High-Intensity Chemotherapy is Associated with Better Prognosis in Young Patients with High-Risk Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A 10-Year Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 27232105
- PMCID: PMC4913830
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.895383
High-Intensity Chemotherapy is Associated with Better Prognosis in Young Patients with High-Risk Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A 10-Year Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
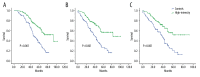
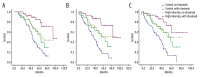
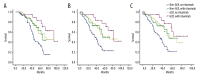
BACKGROUND Patients <60 years old with high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) receiving standard RCHOP(E) treatment display high relapse rates. Here, we compared this standard regimen to a high-intensity regimen in terms of recurrence and long-term survival. MATERIAL AND METHODS Newly diagnosed DLBCL patients <60 years old who were treated at the Second Hospital Affiliated with Xi'an Jiaotong University between January 2004 and December 2013 (n=198, 18-60 years) were included in the study. The high-intensity group included 107 patients (54.0%) who received >8 courses of chemotherapy (high-dose CHOP, CHOP-E, EPOCH, MAED, MMED, and HyperCVAD). The control group included 91 patients (46.0%) who received 6-8 courses of CHOP-based treatment. Response rate (RR), survival, relapse, and adverse effects were compared. RESULTS Baseline characteristics of the patients were similar between the 2 groups. Median follow-up was 64.5 months. RR in the high-intensity and control groups was 88.8% and 84.6% (P=0.387), respectively; 5-year overall survival was 66.4% and 36.3% (P<0.001), respectively; 5-year progression-free survival was 56.1% and 28.6% (P<0.001), respectively; 5-year disease-free survival was 54.2% and 24.2% (P<0.001), respectively; and relapse rate during follow-up was 29.5% and 67.5% (P<0.001), respectively. There were no significant differences in adverse effects between the 2 groups. CONCLUSIONS High-intensity chemotherapy is associated with better prognosis of patients <60 years old with newly diagnosed high-risk DLBCL.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New risk factors and new tendency for central nervous system relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a retrospective study.Chin J Cancer. 2016 Sep 13;35(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0150-y. Chin J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27624700 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting survival in elderly patients with diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma.Leuk Res. 2021 Nov;110:106700. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2021.106700. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Leuk Res. 2021. PMID: 34481125
-
Rituximab in combination with CHOP chemotherapy for the treatment of diffuse large B cell lymphoma in China: a 10-year retrospective follow-up analysis of 437 cases from Shanghai Lymphoma Research Group.Ann Hematol. 2012 Jun;91(6):837-45. doi: 10.1007/s00277-011-1375-0. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Ann Hematol. 2012. PMID: 22160255
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of the addition of rituximab to CHOP in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma.Clin Drug Investig. 2008;28(1):55-65. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200828010-00007. Clin Drug Investig. 2008. PMID: 18081361
-
Extended Course and Increased Dose of Initial Chemotherapy for Extranodal Nasal Type Natural Killer/T (NK/T)-Cell Lymphoma in Patients <60 Years Old: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Nov 11;22:4297-4311. doi: 10.12659/MSM.897650. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27843135 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Retrospective evaluation of clinical outcome after chemotherapy for lymphoma in 15 equids (1991-2017).J Vet Intern Med. 2019 Mar;33(2):953-960. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15411. Epub 2019 Jan 12. J Vet Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30636061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansell SM, Armitage J. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma: diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:1087–97. - PubMed
-
- Jakic-Razumovic J, Aurer I. The World Health Organization classification of lymphomas. Croat Med J. 2002;43:527–34. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Han T, Iqbal J, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Chinese patients: immunophenotypic and cytogenetic analyses of 124 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;133:305–13. - PubMed
-
- Fisher SG, Fisher RI. The epidemiology of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Oncogene. 2004;23:6524–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

