Gene-microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 27230380
- PMCID: PMC4996125
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aad9948
Gene-microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
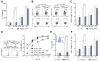
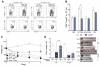
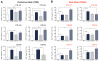
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with risk variants in the human genome and dysbiosis of the gut microbiome, though unifying principles for these findings remain largely undescribed. The human commensal Bacteroides fragilis delivers immunomodulatory molecules to immune cells via secretion of outer membrane vesicles (OMVs). We reveal that OMVs require IBD-associated genes, ATG16L1 and NOD2, to activate a noncanonical autophagy pathway during protection from colitis. ATG16L1-deficient dendritic cells do not induce regulatory T cells (T(regs)) to suppress mucosal inflammation. Immune cells from human subjects with a major risk variant in ATG16L1 are defective in T(reg) responses to OMVs. We propose that polymorphisms in susceptibility genes promote disease through defects in "sensing" protective signals from the microbiome, defining a potentially critical gene-environment etiology for IBD.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

Comment in
-
IBD: Sensing gene-microbiota signals in IBD.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jul;13(7):377. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.89. Epub 2016 May 25. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27251207 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U19 AI109725/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DE023789/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI109725/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R42 DK103361/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM099535/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM099535/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI40646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01DK046763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI079145/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DE023789-01/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- DK100109/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK100109/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI067068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK046763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK097485/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK078938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK097485/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK078938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

