Characterization of leukemias with ETV6-ABL1 fusion
- PMID: 27229714
- PMCID: PMC5060025
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2016.144345
Characterization of leukemias with ETV6-ABL1 fusion
Abstract
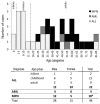
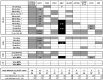
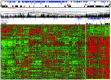
To characterize the incidence, clinical features and genetics of ETV6-ABL1 leukemias, representing targetable kinase-activating lesions, we analyzed 44 new and published cases of ETV6-ABL1-positive hematologic malignancies [22 cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (13 children, 9 adults) and 22 myeloid malignancies (18 myeloproliferative neoplasms, 4 acute myeloid leukemias)]. The presence of the ETV6-ABL1 fusion was ascertained by cytogenetics, fluorescence in-situ hybridization, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and RNA sequencing. Genomic and gene expression profiling was performed by single nucleotide polymorphism and expression arrays. Systematic screening of more than 4,500 cases revealed that in acute lymphoblastic leukemia ETV6-ABL1 is rare in childhood (0.17% cases) and slightly more common in adults (0.38%). There is no systematic screening of myeloproliferative neoplasms; however, the number of ETV6-ABL1-positive cases and the relative incidence of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and myeloproliferative neoplasms suggest that in adulthood ETV6-ABL1 is more common in BCR-ABL1-negative chronic myeloid leukemia-like myeloproliferations than in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The genomic profile of ETV6-ABL1 acute lymphoblastic leukemia resembled that of BCR-ABL1 and BCR-ABL1-like cases with 80% of patients having concurrent CDKN2A/B and IKZF1 deletions. In the gene expression profiling all the ETV6-ABL1-positive samples clustered in close vicinity to BCR-ABL1 cases. All but one of the cases of ETV6-ABL1 acute lymphoblastic leukemia were classified as BCR-ABL1-like by a standardized assay. Over 60% of patients died, irrespectively of the disease or age subgroup examined. In conclusion, ETV6-ABL1 fusion occurs in both lymphoid and myeloid leukemias; the genomic profile and clinical behavior resemble BCR-ABL1-positive malignancies, including the unfavorable prognosis, particularly of acute leukemias. The poor outcome suggests that treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors should be considered for patients with this fusion.
Copyright© Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute leukemias with ETV6/ABL1 (TEL/ABL) fusion: poor prognosis and prenatal origin.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010 Oct;49(10):873-84. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20796. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20589932
-
Variant of ETV6/ABL1 gene is associated with leukemia phenotype.Acta Haematol. 2013;129(2):78-82. doi: 10.1159/000342490. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Acta Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23171811
-
Clonal eosinophils are a morphologic hallmark of ETV6/ABL1 positive acute myeloid leukemia.Haematologica. 2002 Aug;87(8):789-94. Haematologica. 2002. PMID: 12161353
-
BCR-ABL1-like acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: From bench to bedside.Eur J Cancer. 2017 Sep;82:203-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.06.012. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28709134 Review.
-
Mixed-phenotype (B-lymphocytic/myeloid) acute leukemia with ETV6-ABL1 expression.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jul;40(6):1294-1299. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.6.8497. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38952502 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Philadelphia chromosome-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood. 2017 Nov 9;130(19):2064-2072. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-743252. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28972016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ETV6::ABL1-Positive Myeloid Neoplasm: A Case of a Durable Response to Imatinib Mesylate without Additional or Previous Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):118. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010118. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203288 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor response of ABL-class acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the role of kinase type and SH3 domain.Blood. 2024 May 23;143(21):2178-2189. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023023120. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38394665 Free PMC article.
-
ETV6::ABL1 positive myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms with eosinophilia and tyrosine kinase gene fusions (MLN-TK) with blast crisis treated with flumatinib mesylate.Ann Hematol. 2024 Sep;103(9):3801-3804. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05887-6. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38992279
-
The Current Genomic and Molecular Landscape of Philadelphia-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 22;21(6):2193. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062193. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32235787 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hannemann JR, McManus DM, Kabarowski JH, Wiedemann LM. Haemopoietic transformation by the TEL/ABL oncogene. Br J Haematol. 1998;102(2):475–485. - PubMed
-
- Okuda K, Golub TR, Gilliland DG, Griffin JD. p210BCR/ABL, p190BCR/ABL, and TEL/ABL activate similar signal transduction pathways in hematopoietic cell lines. Oncogene. 1996;13(6):1147–1152. - PubMed
-
- Million RP, Aster J, Gilliland DG, Van Etten RA. The Tel-Abl (ETV6-Abl) tyrosine kinase, product of complex (9;12) translocations in human leukemia, induces distinct myeloproliferative disease in mice. Blood. 2002;99(12):4568–4577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

