A genomic approach to identify hybrid incompatibility genes
- PMID: 27230814
- PMCID: PMC4970527
- DOI: 10.1080/19336934.2016.1193657
A genomic approach to identify hybrid incompatibility genes
Abstract
Uncovering the genetic and molecular basis of barriers to gene flow between populations is key to understanding how new species are born. Intrinsic postzygotic reproductive barriers such as hybrid sterility and hybrid inviability are caused by deleterious genetic interactions known as hybrid incompatibilities. The difficulty in identifying these hybrid incompatibility genes remains a rate-limiting step in our understanding of the molecular basis of speciation. We recently described how whole genome sequencing can be applied to identify hybrid incompatibility genes, even from genetically terminal hybrids. Using this approach, we discovered a new hybrid incompatibility gene, gfzf, between Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans, and found that it plays an essential role in cell cycle regulation. Here, we discuss the history of the hunt for incompatibility genes between these species, discuss the molecular roles of gfzf in cell cycle regulation, and explore how intragenomic conflict drives the evolution of fundamental cellular mechanisms that lead to the developmental arrest of hybrids.
Keywords: Drosophila; cell cycle; genomic conflict; hybrid incompatibility; speciation.
Figures
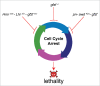
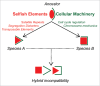
Comment on
- doi: 10.1126/science.aac7504
References
-
- Dobzhansky T. Genetics and the Origin of Species. New York: Columbia University Press; 1937.
-
- Muller HJ. Isolating mechanisms, evolution and temperature. Biol Symp 1942; 6:71-125.
-
- Coyne J, Orr HA. Speciation. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates; 2004.
-
- Barbash DA. Ninety Years of Drosophila melanogaster Hybrids. Genetics 2010; 186:1-8; PMID:20855573; http://dx.doi.org/10.1534/genetics.110.121459 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
