The Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure in young children: responsiveness and minimal clinically important difference
- PMID: 27232584
- PMCID: PMC5113674
- DOI: 10.1111/all.12942
The Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure in young children: responsiveness and minimal clinically important difference
Abstract
Background: The Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) has been recommended as the core patient-reported outcome measure for trials of eczema treatments. Using data from the Choice of Moisturiser for Eczema Treatment randomized feasibility study, we assess the responsiveness to change and determine the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) of the POEM in young children with eczema.
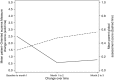
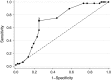
Methods: Responsiveness to change by repeated administrations of the POEM was investigated in relation to change recalled using the Parent Global Assessment (PGA) measure. Five methods of determining the MCID of the POEM were employed; three anchor-based methods using PGA as the anchor: the within-patient score change, between-patient score change and sensitivity and specificity method, and two distribution-based methods: effect size estimate and the one half standard deviation of the baseline distribution of POEM scores.
Results: Successive POEM scores were found to be responsive to change in eczema severity. The MCID of the POEM change score, in relation to a slight improvement in eczema severity as recalled by parents on the PGA, estimated by the within-patient score change (4.27), the between-patient score change (2.89) and the sensitivity and specificity method (3.00) was similar to the one half standard deviation of the POEM baseline scores (2.94) and the effect size estimate (2.50).
Conclusions: The Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure as applied to young children is responsive to change, and the MCID is around 3. This study will encourage the use of POEM and aid in determining sample size for future randomized controlled trials of treatments for eczema in young children.
Keywords: Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure; atopic eczema; minimal clinically important difference; paediatrics; responsiveness.
© 2016 The Authors. Allergy Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Weidinger S, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2016;387:1109–1122. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt J, Spuls P, Thomas K, Simpson E, Furue M, Deckert S. The Harmonising Outcome Measures for Eczema (HOME) statement to assess clinical signs of atopic eczema in trials. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2014;134:800–807. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt J, Spuls P, Boers M, Thomas K, Chalmers J, Roekevisch E et al. Towards global consensus on outcome measures for atopic eczema research: results of the HOME II meeting. Allergy 2012;67:1111–1117. - PubMed
-
- Tofte S, Graber M, Cherill R, Omoto M, Thurston M, Hanifin J. Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI): a new tool to evaluate atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 1998;11:S197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

