of stay and negative affect. Since this review, more detailed bibliographic searching has become possible, additional studies testing psychological preparation for surgery have been completed and hospital procedures have changed. The present review examines whether psychological preparation (procedural information, sensory information, cognitive intervention, relaxation, hypnosis and emotion-focused intervention) has impact on the outcomes of postoperative pain, behavioural recovery, length of stay and negative affect.
Objectives: To review the effects of psychological preparation on postoperative outcomes in adults undergoing elective surgery under general anaesthetic.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2014, Issue 5), MEDLINE (OVID SP) (1950 to May 2014), EMBASE (OVID SP) (1982 to May 2014), PsycINFO (OVID SP) (1982 to May 2014), CINAHL (EBESCOhost) (1980 to May 2014), Dissertation Abstracts (to May 2014) and Web of Science (1946 to May 2014). We searched reference lists of relevant studies and contacted authors to identify unpublished studies. We reran the searches in July 2015 and placed the 38 studies of interest in the `awaiting classification' section of this review.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials of adult participants (aged 16 or older) undergoing elective surgery under general anaesthesia. We excluded studies focusing on patient groups with clinically diagnosed psychological morbidity. We did not limit the search by language or publication status. We included studies testing a preoperative psychological intervention that included at least one of these seven techniques: procedural information; sensory information; behavioural instruction; cognitive intervention; relaxation techniques; hypnosis; emotion-focused intervention. We included studies that examined any one of our postoperative outcome measures (pain, behavioural recovery, length of stay, negative affect) within one month post-surgery.
Data collection and analysis: One author checked titles and abstracts to exclude obviously irrelevant studies. We obtained full reports of apparently relevant studies; two authors fully screened these. Two authors independently extracted data and resolved discrepancies by discussion.Where possible we used random-effects meta-analyses to combine the results from individual studies. For length of stay we pooled mean differences. For pain and negative affect we used a standardized effect size (the standardized mean difference (SMD), or Hedges' g) to combine data from different outcome measures. If data were not available in a form suitable for meta-analysis we performed a narrative review.
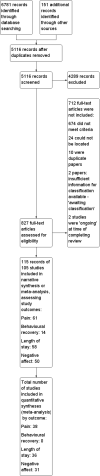
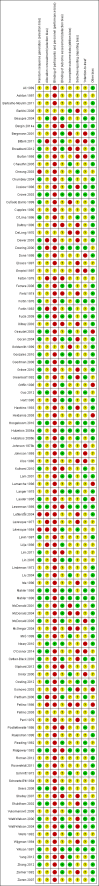
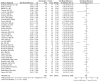
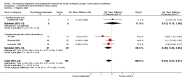
Main results: Searches identified 5116 unique papers; we retrieved 827 for full screening. In this review, we included 105 studies from 115 papers, in which 10,302 participants were randomized. Mainly as a result of updating the search in July 2015, 38 papers are awaiting classification. Sixty-one of the 105 studies measured the outcome pain, 14 behavioural recovery, 58 length of stay and 49 negative affect. Participants underwent a wide range of surgical procedures, and a range of psychological components were used in interventions, frequently in combination. In the 105 studies, appropriate data were provided for the meta-analysis of 38 studies measuring the outcome postoperative pain (2713 participants), 36 for length of stay (3313 participants) and 31 for negative affect (2496 participants). We narratively reviewed the remaining studies (including the 14 studies with 1441 participants addressing behavioural recovery). When pooling the results for all types of intervention there was low quality evidence that psychological preparation techniques were associated with lower postoperative pain (SMD -0.20, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.35 to -0.06), length of stay (mean difference -0.52 days, 95% CI -0.82 to -0.22) and negative affect (SMD -0.35, 95% CI -0.54 to -0.16) compared with controls. Results tended to be similar for all categories of intervention, although there was no evidence that behavioural instruction reduced the outcome pain. However, caution must be exercised when interpreting the results because of heterogeneity in the types of surgery, interventions and outcomes. Narratively reviewed evidence for the outcome behavioural recovery provided very low quality evidence that psychological preparation, in particular behavioural instruction, may have potential to improve behavioural recovery outcomes, but no clear conclusions could be reached.Generally, the evidence suffered from poor reporting, meaning that few studies could be classified as having low risk of bias. Overall,we rated the quality of evidence for each outcome as 'low' because of the high level of heterogeneity in meta-analysed studies and the unclear risk of bias. In addition, for the outcome behavioural recovery, too few studies used robust measures and reported suitable data for meta-analysis, so we rated the quality of evidence as `very low'.
Authors' conclusions: The evidence suggested that psychological preparation may be beneficial for the outcomes postoperative pain, behavioural recovery, negative affect and length of stay, and is unlikely to be harmful. However, at present, the strength of evidence is insufficient to reach firm conclusions on the role of psychological preparation for surgery. Further analyses are needed to explore the heterogeneity in the data, to identify more specifically when intervention techniques are of benefit. As the current evidence quality is low or very low, there is a need for well-conducted and clearly reported research.
Conflict of interest statement
Rachael Powell designed a study, whilst she was a post‐doctoral researcher at the University of Auckland, that would have been eligible for inclusion in this review had it been completed. However, the study did not progress due to recruitment problems (very few data sets were completed and the study was halted). As noted in Sources of support funding from two sources was received to support research assistants working on the review.
Neil W Scott's institution received National Health Service (NHS) Grampian Endowment Research Grants for statistical analysis.
Anne Manyande was the first author on two studies that we considered for inclusion in this review (Manyande 1995; Manyande 1998). We excluded these studies because participants were not randomly allocated to condition.
Julie Bruce: none known.
Marie Johnston and Claus Vögele carried out a systematic review and meta‐analysis in this area (Johnston 1993), but searching techniques have since become more sophisticated due to technological developments.
Lucie Byrne‐Davis: none known.
Mary Unsworth had financial support as a Research Assistant at Aston University and the University of Manchester for part of the submitted work.
Christian Osmer is deceased; no declarations of interest available.
Figures









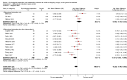
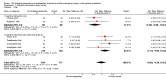

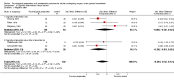




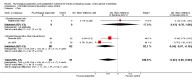

Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Ali 1989 {published data only}
-
- Ali NS, Khalil HZ. Effect of psychoeducational intervention on anxiety among Egyptian bladder cancer patients. Cancer Nursing 1989;12(4):236‐42. - PubMed
Ashton 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ashton C, Whitworth GC, Seldomridge JA, Shapiro PA, Weinberg AD, Michler RE, et al. Self‐hypnosis reduces anxiety following coronary artery bypass surgery: a prospective randomized trial. Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery 1997;38:69‐75. - PubMed
-
- Ashton RC, Whitworth GC, Seldomridge JA, Shapiro PA, Michler RE, Smith CR, et al. The effects of self‐hypnosis on quality of life following coronary artery bypass surgery: preliminary results of a prospective, randomized trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 1995;1(3):285‐90. - PubMed
Barbalho‐Moulim 2011 {published data only}
Barlési 2008 {published data only}
-
- Barlési F, Barrau K, Loundou A, Doddoli C, Simeoni M‐C, Auquier P, et al. Impact of information on quality of life an satisfaction of non‐small cell lung cancer patients: a randomized study of standardized versus individualized information before thoracic surgery. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2008;3(10):1146‐52. - PubMed
Beaupre 2004 {published data only}
-
- Beaupre L A, Lier D, Davies DM, Johnston DBC . The effect of a preoperative exercise and education program on functional recovery, health related quality of life, and health service utilization following primary total knee arthroplasty. Journal of Rheumatology 2004;31(6):1166‐73. - PubMed
Bergin 2014a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bergin C, Kelly K, Travis T, Speroni KG. Interim analysis of the pre‐operative incentive spirometry education (POISE) intervention. Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing (ASPAN National Conference Abstracts) 2010;25(3):196.
-
- Bergin C, Speroni KG, Travis T, Bergin J, Sheridan MJ, Kelly K, et al. Effect of preoperative incentive spirometry patient education on patient outcomes in the knee and hip joint replacement population. Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing 2014;29(1):20‐7. - PubMed
Bergmann 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bergmann P, Huber S, Mächler H, Lieble E, Hinghofer‐Szalkay H, Rehak P, et al. The influence of medical information on the perioperative course of stress in cardiac surgery patients. Cardiovascular Anesthesia 2001;93:1093‐9. - PubMed
Bitterli 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bitterli R, Sieben JM, Hartmann M, Bruin ED. Pre‐surgical sensorimotor training for patients undergoing total hip replacement: a randomised controlled trial. International Journal of Sports Medicine 2011;32(9):725‐32. - PubMed
Broadbent 2012 {published data only}
-
- Broadbent E, Kahokehr A, Booth R, Thomas J, Windsor JA, Buchanan C, et al. Relaxation improves wound healing following surgery: a randomised trial. Psychology and Health 2011;26(S2):13‐4.
-
- Broadbent E, Kahokehr A, Booth RJ, Thomas J, Windsor JA, Buchanan CM, et al. A brief relaxation intervention reduces stress and improves surgical wound healing response: a randomised trial. Brain, Behaviour and Immunity 2012;26(2):212‐7. - PubMed
Burton 1995 {published data only}
-
- Burton MV, Parker RW, Farrell A, Bailey D, Conneely J, Booth S, et al. A randomized controlled trial of preoperative psychological preparation for mastectomy. Psycho‐oncology 1995;4:1‐19.
-
- Burton MV, Parker VW. A randomized controlled trial of preoperative psychological preparation for mastectomy: a preliminary report. In: Watson M, Greer S, Thomas C editor(s). Psychosocial Oncology: Proceedings of the second and third meetings of the British Psychosocial Oncology Group, London & Leicester, 1985 and 1986. Oxford: Pergamon, 1988:133‐58.
Chaudhri 2005 {published data only}
-
- Chaudhri S, Brown L, Hassan I, Horgan AF. Preoperative intensive, community‐based vs. traditional stoma education: a randomized, controlled trial. Diseases of the Colon and Rectum 2005;48:504‐9. - PubMed
Cheung 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Cheung LH, Callaghan P, Chang AM. A controlled trial of psycho‐educational interventions in preparing Chinese women for elective hysterectomy. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2003;40:207‐16. - PubMed
Chumbley 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chumbley GM, Ward L, Hall GM, Salmon P. Pre‐operative information and patient‐controlled analgesia: much ado about nothing. Anaesthesia 2004;59:354‐8. - PubMed
Coslow 1998 {published data only}
-
- Coslow BIF, Eddy ME. Effects of preoperative ambulatory gynecological education: clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction. Journal of PeriAnesthesia nursing 1998;13(1):4‐10. - PubMed
Crowe 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Crowe J, Henderson J. Pre‐arthroplasty rehabilitation is effective in reducing hospital stay. Canadian Journal of Occupational Therapy 2003;70(2):88‐96. - PubMed
Cuñado Barrio 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cuñado Barrio A, Legarre Gil MJ, Ruiz Castón J, Silveira de la Torre J, Cabellero Martínez L, García López F. The effect of a structured, individualized "nursing visit" on the anxiety of surgical patients. A randomized clinical study [Efecto de una “visita enfermera” estructurada e individualizada en la ansiedad de los pacientes quirúrgicos. Ensayo clínico aleatorizado]. Enfermería Clínica 1999;9(3):98‐104.
Cupples 1990 {published data only}
-
- Cupples SA. Effects of preadmission teaching on knowledge and postoperative recovery of coronary artery bypass graft patients. In: Funk S, Tornquist E, Champagne M, Copp L, Weise R editor(s). Key Aspects of Recovery: Improving Nutrition, Rest and Mobility. New York: Springer, 1990:299‐307.
D'Lima 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- D’Lima DD, Colwell CW, Morris BA, Hardwick ME, Kozin F. The effect of preoperative exercise on total knee replacement outcomes. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 1996;326:174‐82. - PubMed
Daltroy 1998 {published data only}
-
- Daltroy LH, Morlino CI, Eaton HM, Poss R, Liang MH. Preoperative education for total hip and knee replacement patients. Arthritis Care and Research 1998;11(6):469‐78. - PubMed
DeLong 1970 {unpublished data only}
-
- DeLong RD. Individual Differences in Patterns of Anxiety Arousal, Stress‐relevant Information and Recovery from Surgery [Dissertation submitted for PhD in Psychology]. Los Angeles: University of California, 1970.
Dewar 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dewar A, Craig K, Muir J, Cole C. Testing the effectiveness of a nursing intervention in relieving pain following day surgery. Journal of Ambulatory Surgery 2003;10:81‐8.
Doering 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Doering S, Katzlberger F, Rumpold G, Roessler S, Hofstoetter B, Schatz DS, et al. Videotape preparation of patients before hip replacement surgery reduces stress. Psychosomatic Medicine 2000;62(3):365‐73. - PubMed
Done 1998 {published data only}
-
- Done LM, Lee A. The use of a video to convey preanesthetic information to patients undergoing ambulatory surgery. Ambulatory Anesthesia 1998;87:531‐6. - PubMed
Elsass 1987 {published data only}
-
- Elsass P, Eikard B, Junge J, Lykke J, Staun P, Feldt‐Rasmussen M. Psychological effect of detailed preanesthetic information. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 1987;31:579‐83. [4041] - PubMed
Enqvist 1997 {published data only}
-
- Enqvist B, Bjöklund C, Engman M, Jakobsson J. Preoperative hypnosis reduces postoperative vomiting after surgery of the breasts: a prospective, randomized and blinded study. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 1997;41:1028‐32. - PubMed
Felton 1976 {published data only}
-
- Felton G, Huss K, Payne EA, Srsic K. Preoperative nursing intervention with the patient for surgery: outcomes of three alternative approaches. International Journal of Nursing Studies 1974;13:83‐96. - PubMed
Ferrara 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ferrara PE, Rabini A, Maggi L, Piazzini DB, Amabile E, Tancredi G, et al. Effect of pre‐operative physiotherapy in patients with end‐stage osteoarthritis undergoing hip arthroplasty. Clinical Rehabilitation 2008;22:977‐86. - PubMed
Field 1974 {published data only}
Fortin 1976 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fortin F, Kirouac S. A randomized controlled trial of preoperative patient education. International Journal of Nursing Studies 1976;13:11‐24. - PubMed
Fortin 1983 {published data only}
-
- Fortin JD. An Investigation of the Effects of a Selected Coping Intervention on Pain and Anxiety in Adult Surgical Patients [PhD dissertation]. Boston, USA: Boston University, 1983.
Furze 2009 {published data only}
Gilbey 2003 {published data only}
-
- Gilbey HG, Ackland TR, Wang AW, Morton AR, Trouchet T, Tapper J. Exercise improves early functional recovery after total hip arthroplasty. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 2003;408:193‐200. - PubMed
-
- Gilbey HJ, Ackland TR, Wang AW, Tapper J, Wang AW. Perioperative exercise improves function following total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Musculoskeletal Research 2003;7(2):111‐23.
Giraudet 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Giraudet‐Le Quintrec J‐S, Coste J, Vastel L Pacault V, Jeanne L, Lamas J‐P, et al. Positive effect of patient education for hip surgery. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 2003;414:112‐20. - PubMed
Gocen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gocen Z, Sen A, Unver B, Karatosun V, Guna I. The effect of preoperative physiotherapy and education on the outcome of total hip replacement: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;18:353‐8. - PubMed
Goldsmith 1999 {published data only}
Gonzales 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gonzales EA, Ledesma RJA, McAllister DJ, Eslinger MR, Perry SM, Dyer CA, et al. The effects of guided imagery on postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing same‐day surgical procedures: a randomized, single‐blind study. Journal of the American Association of Nurse Anesthetists 2010;78(3):181‐8. - PubMed
Goodman 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Goodman H, Parsons A, Davison J, Preedy M, Peters E, Shuldham C, et al. A randomised controlled trial to evaluate a nurse‐led programme of support and lifestyle management for patients awaiting cardiac surgery. European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing 2008;7:189‐95. - PubMed
Gräwe 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gräwe JS, Mirow L, Bouchard R, Lindig M, Hüppe M. Impact of preoperative patient education on postoperative pain in consideration of the individual coping style [Einfluss präoperativer Patienteninformationen auf postoperative Schmerzen unter Berücksichtigung individueller Stressverarbeitung]. Der Schmerz 2010;24:575‐86. - PubMed
Greenleaf 1992 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Greenleaf M, Miaskowski, C, DuHamel K. Hypnotizability and recovery from cardiac surgery. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis 1992;35(2):119‐28. - PubMed
Griffin 1998 {published data only}
-
- Griffin MJ, Brennan L, McShane AJ. Preoperative education and outcome of patient controlled analgesia. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 1998;45(10):943‐8. - PubMed
Guo 2012 {published data only}
-
- Guo P, East L, Arthur A. A preoperative education intervention to reduce anxiety and improve recovery among Chinese cardiac patients: a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2012;49:129‐37. - PubMed
Hart 1980 {published data only}
-
- Hart RR. The influence of a taped hypnotic induction treatment procedure on the recovery of surgery patients. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 1980;28(4):324‐32. - PubMed
Hawkins 1993 {published data only}
-
- Hawkins R, Price K. The effects of an education video on patients’ requests for postoperative pain relief. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing 1993;10(4):32‐40. - PubMed
Heidarnia 2005 {published data only}
-
- Babaee G, Keshavarz M, Hidarnia A, Shayegan M. Evaluation of quality of life in patients with coronary artery bypass surgery using controlled clinical trial. Acta Medica Iranica 2007;45(1):69‐75.
-
- Heidarnia A, Dehdari T, Ghofranipour F, Kazemnejad A, Heidarnia M. The effect of health education on health related quality of life in patients with coronary artery bypass surgery. Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran 2005;18(4):319‐26.
Hoogeboom 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hoogeboom TJ, Dronkers JJ, Ende CHM, Oosting E, Meeteren NLU. Preoperative therapeutic exercise in frail elderly scheduled for total hip replacement: a randomized pilot trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2010;24:901‐10. - PubMed
Hulzebos 2006a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hulzebos EHJ, Meeteren NLU, Buijs BJWM, Bie RA, Rivière AB, Helders PJM. Feasibility of preoperative inspiratory muscle training in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery with a high risk of postoperative pulmonary complications: a randomized controlled pilot study. Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;20:949‐59. - PubMed
Hulzebos 2006b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hulzebos EHJ, Helders PJM, Favié NJ, Bie RA, Riviere AB, Meeteren NLU. Preoperative intensive inspiratory muscle training to prevent postoperative pulmonary complications in high‐risk patients undergoing CABG surgery. JAMA 2006;296(15):1851‐7. - PubMed
Johnson 1978b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Johnson JE, Rice VH, Fuller SS, Endress MP. Sensory information, instruction in a coping strategy, and recovery from surgery. Research in Nursing and Health 1978;1(1):4‐17. - PubMed
Johnson 1985 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Johnson JE, Christman NJ, Stitt C. Personal control interventions: short‐ and long‐term effects on surgical patients. Research in Nursing and Health 1985;8:131‐45. - PubMed
Klos 1980 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Klos D, Cummings KM, Joyce J, Graichen J, Quigley A. A comparison of two methods of delivering presurgical instructions. Patient Counselling and Health Education 1980;2(1):6‐13. - PubMed
Kulkarni 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kulkarni SR, Fletcher E, McConnell AK, Poskitt KR, Whyman MR. Pre‐operative inspiratory muscle training preserves postoperative inspiratory muscle strength following major abdominal surgery – a randomised pilot study. Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England 2010;92:700‐5 (+supplementary online files). - PMC - PubMed
Lam 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lam KK, Chan MTV, Chen PP, Kee, WDN. Structured preoperative patient education for patient‐controlled analgesia. Journal of Clinical Anaesthesia 2001;13:465‐9. - PubMed
Lamarche 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lamarche D, Taddeo R, Pepler C. The preparation of patients for cardiac surgery. Clinical Nursing Research 1998;7(4):390‐405. - PubMed
Langer 1975 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Langer EJ, Janis IL, Wolfer JA. Reduction of psychological stress in surgical patients. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 1975;11:155‐65.
Lauder 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lauder GR, Mcquillan PJ, Pickering RM. Psychological adjunct to perioperative antiemesis. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1995;74:266‐70. - PubMed
Leserman 1989 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Leserman J, Stuart EM, Mamish ME, Benson H. The efficacy of the relaxation response in preparing for cardiac surgery. Behavioral Medicine 1989;15(3):111‐7. - PubMed
Letterstål 2004 {published data only}
-
- Letterstål A, Sandström V, Olafsson P, Forsberg C. Postoperative mobilization of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2004;48(6):560‐8. - PubMed
Levesque 1977 {published data only}
-
- Levesque L, Charlebois M. [Anxiété, foyer de contrôle et les effets d’un enseignement sur l’état physique et émotionel des opérés]. Nursing Papers. Perspectives en Nursing 1977;8(4):11‐26. - PubMed
Lévesque 1984 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lévesque L, Grenier R, Kérouac S, Reidy M. Evaluation of a presurgical group program given at two different times. Research in Nursing and Health 1984;7:227‐36. - PubMed
Levin 1987 {published data only}
-
- Levin RF, Malloy GB, Hayman RB. Nursing management of postoperative pain: use of relaxation techniques with female cholecystectomy patients. Journal of Advanced Nursing 1987;12:463‐72. - PubMed
Lilja 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lilja Y, Rydén S, Fridlund B. Effects of extended preoperative information on perioperative stress: an anaesthetic nurse intervention for patients with breast cancer and total hip replacement. Intensive and Critical Care Nursing 1998;14:276‐82. - PubMed
Lim 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lim L, Chow P, Wong C‐Y, Chung A, Chan Y‐H, Wong W‐K, et al. Doctor‐patient communication, knowledge, and question prompt lists in reducing preoperative anxiety – a randomized control study. Asian Journal of Surgery 2011;34:175‐80. - PubMed
Lin 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lin L‐Y, Wang R‐H . Abdominal surgery, pain and anxiety: preoperative nursing intervention. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2005;51(3):252‐60. - PubMed
Lindeman 1973 {published data only}
-
- Lindeman CA, Stetzer SL. Effect of preoperative visits by operating room nurses. Nursing Research 1973;22(1):4‐16. - PubMed
Liu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Liu W, Lü M. Empowerment model of preoperative education for orthopaedic patients [[Chinese script]]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;8(5):840‐1.
Ma 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ma YI, Qin LJ, Han ZF. Relaxation training on stress response to abdominal surgery [[original title is in Chinese script]]. Chinese Journal of Nursing (Zhonghua Hu Li Za Zhi) 1996;31(7):377‐80. - PubMed
Mahler 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mahler HIM, Kulik JA, Hill MR. Effects of videotape preparations on recovery of female coronary bypass surgery patients. Mind/Body Medicine 1995;1(3):121‐9.
Mahler 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mahler HIM, Kulik JA. Effects of preparatory videotapes on self‐efficacy beliefs and recovery from coronary bypass surgery. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 1998;20(1):39‐46. - PubMed
McDonald 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- McDonald DD, Freeland M, Thomas G, Moore J. Testing a preoperative pain management intervention for elders. Research in Nursing and Health 2001;24:402‐9. - PubMed
McDonald 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- McDonald DD, Molony SL. Postoperative pain communication skills for older adults. Western Journal of Nursing Research 2004;26(8):836‐52. [2583] - PubMed
McDonald 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- McDonald DD, Thomas GJ, Livingston KE, Severson JS. Assisting older adults to communicate their postoperative pain. Clinical Nursing Research 2005;14(2):109‐26. - PubMed
McGregor 2004 {published data only}
-
- McGregor AH, Rylands H, Owen A, Doré CJ, Hughes SPF. Does preoperative hip rehabilitation advice improve recovery and patient satisfaction?. Journal of Arthroplasty 2004;19(4):464‐8. - PubMed
Miró 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Miró J, Raich RM. Effects of a brief and economical intervention in preparing patients for surgery: does coping style matter?. Pain 1999;83:471‐5. - PubMed
Neary 2010 {published data only}
-
- Neary PM, Sung R, Corrigan M, O’Donovan M, Cahill RA, Redmond HP. The benefits of an interactive, individualized online patient pathway for patients undergoing minimally invasive radioguided parathyroidectomy: a prospective, double‐blinded, randomized clinical trial. Surgical Innovation 2010;17(3):236‐41. - PubMed
O'Connor 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- O’Connor G, Coates V, O’Neill S. Randomised controlled trial of a tailored information pack for patients undergoing surgery and treatment for rectal cancer. European Journal of Oncology Nursing 2014;18:183‐91. - PubMed
Oetker‐Black 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Oetker‐Black SL, Jones S, Estok P, Ryan M, Gale N, Parker C. Preoperative teaching and hysterectomy outcomes. AORN Journal 2003;77(6):1215‐31. - PubMed
Oliphant 2013 {published data only}
-
- Oliphant SS, Lowder JL, Ghetti C, Zyczynski HM. Effect of a preoperative self‐catheterization video on anxiety: a randomised controlled trial. International Urogynecology Journal 2013;24:419‐24. - PubMed
Omlor 2000 {published data only}
-
- Omlor G, Kiewitz S, Pietschmann S, Roesler S. The benefit of preoperative psychotherapy on surgical outcome after inguinal hernia repair and thyroid gland surgery [Einfluss einer präoperativen Visualisierungstherapie auf die postoperativen Ergebnisse nach Leistenherniotomie und Strumaresektion]. Zentralblatt für Chirurgie 2000;125:380‐6. - PubMed
Oosting 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Oosting E, Jans MP, Dronkers JJ, Naber RH, Dronkers‐Landman CM, Appelman‐de Vries SM, et al. Preoperative home‐based physical therapy versus usual care to improve functional health of frail older adults scheduled for elective total hip arthroplasty: a pilot randomised controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2012;93:610‐6. - PubMed
Osinowo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Osinowo HO, Olley BO, Adejumo AO. Evaluation of the effect of cognitive therapy on perioperative anxiety and depression among Nigerian surgical patients. West African Journal of Medicine 2003;22(4):338‐42. - PubMed
Parthum 2006 {published data only}
-
- Parthum A, Weinzierl A, Gräßel E, Koppert W. Preoperative pain training. No influence on postoperative pain perception in patients undergoing cardiac surgery [Präoperative Schmerzschulung: Fehlender Einfluss auf postoperative erlebtes Schmerzempfinden kardiochirurgischer Patienten]. Der Schmerz 2006;20:301‐26. - PubMed
Pellino 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pellino T, Tluczek A, Collins M, Trimborn S, Norwick H, Engelke ZK, et al. Increasing self‐efficacy through empowerment: preoperative education for orthopaedic patients. Orthopaedic Nursing 1998;17(4):48‐59. - PubMed
Pellino 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pellino TA, Gordon DB, Engelke ZK, Busse KL, Collins MA. Use of nonpharmacologic interventions for pain and anxiety after total hip and total knee arthroplasty. Orthopaedic Nursing 2005;24(3):182‐90. - PubMed
Perri 1979 {published data only}
-
- Perri KD, Perri MG. Use of relaxation training to reduce pain following vaginal hysterectomy. Perceptual and Motor Skills 1979;48:478. - PubMed
Postlethwaite 1986 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Postlethwaite R, Stirling G, Peck CL . Stress inoculation for acute pain: a clinical trial. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 1986;9(2):219‐27. - PubMed
Rajendran 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ranjendran AJ, Pandurangi UM, Murali R, Gomathi S, Vijayan VK, Cherian KM. Pre‐operative short‐term pulmonary rehabilitation for patients of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Indian Heart Journal 1998;50:531‐4. - PubMed
Reading 1982 {published data only}
-
- Reading AE. The effects of psychological preparation for pain and recovery after minor gynaecological surgery: a preliminary report. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1982;38(3):504‐12. - PubMed
Ridgeway 1982 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ridgeway V, Mathews A. Psychological preparation for surgery: a comparison of methods. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1982;21:271‐80. - PubMed
Roman 2012 {published data only}
-
- Roman A, Moldovan R, Balázsi R, Câmpian R, Soanca A, Stratul S, et al. The role of cognitive behavioural therapy in the periodontal surgical treatment: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Cognitive and Behavioral Psychotherapies 2012;12(1):1‐14.
Rosenfeldt 2011 {published data only}
Schmitt 1973 {published data only}
-
- Schmitt EF, Wooldridge PJ. Psychological preparation of surgical patients. Nursing Research 1973;22(2):108‐16. - PubMed
Schwartz‐B'tt 1994 {published data only}
-
- Schwartz‐Barcott D, Fortin JD, Kim HS . Client‐nurse interaction: testing for its impact in preoperative instruction. International Journal of Nursing Studies 1994;31(1):23‐35. - PubMed
Seers 2008 {published data only}
-
- Seers K, Crichton N, Tutton L, Smith L, Saunders T. Effectiveness of relaxation for postoperative pain and anxiety: randomized controlled trial. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2008;62(6):681‐8. - PubMed
Shelley 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shelley M, Pakenham K. The effects of preoperative preparation on postoperative outcomes: the moderating role of control appraisals. Health Psychology 2007;26(2):183‐91. - PubMed
Shuldham 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shuldham CM, Fleming S, Goodman H. The impact of pre‐operative education on recovery following coronary artery bypass surgery: a randomized controlled clinical trial. European Heart Journal 2002;23(8):666‐74. - PubMed
Vukomanović 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Vukomanović A, Popović Z, Đurović A, Krstić L. The effects of short‐term preoperative physical therapy and education on early functional recovery of patients younger than 70 undergoing total hip arthroplasty [Alternative title: Efekti kratkotrayne preoperativne fizikalne terapije I edukacije na rani funkcijski oporavak bolesnika mlađih od 70 godina sa totalnom artroplastikom kuka]. Vojnosanitetski Pregled 2008;65(4):291‐7. - PubMed
Watt‐Watson 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Watt‐Watson J, Stevens B, Costello J, Katz J, Reid G. Impact of preoperative education on pain management outcomes after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a pilot. Canadian Journal of Nursing Research 2000;31(4):41‐56. - PubMed
Watt‐Watson 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Watt‐Watson J, Stevens B, Katz J, Costello J, Reid GJ, David T. Impact of preoperative education on pain outcomes after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Pain 2004;109:73‐85. - PubMed
Wells 1982 {published data only}
-
- Wells N. The effect of relaxation on postoperative muscle tension and pain. Nursing Research 1982;31(4):236‐8. - PubMed
Wijgman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Wijgman AJ, Dekkers GHG, Waltje E, KrekelsT, Arens HJ. No positive effect of preoperative physical therapy and instruction of patients to be subjected to hip arthroplasty [Geen positief effect van properatieve oefentherapie en instructive bij patiënten die heupartroplastiek zullen ondergaan]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 1994;138(19):949‐52. - PubMed
Wilson 1981 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wilson JF. Behavioural preparation for surgery: benefit or harm?. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 1981;4(1):79‐101. - PubMed
Yang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yang C‐L, Tan Y‐H, Jiang X‐X, Meng F‐Y, Wu Y‐L, Chen, Q‐L, et al. Pre‐operative education and counselling are associated with reduced anxiety symptoms following carotid endarterectomy: a randomized and open‐label study. European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing 2012;11(3):284‐8. - PubMed
Zhang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zhang C‐Y, Jiang Y, Yin Q‐Y, Chen F‐J, Ma L‐L, Wang L‐X. Impact of nurse‐initiated preoperative education on postoperative anxiety symptoms and complications after coronary artery bypass grafting. Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing 2012;27(1):84‐8. - PubMed
Ziemer 1982 {published data only}
-
- Ziemer M. Providing patients with information prior to surgery and the reported frequency of coping behaviors and development of symptoms following surgery. Dissertation Abstracts International 1983;43:2465B.
-
- Ziemer MM. Providing Patients with Information Prior to Surgery and the Reported Frequency of Coping Behaviors and Development of Symptoms Following Surgery [Dissertation for Degree of Doctor of Nursing Science]. School of Nursing, University of Pennsylvania, 1982.
-
- Ziemer MM. Effects of information on postsurgical coping. Nursing Research 1982;32(5):282‐7. - PubMed
Zieren 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zieren J, Menenakos C, Mueller JM. Does an informative video before inguinal hernia surgical repair influence postoperative quality of life? Results of a prospective randomized study. Quality of Life Research 2007;16:725‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Anderson 1987 {published data only}
-
- Anderson EA. Preoperative preparation for cardiac surgery facilitates recovery, reduces psychological distress, and reduces the incidence of acute postoperative hypertension. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1987;55(4):513‐20. - PubMed
Blay 2005 {published data only}
-
- Blay N, Donoghue J. The effect of pre‐admission education on domiciliary recovery following laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing 2005;22(4):14‐9. - PubMed
Boore 1978 {published data only}
-
- Boore JRP. An Investigation Into the Effect of Some Aspects of Pre‐operative Preparation of Patients on Post‐operative Stress and Recovery [PhD thesis]. University of Manchester, 1976.
-
- Boore JRP. Prescription for Recovery: The Effect of Pre‐Operative Preparation of Surgical Patients on Post‐Operative Stress, Recovery and Infection. Royal College of Nursing Research Series. London: Royal College of Nursing, 1978.
Burton 1991 {published data only}
-
- Burton MV, Parker RW, Wollner JM. The psychotherapeutic value of a "chat": a verbal response modes study of a placebo attention control with breast cancer patients. Psychotherapy Research 1991;1(1):39‐61.
Burton 1994 {published data only}
-
- Burton MV, Parker, RW. Satisfaction of breast cancer patients with their medical and psychological care. Journal of Psychosocial Oncology 1994;12(1/2):41‐63.
Croog 1994 {published data only}
-
- Croog SH, Baume RM, Nalbandian J. Pain response after psychological preparation for repeated periodontal surgery. Journal of the American Dental Association 1994;125:1353‐60. - PubMed
Domar 1987 {published data only}
-
- Domar AD, Noe JM, Ransil B, Benson H. The preoperative use of the relaxation response with ambulatory surgery patients. Journal of Human Stress 1987;13(3):101‐7. - PubMed
Enqvist 1995 {published data only}
-
- Enqvist B, Konow L, Bystedt H . Pre‐ and perioperative suggestion in maxillofacial surgery: effects on blood loss and recovery. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 1995;43(3):284‐94. - PubMed
Eremin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Eremin O, Walker MB, Simpson E, Heys SD, Ah‐See AK, Hutcheon AW, et al. Immuno‐modulatory effects of relaxation training and guided imagery in women with locally advanced breast cancer undergoing multimodality therapy: a randomised controlled trial. The Breast 2000;18(1):17‐25. - PubMed
Huang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Huang S‐W, Chen P‐H, Chou Y‐H. Effects of a preoperative simplified home rehabilitation education program on length of stay for total knee arthroplasty patients. Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research 2012;98:259‐64. - PubMed
Johnson 1978a {published data only}
-
- Johnson JE, Fuller SS, Endress MP, Rice VH. Altering patients’ responses to surgery: an extension and replication. Research in Nursing and Health 1978;1(3):111‐21. - PubMed
Lengacher 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lengacher CA, Bennett MP, Gonzalez L, Gilvary D, Cox CE, Cantor A, et al. Immune responses to guided imagery during breast cancer treatment. Biological Research Nursing 2008;9(3):205‐14. - PubMed
Liu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Liu L, Li J. Observation of the postoperative analgesic effect of Lornoxicam preemptive analgesia combined with psychotherapy for elderly cancer patients. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology 2013;40(11):664‐7.
Manyande 1995 {published data only}
-
- Manyande A, Berg S, Gettins D, Stanford SC, Mazhero S, Marks DF, et al. Preoperative rehearsal of active coping imagery influences subjective and hormonal responses to abdominal surgery. Psychosomatic Medicine 1995;57:177‐82. - PubMed
Manyande 1998 {published data only}
-
- Manyande A, Salmon P. Effects of pre‐operative relaxation on post‐operative analgesia: immediate increase and delayed reduction. British Journal of Health Psychology 1998;3(3):215‐24.
Mitchell 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell M. Psychological preparation for patients undergoing day surgery. Ambulatory Surgery 2000;8:19‐29.
Montgomery 2002 {published data only}
-
- Montgomery GH, Weltz CR, Seltz M, Bovbjerg DH. Brief presurgical hypnosis reduces distress and pain in excisional breast biopsy patients. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 2002;50(1):17‐32. - PubMed
Montgomery 2007 {published data only}
-
- Montgomery GH, Bovbjerg DH, Schnur JB, David D, Goldfarb A, Weltz CR, et al. A randomized clinical trial of a brief hypnosis intervention to control side effects in breast surgery patients. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2007;99(17):1304‐12. - PubMed
Sheard 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sheard C, Garrud P. Evaluation of generic patient information: effects on health outcomes, knowledge and satisfaction. Patient Education and Counselling 2006;64:43‐7. - PubMed
Shelley 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shelley M, Pakenham KI, Frazer I. Cortisol changes interact with the effects of a cognitive behavioural psychological preparation for surgery on 12‐month outcomes for surgical heart patients. Psychology and Health 2009;24(10):1139‐52. - PubMed
Stergiopoulou 2006 {published data only}
-
- Stergiopoulou A, Birbas K, Katostaras T, Diomidous M, Mantas J. The effect of a multimedia health educational program on the postoperative recovery of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Studies in Health Technology & Informatics 2006;124:920‐5. - PubMed
Sugai 2013 {published data only}
Surman 1974 {published data only}
-
- Surman OS, Hackett TP, Silverberg EL, Behrendt DM. Usefulness of psychiatric intervention in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;30:830‐5. - PubMed
Timmons 1993 {published data only}
-
- Timmons ME, Bower FL. The effect of structured preoperative teaching on patients' use of patient‐controlled analgesia (PCA) and their management of pain. Orthopaedic Nursing 1993;12(1):23‐31. - PubMed
Voshall 1980 {published data only}
-
- Voshall B. The effects of preoperative teaching on postoperative pain. Topics in Clinical Nursing 1980;2:39‐43. - PubMed
Wang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wang AW, Gilbey HJ, Ackland TR. Perioperative exercise programs improve early return of ambulatory function after total hip arthroplasty. A randomized, controlled trial. American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2002;81(11):801‐6. - PubMed
Wells 1986 {published data only}
-
- Wells JK, Howard GS, Nowlin WF, Vargas MJ. Presurgical anxiety and postsurgical pain and adjustment: effects of a stress inoculation procedure. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1986;54(6):831‐5. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Akinci 2015 {published data only}
-
- Akinci B, Yeldan I, Bayramoglu Z, Akpinar TB. The effects of posture and relaxation training on sleep, dyspnoea, pain and, quality of life in the short‐term after cardiac surgery: a pilot study. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology 2015;22(S1):S171‐2.
Angioli 2014 {published data only}
-
- Angioli R, Plotti F, Capriglione S, Aloisi A, Aloisi ME, Luvero D, et al. The effects of giving patients verbal or written pre‐operative information in gynecologic oncology surgery: a randomized study and the medical‐legal point of view. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2014;177:67‐71. - PubMed
Attias 2014 {published data only}
-
- Attias S, Keinan‐Boker L, Sroka G, Matter I, Arnon Z, Schiff E. The effectiveness of a generic guided imagery CD compared with individualized complementary therapies and standard of care for reducing preoperative anxiety: preliminary results. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2014;20(5):A137.
Bergin 2014b {published data only}
-
- Bergin C, Speroni KG, Travis T, Bergin J, Sheridan MJ, Kelly K, et al. Effect of preoperative incentive spirometry patient education on patient outcomes in the knee and hip joint replacement population. Journal of Perianesthesia Nursing 2014;29(1):20‐7. - PubMed
Calsinski Assis 2014 {published data only}
-
- Calsinski Assis C, Lima Lopes J, Nogueira‐Martins L A, Bottura Leite de Barros AL. Embracement and anxiety symptoms in patients before cardiac surgery [Acolhimento e sintomas de ansiedade em pacientes no pré‐operatório de cirurgia cardíaca]. Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem 2014;67(3):401‐7. - PubMed
Chevillon 2014 {published data only}
-
- Chevillon C, Hellyar M, Madani C, Kerr K, Son Chae K. Preoperative education on postoperative delirium, anxiety, and knowledge in pulmonary thromboendarterectomy patients. American Journal of Critical Care 2015;24(2):164‐71. - PubMed
Chow 2014 {published data only}
-
- Chow KM, Chan CWH, Chan JCY, Choi KKC, Siu KY. A feasibility study of a psychoeducational intervention program for gynecological cancer patients. European Journal of Oncology Nursing 2014;18(4):385‐92. - PubMed
Dathatri 2014 {published data only}
-
- Dathatri S, Gruberg L, Anand J, Romeiser J, Sharma S, Finnin E, et al. Informed consent for cardiac procedures: deficiencies in patient comprehension with current methods. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2014;97(5):1505‐12. - PubMed
Eckhouse 2014 {published data only}
-
- Eckhouse DR, Hurd M, Cotter‐Schaufele S, Sulo S, Sokolowski M, Barbour L. A randomized controlled trial to determine the effects of music and relaxation interventions on perceived anxiety in hospitalized patients receiving orthopaedic or cancer treatment. Orthopaedic Nursing 2014;33(6):342‐51. - PubMed
El Azem 2014 {published data only}
-
- Azem A, Benington PCM, Khambay BS, Ayoub AF. Evaluation of an interactive multi‐media device for delivering information on Le Fort I osteotomy. Journal of Cranio‐Maxillofacial Surgery 2014;42(6):885‐9. - PubMed
Ellett 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ellett L, Villegas R, Beischer A, Ong N, Maher P. Use of a multimedia module to aid the informed consent process in patients undergoing gynecologic laparoscopy for pelvic pain: randomized controlled trial. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 2014;21(4):602‐11. - PubMed
Foji 2015 {published data only}
-
- Foji S, Tadayonfar MA, Mohsenpour M, Rakhshani MH. The study of the effect of guided imagery on pain, anxiety and some other hemodynamic factors in patients undergoing coronary angiography. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice 2015;21(2):119‐23. - PubMed
Fraval 2015 {published data only}
Furuya 2015 {published data only}
-
- Furuya RK, Arantes EC, Dessotte CAM, Ciol MA, Hoffman JM, Schmidt A, et al. A randomized controlled trial of an educational programme to improve self‐care in Brazilian patients following percutaneous coronary intervention. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2015;71(4):895‐908. - PubMed
Gade 2014 {published data only}
Gillis 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gillis C, Li C, Lee L, Awasthi R, Augustin B, Gamsa A, et al. Prehabilitation versus rehabilitation: a randomized control trial in patients undergoing colorectal resection for cancer. Anesthesiology 2014;121(5):937‐47. - PubMed
Gyulaházi 2015 {published data only}
Hansen 2015 {published data only}
Henney 2014 {published data only}
-
- Henney S, Irving R. Prospective, randomised, controlled trial comparing delivery of patient information for functional endoscopic sinus surgery via website versus printed leaflet. Journal of Laryngology & Otology 2014;128(3):249‐54. - PubMed
Heras 2014 {published data only}
-
- Heras P, Natsis V, Sirbilantze T. Preventing anxiety and depression in breast cancer: a randomized controlled trial. Supportive Care in Cancer 2014;22:S175‐6.
Hoppe 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hoppe DJ, Denkers M, Hoppe FM, Wong IH. The use of video before arthroscopic shoulder surgery to enhance patient recall and satisfaction: a randomized‐controlled study. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery 2014;23(6):e134‐9. - PubMed
Huber 2015 {published data only}
Johansson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Johansson K, Salanterä S, Katajisto J. Empowering orthopaedic patients through preadmission education: results from a clinical study. Patient Education and Counseling 2007;66:84‐91. - PubMed
Kol 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kol E, Alpar SE, Erdoğan A. Preoperative education and use of analgesic before onset of pain routinely for post‐thoracotomy pain control can reduce pain effect and total amount of analgesics administered postoperatively. Pain Management Nursing 2014;15(1):331‐9. - PubMed
Lai Ngor 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lai Ngor C, Lai CKY. The effect of patient education with telephone follow‐up on wound healing in adult patients with clean wounds: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing 2014;41(4):345‐55. - PubMed
Lookinland 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lookinland S, Pool M . Study on effect of methods of preoperative education in women. Association of Operating Room Nurses Journal 1998;67(1):203‐13. - PubMed
Louw 2014 {published data only}
-
- Louw A, Diener I, Landers MR, Puentedura EJ. Preoperative pain neuroscience education for lumbar radiculopathy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial with 1‐year follow‐up. Spine 2014;39(18):1449‐57. - PubMed
Mohammadi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Mohammadi A, Mirbagher Ajorpaz N, Torabi M, Mirsane A, Moradi F. Effects of music listening on preoperative state anxiety and physiological parameters in patients undergoing general surgery: a randomized quasi‐experimental trial. Central European Journal of Nursing & Midwifery 2014;5(4):156‐60.
Novick 2014 {published data only}
-
- Novick BJ, Angie M, Walker E, Kitay R, Monday K, Albert NM. The effect of intensive education on urinary incontinence following radical prostatectomy: a randomized control trial. Urologic Nursing 2014;34(5):246‐51. - PubMed
Paul 2015 {published data only}
-
- Paul L, Rongen S, Hoeken D, Deen M, Klaassen R, Biter LU, et al. Does cognitive behavioral therapy strengthen the effect of bariatric surgery for obesity? Design and methods of a randomized and controlled study. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2015;42:252‐6. - PubMed
Rolving 2014 {published data only}
-
- Rolving N, Nielsen CV, Christensen FB, Holm R, Bunger C, Østergaard L. Does a preoperative cognitive‐behavioural intervention affect postsurgical pain, mobilisation and length of hospitalisation in lumbar spinal fusion patients?. European Spine Journal 2014;23(5 (Suppl)):S572.
Saleh 2015 {published data only}
Shahmansouri 2014 {published data only}
-
- Shahmansouri N, Janghorbani M, Salehi Omran A, Karimi AA, Noorbala AA, Arjmandi A, et al. Effects of a psychoeducation intervention on fear and anxiety about surgery: randomized trial in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Psychology, Health & Medicine 2014;19(4):375‐83. - PubMed
Umpierres 2014 {published data only}
-
- Umpierres CS, Ribeiro TA, Marchisio ÂE, Galvão L, Borges ÍNK, Souza Macedo CA, et al. Rehabilitation following total hip arthroplasty evaluation over short follow‐up time: randomized clinical trial. Journal of Rehabilitation Research & Development 2014;51(10):1567‐78. - PubMed
Van Acker 2014 {published data only}
West 2014 {published data only}
-
- West AM, Bittner EA, Ortiz VE. The effects of preoperative, video‐assisted anesthesia education in Spanish on Spanish‐speaking patients' anxiety, knowledge, and satisfaction: a pilot study. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2014;26(4):325‐9. - PubMed
Würtzen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Würtzen H, Dalton SO, Christensen J, Andersen KK, Elsass P, Flyger HL, et al. Effect of mindfulness‐based stress reduction on somatic symptoms, distress, mindfulness and spiritual wellbeing in women with breast cancer: results of a randomized controlled trial. Acta Oncologica 2015;54(5):712‐9. - PubMed
Xin 2015 {published data only}
-
- Xin YH, Xiao CR. Effect of holistic health education prescription in colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery. World Chinese Journal of Digestology 2015;23(2):338‐42.
References to ongoing studies
Hansen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hansen MM. Impact of complementary therapies via mobile technologies on Icelandic same day surgical patients' reports of anxiety, pain and self‐efficacy in healing: A randomized controlled trial in process. Studies in Health Technology & Informatics 2013;192:1165. - PubMed
Jong 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jong M, Pijl A, Gast H, Sjoling M. The effects of guided imagery on preoperative anxiety and pain management in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a multi‐centre RCT study. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012;12(Suppl 1):184.
Additional references
Abraha 2010
APA 1980
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association, 1980.
APA 2005
-
- Executive Committee of the American Psychological Association, Division of Psychological Hypnosis. New Definition: Hypnosis. The Division 30 Definition and Description of Hypnosis. http://www.apa.org/divisions/div30/define_hypnosis.html (accessed 21 October 2009) 2005.
Arpino 2004
-
- Arpino L, Iavarone A, Parlato C, Moraci A. Prognostic role of depression after lumbar disc surgery. Neurological Sciences 2004;3:145‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bellamy 1988
-
- Bellamy N, Buchanan W, Goldsmith C, Campbell J, Sitt L. Validation study of WOMAC: A health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy inpatients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Journal of Rheumatology 1988;15:1833‐40. - PubMed
Billewicz 1964
Bruce 2012
-
- Bruce J, Thornton AJ, Scott NW, Marfizo S, Powell R, Johnston M, et al. on behalf of the Recovery Study Group. Chronic preoperative pain and psychological robustness predict acute postoperative pain outcomes after surgery for breast cancer. British Journal of Cancer 2012;107:937‐46. [DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.341] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Cohen 1983
-
- Cohen S Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress. Journal of Health and Social Behaviour 1983;24:385‐96. - PubMed
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Second Edition. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988.
Daut 1983
-
- Daut R, Cleeland C, Flanery R. Development of the Wisconsin Brief Pain Inventory to assess pain in cancer and other diseases. Pain 1983;1:197‐210. - PubMed
de Bruin 2009
-
- Bruin M, Viechtbauer W, Hospers HJ, Schaalma HP, Kok G. Standard care quality determines treatment outcomes in control groups of HAART‐adherence intervention studies: implications for the interpretation and comparison of intervention effects. Health Psychology 2009;28(6):668‐74. [DOI: 10.1037/a0015989] - DOI - PubMed
Dupuy 1984
-
- Dupuy HJ. The psychological general well‐being (PGWB) index. In: Wenger NK, Matson MI, Furberg CD, Elinson J editor(s). Assessment of Quality of Life in Clinical Trials of Cardiovascular Therapies. New York: Le Jacq Publ Inc, 1984:170‐83. - PubMed
Geissner 1996
-
- Geissner E. Die Schmerzempfindungs‐Skala. Test und Handanweisung. Göttingen: Hogrefe, 1996.
Goldberg 1978
-
- Goldberg D. Manual of the General Health Questionnaire. Windsor: NEFR‐Nelson, 1978.
Granot 2005
-
- Granot M, Ferber SG. The roles of pain catastrophizing and anxiety in the prediction of postoperative pain intensity: a prospective study. Clinical Journal of Pain 2005;21(5):439‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gurusamy 2014
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hollis 1999
Hulzebos 2012
Hunt 1983
-
- Hunt SM, McEwen J. The development of a subjective health indicator. Sociology of Health and Illness 1983;2:231‐45. - PubMed
Jacobsen 1938
-
- Jacobsen E. Progressive Relaxation. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1938.
Janke 1994
-
- Janke W, Hüppe M. [Befindlichkeitsskalierung durch Kategorien und Eigenschaftswörter: BSKE (EWL)]. In: Janke W, Debus G, Erdman G, Hüppe M editor(s). Test und Handanweisung. Würzburg: Unveröffentlichter Institutsbericht. Institut für Psychologie I, 1994.
Jette 1987
-
- Jette AM, Cleary PD. Functional Disability Assessment. Physical Therapy 1987;67:1854‐9. - PubMed
Johnson 1973
-
- Johnson JE. Effects of accurate expectations about sensations on the sensory and distress components of pain. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1973;27(2):261‐75. - PubMed
Johnston 1980
-
- Johnston M. Anxiety in surgery patients. Psychological Medicine 1980;10:145‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Johnston 1993
-
- Johnston M, Vögele C. Benefits of psychological preparation for surgery: a meta‐analysis. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 1993;15(4):245‐56.
Jüni 2001
Kekecs 2014
-
- Kekecs Z, Nagy T, Varga K. The effectiveness of suggestive techniques in reducing postoperative side effects: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesia & Analgesia 2014;119(6):1407‐19. - PubMed
Kiecolt‐Glaser 1998
Louw 2013
-
- Louw A, Diener I, Butler DS, Puentedura EJ. Preoperative education addressing postoperative pain in total joint arthroplasty: review of content and educational delivery methods. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice 2013;29(3):175‐94. - PubMed
Lucente 1972
-
- Lucente FE, Fleck MD. A study of hospitalization anxiety in 408 medical and surgical patients. Psychosomatic Medicine 1972;34(4):304‐12. - PubMed
Mahoney 1965
-
- Mahoney FI, Barthel DW. Functional evaluation: The Barthel Index. Maryland State Medical Journal 1965;14:61‐5. - PubMed
Maple 2015
-
- Maple H, Chilcot J, Lee V, Simmonds S, Weinman J, Mamode N. Stress predicts the trajectory of wound healing in living kidney donors as measured by high‐resolution ultrasound. Brain, Behavior and Immunity 2015;43:19‐26. [10.1016/j.bbi.2014.06.012] - PubMed
Marucha 1998
-
- Marucha PT, Kiecolt‐Glaser JK, Favegehi M. Mucosal wound healing is impaired by examination stress. Psychosomatic Medicine 1998;60:362‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mathews 1981
-
- Mathews A, Ridgeway V. Personality and surgical recovery: a review. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1981;2:243‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mathews 1984
-
- Mathews A, Ridgeway V. Psychological preparation for surgery. In: Steptoe A, Mathews A editor(s). Health Care and Human Behaviour. London: Academic Press, 1984:231‐59.
McDonald 2014
McNair 1971
-
- McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF. Profile of Mood States Manual. San Diego: Educational and Industrial Testing Service, 1971.
Melzack 1975
-
- Melzack R. The McGill Pain Questionnaire: major properties and scoring methods. Pain 1975;1:277‐99. [PUBMED: 1235985] - PubMed
Melzack 1987
-
- Melzack R. The short‐form McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain 1987;30:191‐7. - PubMed
Michie 2008
-
- Michie S, Johnston M, Francis JJ, Hardeman W, Eccles M. From theory to intervention: mapping theoretically derived behavioural determinants to behaviour change techniques. Applied Psychology: An International Review 2008;57:660‐80.
Michie 2013
-
- Michie S, Richardson M, Johnston M, Hardeman W, Eccles MP, Cane J, et al. The Behavior Change Technique Taxonomy (v1) of 93 hierarchically clustered techniques: building an international consensus for the reporting of behavior change interventions. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2013;46(1):81‐95. - PubMed
Miller 1983
-
- Miller SM, Manan CE. Interacting effects of information and coping style in adapting to gynecologic stress: should the doctor tell all?. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1983;45(1):223‐36. [PUBMED: 6886967] - PubMed
Miller 1987
-
- Miller SM. Monitoring and blunting: validation of a questionnaire to assess styles of information seeking under threat. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1987;52:345‐53. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz K, Altman D. Revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel group randomized trials. http://www.consort‐statement.org/statement/revisedstatement.htm (accessed 6 July 2004) 2001.
Munafó 2001
-
- Munafó MR, Stevenson J. Anxiety and surgical recovery: reinterpreting the literature. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 2001;51:589‐96. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Newell 1992
-
- Newell DJ. Intention‐to‐treat analysis: implications for quantitative and qualitative research. International Journal of Epidemiology 1992;21:837‐41. - PubMed
Nicholson 2013
-
- Nicholson A, Lewis SR, Lee A, Smith AF, Coldwell CH. Different formats and timing of educational interventions for surgical patients. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010889] - DOI
Radloff 1968
-
- Radloff R, Helmreich R. Groups Under Stress. New York: Appleton‐Century‐Crofts, 1968.
Rainville 2005
-
- Rainville P, Bao QVH, Chrétien P. Pain‐related emotions modulate experimental pain perception and autonomic responses. Pain 2005;118:306‐18. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Royal College of Surgeons 2016
-
- Royal College of Surgeons. Surgery and the NHS in numbers. Surgery in numbers: England. https://www.rcseng.ac.uk/media/media‐background‐briefings‐and‐statistics... (accessed 11 March 2016). Data from Health and Social Care Information Centre (HSCIC), Hospital Episode Statistics 2013/14. London: The Royal College of Surgeons of England, 2016.
Schulz 2010
Shields 1995
-
- Shields RK, Enloe LJ, Evans RE, Smith KB, Steckel SD. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of functional tests in patients with total joint replacement. Physical Therapy 1995;75(3):169‐76. - PubMed
Spiegal 1977
-
- Spiegal H. The Hypnotic Induction Profile (HIP): a review of its development. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 1977;296:129‐42. - PubMed
Spielberger 1983
-
- Spielberger C. Manual for the State Trait Anxiety Inventory STAI (form Y). Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press, 1983.
Sullivan 1995
-
- Sullivan MJL, Bishop SR, Pivik J. The pain catastrophizing scale: development and validation. Psychological Assessment 1995;7(4):524‐32.
Tait 1982
-
- Tait A, Maguire P, Faulkner A, Brooke M, Wilkinson S, Thomson L, et al. Improving communication skills: standardised assessments may help nurses to detect psychiatric problems as they develop in mastectomy patients. Nursing Times 1982;78:2181‐4. - PubMed
Tefikow 2013
-
- Tefikow S, Barth J, Maichrowitz S, Beelmann A, Strauss B, Rosendahl J. Efficacy of hypnosis in adults undergoing surgery or medical procedures: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clinical Psychology Review 2013;33:623‐36. - PubMed
van Middendorp 2010
Walburn 2009
Ware 2000
-
- Ware JE, Koskinski M, Dewey JE. How to Score Version 2 of the SF‐36 (R) Health Survey. Lincoln, RI: Quality Metric Incorporated, 2000.
Watson 1988
-
- Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1988;47:1063‐70. - PubMed
Zigmond 1983
-
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavia 1983;67:361‐70. - PubMed
Zuckerman 1965
-
- Zuckerman M, Lubin B. The development of an affect adjective check list for the measurement of anxiety. Manual for the Multiple Affect Adjective Check List. Carolina: Educational and Industrial Testing Service, 1965.
Zung 1971
-
- Zung WWK. A rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics 1971;12:371‐9. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

