Restrictive influence of SAMHD1 on Hepatitis B Virus life cycle
- PMID: 27229711
- PMCID: PMC4882586
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26616
Restrictive influence of SAMHD1 on Hepatitis B Virus life cycle
Abstract
Deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) are essential for efficient hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication. Here, we investigated the influence of the restriction factor SAMHD1, a dNTP hydrolase (dNTPase) and RNase, on HBV replication. We demonstrated that silencing of SAMHD1 in hepatic cells increased HBV replication, while overexpression had the opposite effect. SAMHD1 significantly affected the levels of extracellular viral DNA as well as intracellular reverse transcription products, without affecting HBV RNAs or cccDNA. SAMHD1 mutations that interfere with the dNTPase activity (D137N) or in the catalytic center of the histidine-aspartate (HD) domain (D311A), and a phospho-mimetic mutation (T592E), abrogated the inhibitory activity. In contrast, a mutation diminishing the potential RNase but not dNTPase activity (Q548A) and a mutation disabling phosphorylation (T592A) did not affect antiviral activity. Moreover, HBV restriction by SAMHD1 was rescued by addition of deoxynucleosides. Although HBV infection did not directly affect protein level or phosphorylation of SAMHD1, the virus upregulated intracellular dATPs. Interestingly, SAMHD1 was dephosphorylated, thus in a potentially antiviral-active state, in primary human hepatocytes. Furthermore, SAMHD1 was upregulated by type I and II interferons in hepatic cells. These results suggest that SAMHD1 is a relevant restriction factor for HBV and restricts reverse transcription through its dNTPase activity.
Figures
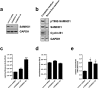
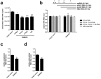
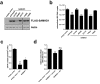
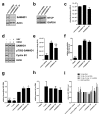

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by a dNTPase-dependent function of the host restriction factor SAMHD1.Virology. 2016 Aug;495:71-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 May 11. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27179347
-
Cyclin E2-CDK2 mediates SAMHD1 phosphorylation to abrogate its restriction of HBV replication in hepatoma cells.FEBS Lett. 2018 Jun;592(11):1893-1904. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13105. Epub 2018 Jun 6. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 29782647
-
A Cyclin-Binding Motif in Human SAMHD1 Is Required for Its HIV-1 Restriction, dNTPase Activity, Tetramer Formation, and Efficient Phosphorylation.J Virol. 2018 Feb 26;92(6):e01787-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01787-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29321329 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of SAMHD1 in antiviral defense, autoimmunity and cancer.Rev Med Virol. 2017 Jul;27(4). doi: 10.1002/rmv.1931. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Rev Med Virol. 2017. PMID: 28444859 Review.
-
The missing link: allostery and catalysis in the anti-viral protein SAMHD1.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Aug 30;47(4):1013-1027. doi: 10.1042/BST20180348. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31296733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Proteomics Identification of IFN-λ3-regulated Antiviral Proteins in HBV-transfected Cells.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018 Nov;17(11):2197-2215. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.000735. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 30097535 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of SAMHD1 and its mutation on prognosis of colon cancer.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jul 8;24(3):303. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13423. eCollection 2022 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35949607 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired influenza A virus replication by the host restriction factor SAMHD1 which inhibited by PA-mediated dephosphorylation of the host transcription factor IRF3.Virol J. 2024 Jan 29;21(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02295-0. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38287375 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence of a Circulating Hepatitis B Virus Genotype C Strain Isolated from a Chronically Infected Patient Identified at an Outdoor Hospital in Bangladesh.Genome Announc. 2018 Mar 1;6(9):e01601-17. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01601-17. Genome Announc. 2018. PMID: 29496845 Free PMC article.
-
Dephosphorylation of the HIV-1 restriction factor SAMHD1 is mediated by PP2A-B55α holoenzymes during mitotic exit.Nat Commun. 2018 Jun 8;9(1):2227. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04671-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29884836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kluge S. F., Sauter D. & Kirchhoff F. SnapShot: Antiviral Restriction Factors. Cell 163, 774–774.e1 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Turelli P., Mangeat B., Jost S., Vianin S. & Trono D. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by APOBEC3G. Science (New York, N.Y.) 303, 1829 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Rösler C. et al. APOBEC-mediated interference with hepadnavirus production. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 42, 301–309 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Beggel B. et al. Full genome ultra-deep pyrosequencing associates G-to-A hypermutation of the hepatitis B virus genome with the natural progression of hepatitis B. Journal of viral hepatitis 20, 882–889 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

