Efficacy and Safety Outcomes of Extended Criteria Donor Kidneys by Subtype: Subgroup Analysis of BENEFIT-EXT at 7 Years After Transplant
- PMID: 27232116
- PMCID: PMC5215636
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.13886
Efficacy and Safety Outcomes of Extended Criteria Donor Kidneys by Subtype: Subgroup Analysis of BENEFIT-EXT at 7 Years After Transplant
Abstract
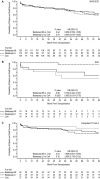
The phase III Belatacept Evaluation of Nephroprotection and Efficacy as First-Line Immunosuppression Trial-Extended Criteria Donors Trial (BENEFIT-EXT) study compared more or less intensive belatacept-based immunosuppression with cyclosporine (CsA)-based immunosuppression in recipients of extended criteria donor kidneys. In this post hoc analysis, patient outcomes were assessed according to donor kidney subtype. In total, 68.9% of patients received an expanded criteria donor kidney (United Network for Organ Sharing definition), 10.1% received a donation after cardiac death kidney, and 21.0% received a kidney with an anticipated cold ischemic time ≥24 h. Over 7 years, time to death or graft loss was similar between belatacept- and CsA-based immunosuppression, regardless of donor kidney subtype. In all three donor kidney cohorts, estimated mean GFR increased over months 1-84 for belatacept-based treatment but declined for CsA-based treatment. The estimated differences in GFR significantly favored each belatacept-based regimen versus the CsA-based regimen in the three subgroups (p < 0.0001 for overall treatment effect). No differences in the safety profile of belatacept were observed by donor kidney subtype.
Keywords: calcineurin inhibitor: cyclosporine A (CsA); clinical research/practice; donors and donation: deceased; donors and donation: donation after circulatory death (DCD); donors and donation: extended criteria; immunosuppressant; kidney transplantation/nephrology.
© 2016 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures


References
-
- Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL, Ojo AO, Ettenger RE, Held PJ, et al. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 1725–1730. - PubMed
-
- Ojo AO, Hanson JA, Meier‐Kriesche H, et al. Survival in recipients of marginal cadaveric donor kidneys compared with other recipients and wait listed candidates. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001; 12: 589–597. - PubMed
-
- Niu SF, Li IC. Quality of life of patients having renal replacement therapy. J Adv Nurs 2005; 51: 15–21. - PubMed
-
- Cohen B, Smits JM, Haase B, Persijn G, Vanrenterghem Y, Frei U. Expanding the donor pool to increase renal transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2005; 20: 34–41. - PubMed
-
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) and Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR) . OPTN/SRTR 2012 Annual Data Report. Rockville, MD: Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration; 2014. [cited 2015 Feb 4]. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ajt.v14.s1/issuetoc. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

