Ultraviolet-B induces ERCC6 repression in lens epithelium cells of age-related nuclear cataract through coordinated DNA hypermethylation and histone deacetylation
- PMID: 27231489
- PMCID: PMC4880862
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0229-y
Ultraviolet-B induces ERCC6 repression in lens epithelium cells of age-related nuclear cataract through coordinated DNA hypermethylation and histone deacetylation
Abstract
Background: Ultraviolet-B (UVB) exposure attributes to the formation of age-related nuclear cataract (ARNC), which is mediated with DNA damage. DNA damage, an important factor for pathogenesis of ARNC, is induced by UVB, and is generally resolved by the nucleotide excision repair (NER) repair mechanism. Cockayne syndrome complementation group B (CSB) protein coded by ERCC6 is a vital component for NER. However, we found no association between selected ERCC6 polymorphisms and ARNC. In this study, we investigated whether UVB exposure could alter ERCC6 expression and the process could involve epigenetic changes of DNA methylation and/or histone acetylation of ERCC6 in the lens epithelial cells (LECs). We also assessed the involvement of those coordinated changes in lens tissue from ARNC patients.
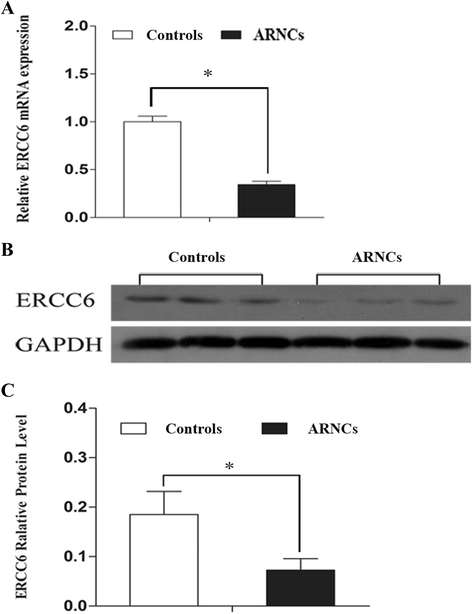
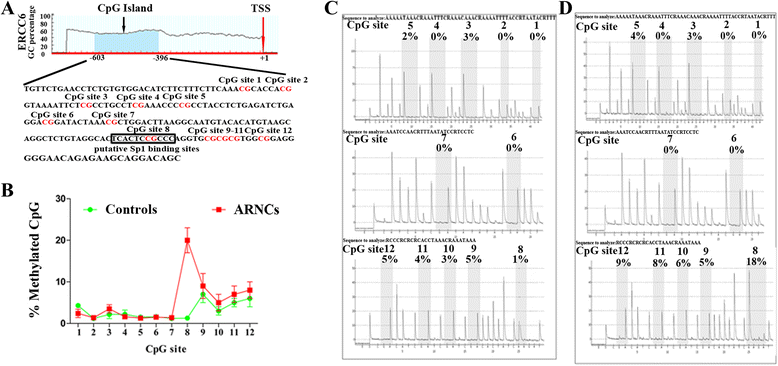
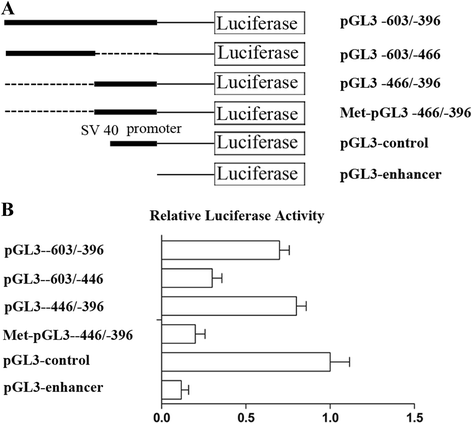
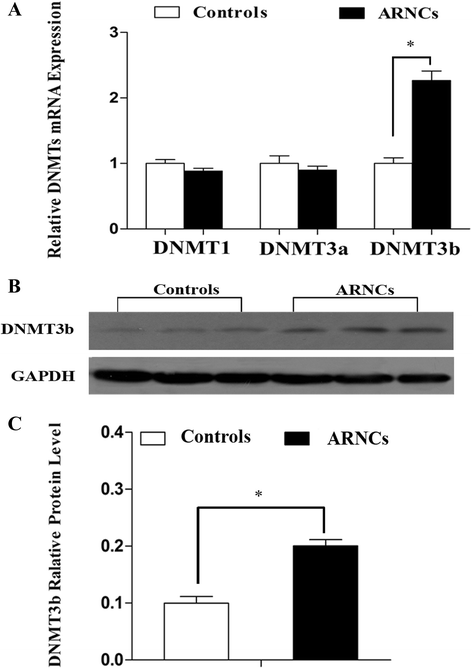
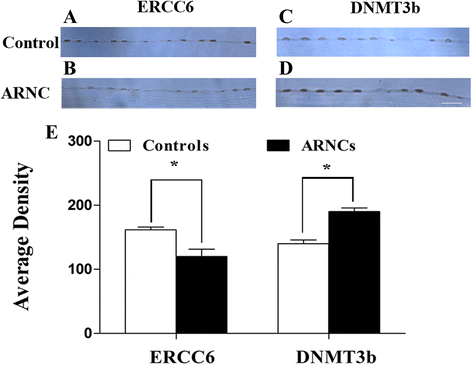
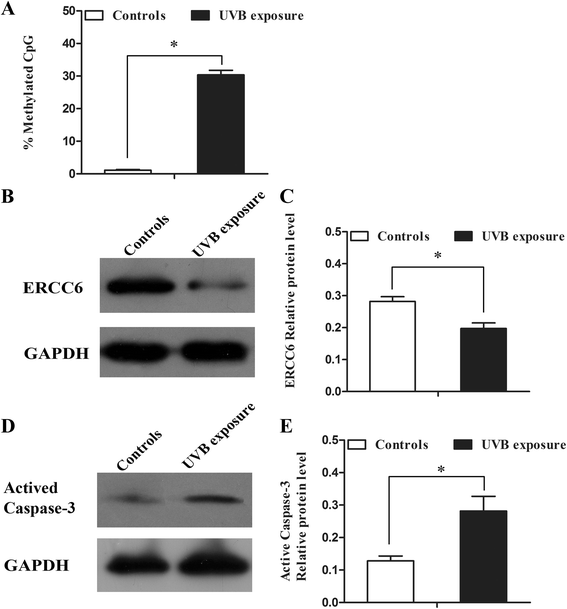
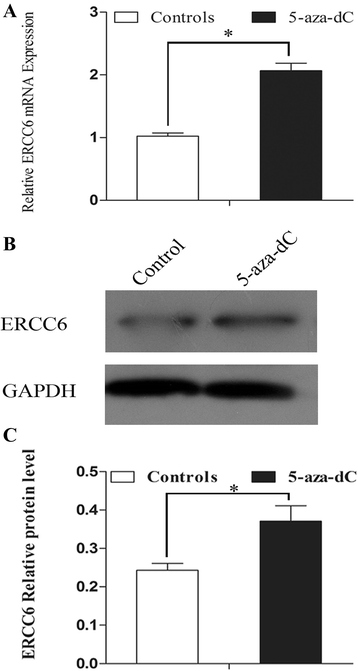
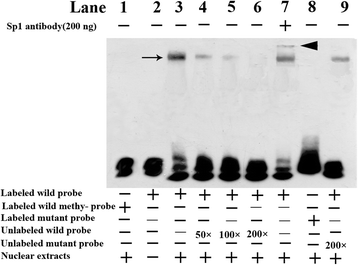
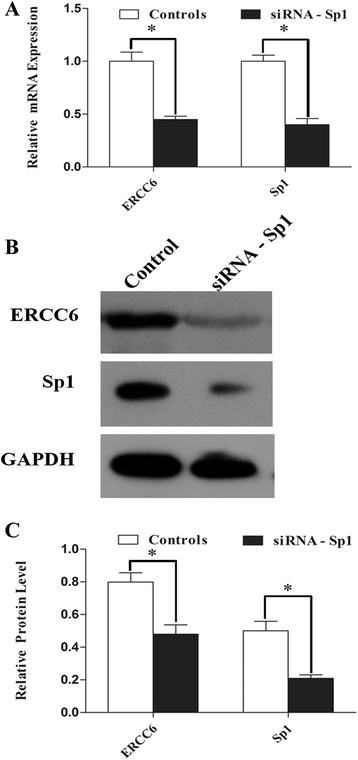
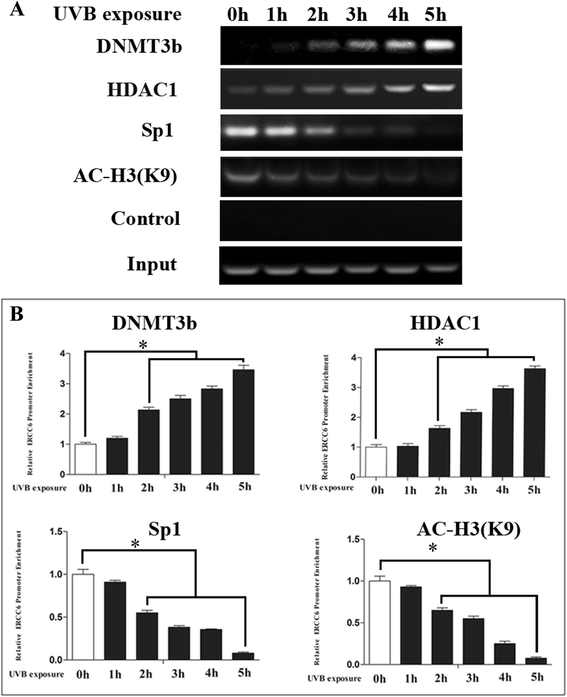
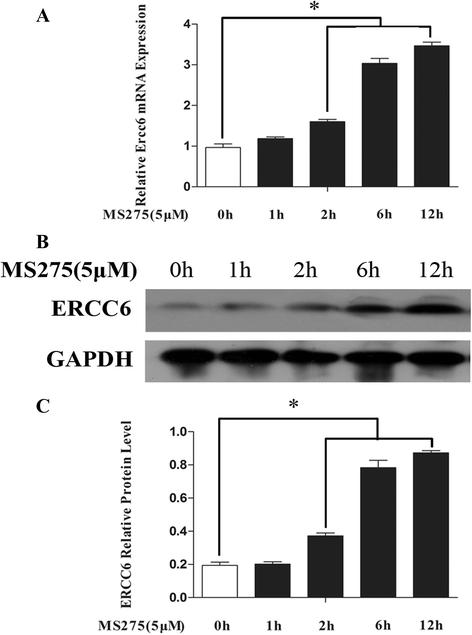
Results: mRNA and protein expression of ERCC6 in lens tissue (LECs) were lower in ARNCs than those in the controls. This reduction corresponded to methylation of a CpG site at the ERCC6 promoter and histone modifications (methylation and acetylation) nearby this site. UVB-treated human lens epithelium B3 (HLE-B3) and 239T cell presented (1) increased apoptosis, suggesting reduced UV-damage repair, (2) hypermethylation of the CpG site located at position -441 (relative to transcription start site) within the binding region for transcriptional factor Sp1 in the ERCC6 promoter, (3) the enhancement of histone H3K9 deacetylation, (4) induction in DNA methyltransferases 3b (DNMT3b) and histone deacetylase1 (HDAC1) associated to the CpG site of ERCC6 by CHIP assay.
Conclusions: These findings suggest an orchestrated mechanism triggered by UVB radiation where the concurrent association of specific hypermethylation CpG site, H3K9 deacetylation of ERCC6, and repression of ERCC6 gene expression. Taken together, with the similar changes in the lens tissue from ARNC patients, our data unveiled a possible mechanism of epigenetic modification of DNA repair gene in the pathogenesis of ARNC.
Keywords: Age-related nuclear cataract (ARNC); DNA methylation; ERCC6; Histone deacetylation; Lens epithelial cells (LECs); Sp1; Ultraviolet (UV).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aberrant Epigenetic Alterations of Glutathione-S-Transferase P1 in Age-Related Nuclear Cataract.Curr Eye Res. 2017 Mar;42(3):402-410. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2016.1185129. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Curr Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27348130
-
MicroRNA Let-7c-5p-Mediated Regulation of ERCC6 Disrupts Autophagic Flux in Age-Related Cataract via the Binding to VCP.Curr Eye Res. 2021 Sep;46(9):1353-1362. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2021.1900273. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Curr Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33703976
-
Epigenetic repression of LEDGF during UVB exposure by recruitment of SUV39H1 and HDAC1 to the Sp1-responsive elements within LEDGF promoter CpG island.Epigenetics. 2013 Mar;8(3):268-80. doi: 10.4161/epi.23861. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Epigenetics. 2013. PMID: 23386123 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of DNA Methylation in Lens Development and Cataract Formation.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Aug;37(6):979-984. doi: 10.1007/s10571-016-0447-z. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27858287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between vitamin D level and cataract: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2025 Jan;263(1):147-156. doi: 10.1007/s00417-024-06592-w. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39179900 Free PMC article.
-
DNA hypermethylation of COL4A1 in ultraviolet-B-induced age-related cataract models in vitro and in vivo.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 18;17(10):1791-1799. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.10.04. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39430019 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of N6-Methyladenosine CircRNAs and Methyltransferases in the Lens Epithelium Cells From Age-Related Cataract.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Aug 3;61(10):13. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.10.13. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32761139 Free PMC article.
-
Blockage of ERCC6 Alleviates Spinal Cord Injury Through Weakening Apoptosis, Inflammation, Senescence, and Oxidative Stress.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 22;9:853654. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.853654. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35392536 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Role of Epigenetics and Network Analysis in Eye Diseases: A Translational Science Review.J Ophthalmol. 2019 Dec 23;2019:2424956. doi: 10.1155/2019/2424956. eCollection 2019. J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31976085 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbasi R, Ramroth H, Becher H, Dietz A, Schmezer P, Popanda O. Laryngeal cancer risk associated with smoking and alcohol consumption is modified by genetic polymorphisms in ERCC5, ERCC6 and RAD23B but not by polymorphisms in five other nucleotide excision repair genes. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(6):1431–9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24442. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

