Kynurenine metabolic balance is disrupted in the hippocampus following peripheral lipopolysaccharide challenge
- PMID: 27233247
- PMCID: PMC4884395
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0590-y
Kynurenine metabolic balance is disrupted in the hippocampus following peripheral lipopolysaccharide challenge
Abstract
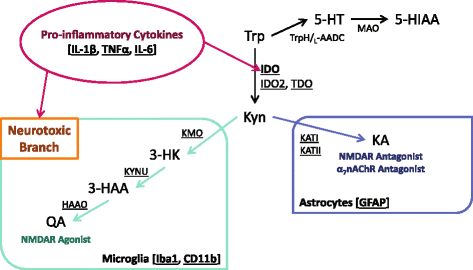
Background: Inflammation increases the risk of developing depression-related symptoms, and tryptophan metabolism is an important mediator of these behavior changes. Peripheral immune activation results in central up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, microglia activation, and the production of neurotoxic kynurenine metabolites. The neuroinflammatory and kynurenine metabolic response to peripheral immune activation has been largely characterized at the whole brain level. It is unknown if this metabolic response exhibits regional specificity even though the unique indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-dependent depressive-like behaviors are known to be controlled by discrete brain regions. Therefore, regional characterization of neuroinflammation and kynurenine metabolism might allow for better understanding of the potential mechanisms that mediate inflammation-associated behavior changes.
Methods: Following peripheral immune challenge with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), brain tissue from behaviorally relevant regions was analyzed for changes in mRNA of neuroinflammatory targets and kynurenine pathway enzymes. The metabolic balance of the kynurenine pathway was also determined in the peripheral circulation and these brain regions.
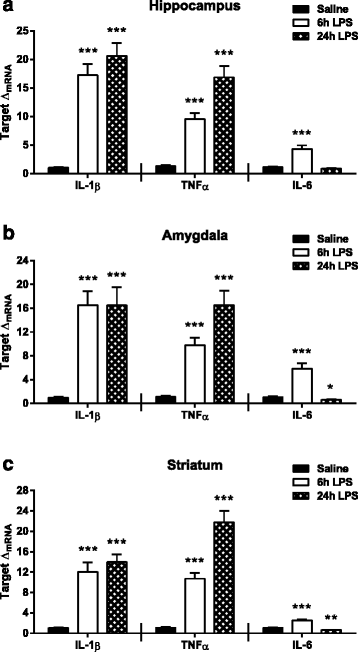
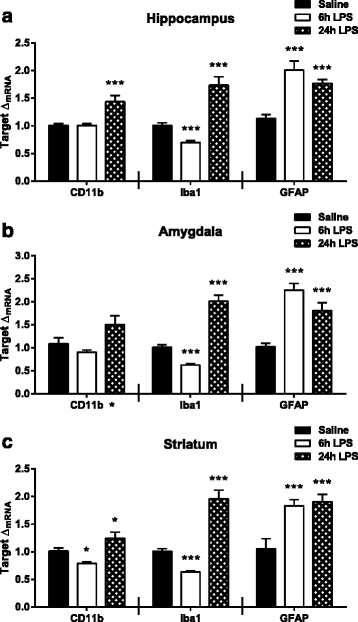
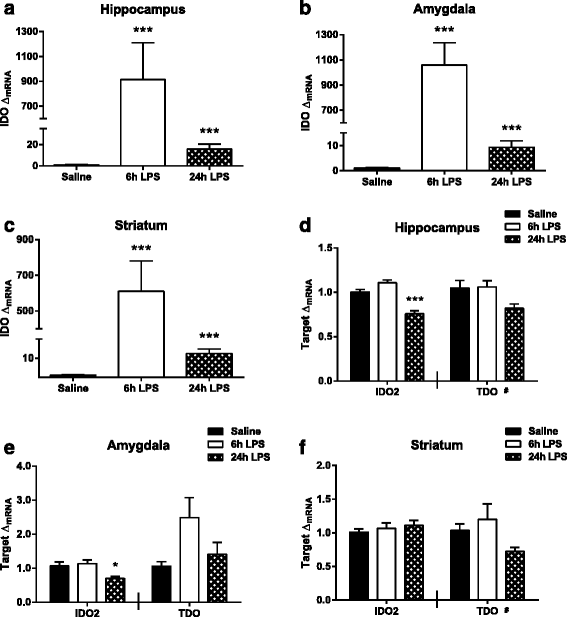
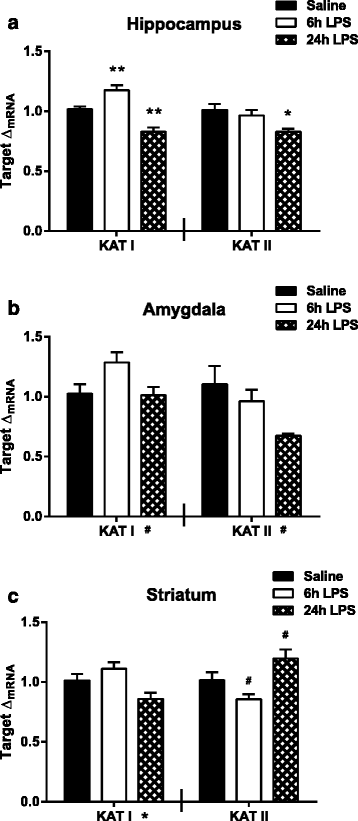
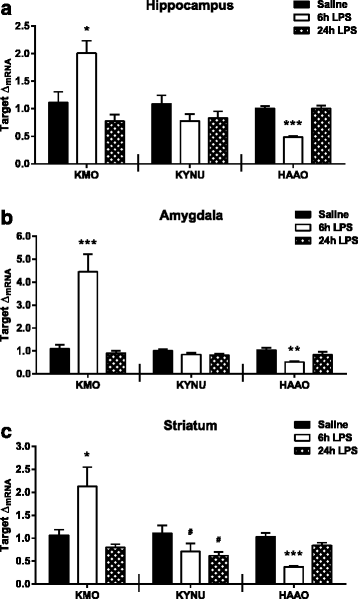
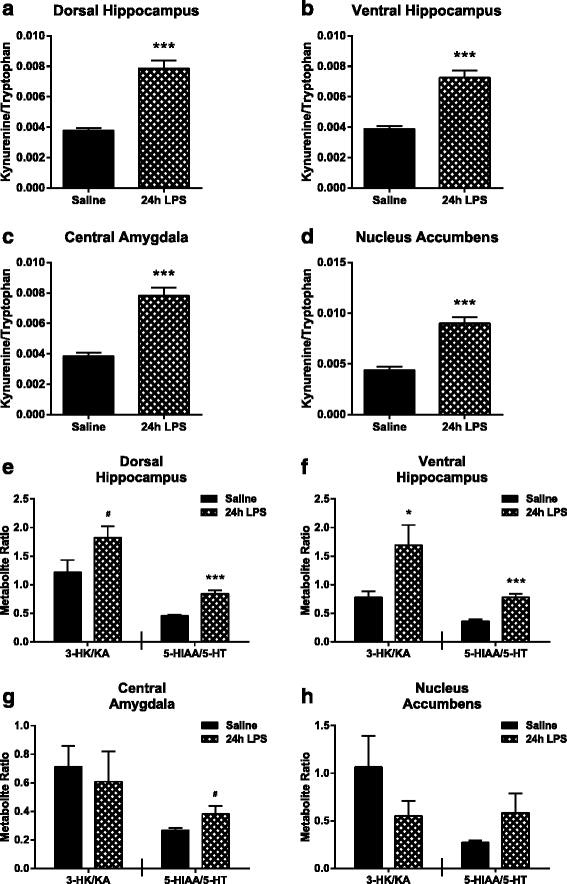
Results: Peripheral LPS treatment resulted in region-independent up-regulation of brain expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and glial cellular markers indicative of a neuroinflammatory response. The expression of kynurenine pathway enzymes was also largely region-independent. While the kynurenine/tryptophan ratio was elevated significantly in both the plasma and in each brain regions evaluated, the balance of kynurenine metabolism was skewed toward production of neurotoxic metabolites in the hippocampus.
Conclusions: The upstream neuroinflammatory processes, such as pro-inflammatory cytokine production, glial cell activation, and kynurenine production, may be similar throughout the brain. However, it appears that the balance of downstream kynurenine metabolism is a tightly regulated brain region-dependent process.
Keywords: Brain regions; Hippocampus; Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; Kynurenine; Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; Microglia; Neuroinflammation; Pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurotoxic kynurenine metabolism is increased in the dorsal hippocampus and drives distinct depressive behaviors during inflammation.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Oct 18;6(10):e918. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.200. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27754481 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-induced brain activation of the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and depressive-like behavior are impaired in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014 Feb;40:48-59. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.10.014. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24485475
-
Activation of Brain Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase Contributes to Depressive-Like Behavior Induced by an Intracerebroventricular Injection of Streptozotocin in Mice.Neurochem Res. 2017 Oct;42(10):2982-2995. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2329-2. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28631232
-
The new '5-HT' hypothesis of depression: cell-mediated immune activation induces indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, which leads to lower plasma tryptophan and an increased synthesis of detrimental tryptophan catabolites (TRYCATs), both of which contribute to the onset of depression.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Apr 29;35(3):702-21. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.12.017. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21185346 Review.
-
Kynurenine pathway metabolism and immune activation: Peripheral measurements in psychiatric and co-morbid conditions.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Jan;112(Pt B):286-296. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.02.030. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 26924709 Review.
Cited by
-
Gamma-oryzanol Prevents LPS-induced Brain Inflammation and Cognitive Impairment in Adult Mice.Nutrients. 2019 Mar 29;11(4):728. doi: 10.3390/nu11040728. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30934852 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenine pathway metabolic balance influences microglia activity: Targeting kynurenine monooxygenase to dampen neuroinflammation.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Aug;94:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.04.019. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29734055 Free PMC article.
-
Quinolinic acid potentially links kidney injury to brain toxicity.JCI Insight. 2025 Feb 13;10(6):e180229. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.180229. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 39946208 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxic kynurenine metabolism is increased in the dorsal hippocampus and drives distinct depressive behaviors during inflammation.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Oct 18;6(10):e918. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.200. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27754481 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of Stress-Induced Depressive-like Behavior by Saffron Extract Is Associated with Modulation of Kynurenine Pathway and Monoamine Neurotransmission.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 14;13(12):2155. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122155. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959434 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

