The Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenesis Effects of Kefir Water on Murine Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 27230756
- PMCID: PMC5739168
- DOI: 10.1177/1534735416642862
The Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenesis Effects of Kefir Water on Murine Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
Background: Kefir is a unique cultured product that contains beneficial probiotics. Kefir culture from other parts of the world exhibits numerous beneficial qualities such as anti-inflammatory, immunomodulation, and anticancer effects. Nevertheless, kefir cultures from different parts of the world exert different effects because of variation in culture conditions and media. Breast cancer is the leading cancer in women, and metastasis is the major cause of death associated with breast cancer. The antimetastatic and antiangiogenic effects of kefir water made from kefir grains cultured in Malaysia were studied in 4T1 breast cancer cells.
Methods: 4T1 cancer cells were treated with kefir water in vitro to assess its antimigration and anti-invasion effects. BALB/c mice were injected with 4T1 cancer cells and treated orally with kefir water for 28 days.
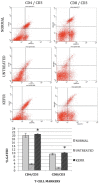
Results: Kefir water was cytotoxic toward 4T1 cells at IC50 (half-maximal inhibitory concentration) of 12.5 and 8.33 mg/mL for 48 and 72 hours, respectively. A significant reduction in tumor size and weight (0.9132 ± 0.219 g) and a substantial increase in helper T cells (5-fold) and cytotoxic T cells (7-fold) were observed in the kefir water-treated group. Proinflammatory and proangiogenic markers were significantly reduced in the kefir water-treated group.
Conclusions: Kefir water inhibited tumor proliferation in vitro and in vivo mainly through cancer cell apoptosis, immunomodulation by stimulating T helper cells and cytotoxic T cells, and anti-inflammatory, antimetastatic, and antiangiogenesis effects. This study brought out the potential of the probiotic beverage kefir water in cancer treatment.
Keywords: 4T1 cell; antiangiogenesis; antimetastasis; breast cancer; immunomodulatory; kefir; kefir water.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Siege R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9-29. - PubMed
-
- Scully OJ, Bay BH, Yip G, Yu Y. Breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2012;9:311-320. - PubMed
-
- Altonsy MO, Andrews SC, Tuohy KM. Differential induction of apoptosis in human colonic carcinoma cells (caco-2) by atopobium, and commensal, probiotic and enteropathogenic bacteria: mediation by the mitochondrial pathway. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010;137:190-203. - PubMed
-
- Le Leu RK, Brown IL, Hu Y, et al. A synbiotic combination of resistant starch and Bifidobacterium lactis facilitates apoptotic deletion of carcinogen-damaged cells in rat colon. J Nutr. 2005;135:996-1001. - PubMed
-
- de Moreno de LeBlanc A, Matar C, Farnworth E, Perdigon G. Study of cytokines involved in the prevention of a murine experimental breast cancer by kefir. J Dairy Res. 2006;90:1920-1928. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

