Expression and function of pannexins in the inner ear and hearing
- PMID: 27229462
- PMCID: PMC4896268
- DOI: 10.1186/s12860-016-0095-7
Expression and function of pannexins in the inner ear and hearing
Abstract
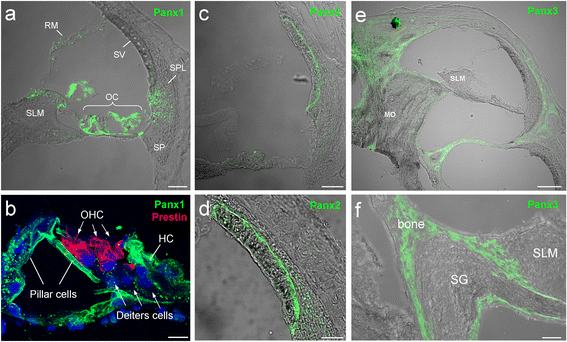
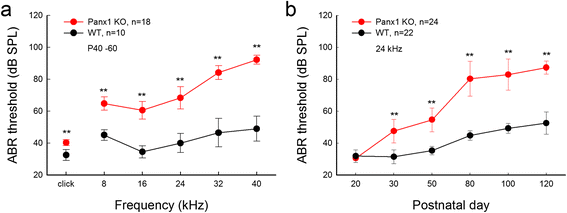
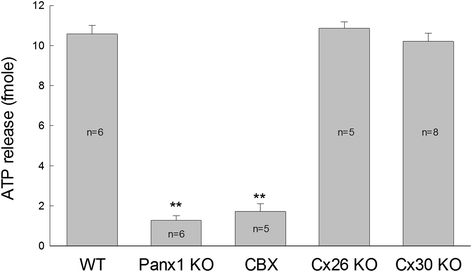
Pannexin (Panx) is a gene family encoding gap junction proteins in vertebrates. So far, three isoforms (Panx1, 2 and 3) have been identified. All of three Panx isoforms express in the cochlea with distinct expression patterns. Panx1 expresses in the cochlea extensively, including the spiral limbus, the organ of Corti, and the cochlear lateral wall, whereas Panx2 and Panx3 restrict to the basal cells of the stria vascularis in the lateral wall and the cochlear bony structure, respectively. However, there is no pannexin expression in auditory sensory hair cells. Recent studies demonstrated that like connexin gap junction gene, Panx1 deficiency causes hearing loss. Panx1 channels dominate ATP release in the cochlea. Deletion of Panx1 abolishes ATP release in the cochlea and reduces endocochlear potential (EP), auditory receptor current/potential, and active cochlear amplification. Panx1 deficiency in the cochlea also activates caspase-3 cell apoptotic pathway leading to cell degeneration. These new findings suggest that pannexins have a critical role in the cochlea in regard to hearing. However, detailed information about pannexin function in the cochlea and Panx mutation induced hearing loss still remain largely undetermined. Further studies are required.
Keywords: ATP release; Active cochlear amplification; Cell degeneration; Endocochlear potential; Hearing loss; Inner ear; Pannexin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pannexin1 channels dominate ATP release in the cochlea ensuring endocochlear potential and auditory receptor potential generation and hearing.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 2;5:10762. doi: 10.1038/srep10762. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26035172 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin 1 deficiency can induce hearing loss.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jul 17-24;463(1-2):143-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.05.049. Epub 2015 May 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26002464 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of pannexin expression in the mammalian cochlea.J Comp Neurol. 2009 Jan 20;512(3):336-46. doi: 10.1002/cne.21898. J Comp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19009624 Free PMC article.
-
The role of an inwardly rectifying K(+) channel (Kir4.1) in the inner ear and hearing loss.Neuroscience. 2014 Apr 18;265:137-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.01.036. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24480364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potassium ion recycling pathway via gap junction systems in the mammalian cochlea and its interruption in hereditary nonsyndromic deafness.Med Electron Microsc. 2000;33(2):51-6. doi: 10.1007/s007950070001. Med Electron Microsc. 2000. PMID: 11810458 Review.
Cited by
-
Practical aspects of inner ear gene delivery for research and clinical applications.Hear Res. 2020 Sep 1;394:107934. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2020.107934. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Hear Res. 2020. PMID: 32204962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse Panx1 Is Dispensable for Hearing Acquisition and Auditory Function.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Nov 28;10:379. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00379. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29234270 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic Signaling and Aminoglycoside Ototoxicity: The Opposing Roles of P1 (Adenosine) and P2 (ATP) Receptors on Cochlear Hair Cell Survival.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 May 15;13:207. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00207. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31156393 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic Signalling in the Cochlea.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 28;23(23):14874. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314874. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Potential Compensatory Role of Panx3 in the VNO of a Panx1 Knock Out Mouse Model.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Apr 26;11:135. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00135. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29780304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baranova A, Ivanov D, Petrash N, Pestova A, Skoblov M, Kelmanson I, Shagin D, Nazarenko S, Geraymovych E, Litvin O, Tiunova A, Born TL, Usman N, Staroverov D, Lukyanov S, Panchin Y. The mammalian pannexin family is homologous to the invertebrate innexin gap junction proteins. Genomics. 2004;83:706–716. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2003.09.025. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

