Defining filled and empty space: reassessing the filled space illusion for active touch and vision
- PMID: 27233286
- PMCID: PMC4978768
- DOI: 10.1007/s00221-016-4673-x
Defining filled and empty space: reassessing the filled space illusion for active touch and vision
Abstract
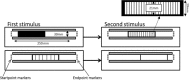
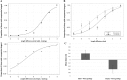
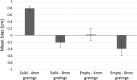
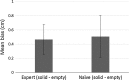
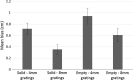
In the filled space illusion, an extent filled with gratings is estimated as longer than an equivalent extent that is apparently empty. However, researchers do not seem to have carefully considered the terms filled and empty when describing this illusion. Specifically, for active touch, smooth, solid surfaces have typically been used to represent empty space. Thus, it is not known whether comparing gratings to truly empty space (air) during active exploration by touch elicits the same illusionary effect. In Experiments 1 and 2, gratings were estimated as longer if they were compared to smooth, solid surfaces rather than being compared to truly empty space. Consistent with this, Experiment 3 showed that empty space was perceived as longer than solid surfaces when the two were compared directly. Together these results are consistent with the hypothesis that, for touch, the standard filled space illusion only occurs if gratings are compared to smooth, solid surfaces and that it may reverse if gratings are compared to empty space. Finally, Experiment 4 showed that gratings were estimated as longer than both solid and empty extents in vision, so the direction of the filled space illusion in vision was not affected by the nature of the comparator. These results are discussed in relation to the dual nature of active touch.
Keywords: Cutaneous; Filled space illusion; Kinaesthetic; Length; Touch; Vision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Filled and empty motor reproductions of filled and empty intervals: Is there also a filled - reproduction illusion?Atten Percept Psychophys. 2017 Oct;79(7):2143-2152. doi: 10.3758/s13414-017-1370-1. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2017. PMID: 28695540
-
Determinants of filled/empty optical illusion: differential effects of patterning.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2012;72(1):89-94. doi: 10.55782/ane-2012-1883. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2012. PMID: 22508087
-
Factors affecting the haptic filled-space illusion for dynamic touch.Exp Brain Res. 2009 Feb;192(4):717-22. doi: 10.1007/s00221-008-1635-y. Epub 2008 Nov 12. Exp Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19002674
-
Visual and haptic perception of the horizontal-vertical illusion.Percept Mot Skills. 2001 Feb;92(1):167-70. doi: 10.2466/pms.2001.92.1.167. Percept Mot Skills. 2001. PMID: 11322582
-
Inter-lateral Referral of Sensation in Health and Disease Using a Mirror Illusion-A Scoping Review.Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2022 May 16;37(4):849-864. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acab039. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2022. PMID: 34152397 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of the number and diversity of visual stimuli on the reproduction of short time intervals.Perception. 2023 Sep;52(9):662-669. doi: 10.1177/03010066231190220. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Perception. 2023. PMID: 37583299 Free PMC article.
-
Active touch in tactile perceptual discrimination: brain activity and behavioral responses to surface differences.Exp Brain Res. 2025 Mar 6;243(4):84. doi: 10.1007/s00221-025-07034-7. Exp Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40047968 Free PMC article.
-
Size Perception of a Sport Target as a Function of Practice Success Conditions.Front Psychol. 2022 Jan 18;12:768131. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.768131. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35115983 Free PMC article.
-
The finishing touches: the role of friction and roughness in haptic perception of surface coatings.Exp Brain Res. 2020 Jun;238(6):1511-1524. doi: 10.1007/s00221-020-05831-w. Epub 2020 May 23. Exp Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32447410 Free PMC article.
-
It's out of my hands! Grasping capacity may not influence perceived object size.J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform. 2017 Apr;43(4):749-769. doi: 10.1037/xhp0000331. Epub 2017 Feb 13. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform. 2017. PMID: 28191987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergmann Tiest WM, Hayward V (2015) Inside versus outside: haptic perception of object size. In: World haptics conference, IEEE, pp 94–99
-
- Bergmann Tiest WM, Van der Hoff LM, Kappers AML (2011) Cutaneous and kinaesthetic perception of traversed distance. In: World haptics conference, IEEE, pp 593–597
-
- Coren S, Girgus JS. Seeing is deceiving: the psychology of visual illusions. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum; 1978.
-
- Davidon RS, Cheng MFH. Apparent distance in a horizontal plane with tactile-kinesthetic stimuli. Q J Exp Psychol. 1964;16(3):277–281. doi: 10.1080/17470216408416380. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

