Plasma neuronal exosomal levels of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in normal aging
- PMID: 27231710
- PMCID: PMC4863753
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.309
Plasma neuronal exosomal levels of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in normal aging
Abstract
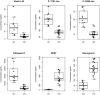
Plasma neuronal exosomal levels of pathogenic Alzheimer's disease (AD) proteins, cellular survival factors, and lysosomal proteins distinguish AD patients from control subjects, but changes in these exosomal proteins associated with normal aging have not been described for cognitively intact subjects. Plasma neuronal exosomal levels of P-T181-tau, P-S396-tau, Aβ 1-42, cathepsin D, repressor element 1-silencing transcription factor, and neurogranin were quantified longitudinally in cognitively intact older adults using two samples collected at 3- to 11-year intervals. Except for P-S396-tau, exosomal protein levels changed significantly with aging, but were largely outside the range observed in AD patients.
Figures
References
-
- Marzesco AM, Janich P, Wilsch‐Brauninger M, et al. Release of extracellular membrane particles carrying the stem cell marker prominin‐1 (CD133) from neural progenitors and other epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 2005;118:2849–2858. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources